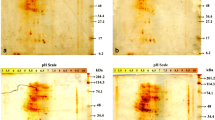
Abstract
Calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) is member of one of the most important signalling cascades operating inside the plant system due to its peculiar role as thermo-sensor. Here, we identified 28 full length putative CDPKs from wheat designated as TaCDPK (1-28). Based on digital gene expression, we cloned full length TaCPK-1 gene of 1691 nucleotides with open reading frame (ORF) of 548 amino acids (accession number OP125853). The expression of TaCPK-1 was observed maximum (3.1-fold) in leaf of wheat cv. HD2985 (thermotolerant) under T2 (38 ± 3 °C, 2 h), as compared to control. A positive correlation was observed between the expression of TaCPK-1 and other stress-associated genes (MAPK6, CDPK4, HSFA6e, HSF3, HSP17, HSP70, SOD and CAT) involved in thermotolerance. Global protein kinase assay showed maximum activity in leaves, as compared to root, stem and spike under heat stress. Immunoblot analysis showed abundance of CDPK protein in wheat cv. HD2985 (thermotolerant) in response to T2 (38 ± 3 °C, 2 h), as compared to HD2329 (thermosusceptible). Calcium ion (Ca2+), being inducer of CDPK, showed strong Ca-signature in the leaf tissue (Ca—622 ppm) of thermotolerant wheat cv. under heat stress, whereas it was minimum (Ca—201 ppm) in spike tissue. We observed significant variations in the ionome of wheat under HS. To conclude, TaCPK-1 plays important role in triggering signaling network and in modulation of HS-tolerance in wheat.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data have been presented in the manuscript and supplementary information. As such, we dont have any external data.
References
Ahmadi H, Abbasi A, Taleei A et al (2022) Antioxidant response and calcium-dependent protein kinases involvement in Canola (Brassica napus L.) tolerance to drought. Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010125
Aury JM, Engelen S, Istace B, Monat C et al (2022) Long-read and chromosome-scale assembly of the hexaploid wheat genome achieves high resolution for research and breeding. GigaScience 11:giac034
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Cheng SH, Willmann MR, Chen HC, Sheen J (2002) Calcium signaling through protein kinases. The Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase gene family. Plant Physiol 129:469–485
Chunduri V, Kaur A, Kaur S, Kumar A et al (2021) Gene expression and proteomics studies suggest an involvement of multiple pathways under day and day–night combined heat stresses during grain filling in wheat. Front Plant Sci 12:660446. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.660446
Ciésla A, Mituła F, Misztal L et al (2016) A role for barley calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK2a in the response to drought. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01550
Ding Y, Cao J, Ni L, Zhu Y et al (2012) ZmCPK11 is involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and functions upstream of ZmMPK5 in abscisic acid signalling in maize. J Exp Bot 64:871–884
Dong H, Wu C, Luo C, Wei M, Qu S, Wang S (2020) Overexpression of MdCPK1a gene, a calcium dependent protein kinase in apple, increase tobacco cold tolerance via scavenging ROS accumulation. PLoS ONE 15(11):e0242139
Fernando DR, Moroni SJ, Scott BJ et al (2016) Temperature and light drive manganese accumulation and stress in crops across three major plant families. Environ Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.08.008
He SL, Jiang JZ, Chen BH et al (2018) Overexpression of a constitutively active truncated form of OsCDPK1 confers disease resistance by affecting OsPR10a expression in rice. Sci Rep 81(8):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18829-2
Hu Z, Lv X, Xia X et al (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase in tomato. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00469
Hu CH, Li BB, Chen P, Shen HY, Xi WG, Zhang Y, Yue ZH, Wang HX, Ma KS, Li LL, Chen KM (2023) Identification of CDPKs involved in TaNOX7 mediated ROS production in wheat. Front Plant Sci 13:1108622
Huang K, Peng L, Liu Y et al (2018) Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase AtCPK1 plays a positive role in salt/drought-stress response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.175
International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC) et al (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 361(6403):eaar7191
Jeandroz S, Lamotte O (2017) Editorial: plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses: lessons from cell signaling. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01772
Jing X, Cai C, Fan S et al (2019) Spatial and temporal calcium signaling and its physiological effects in Moso Bamboo under drought stress. Forests. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10030224
Kim H-M, Kim S-H (2021a) Expression analysis of OsCPK11 by ND0001 oscpk11 mutants of Oryza sativa L. under salt, cold and drought stress conditions. J Life Sci 31:115–125. https://doi.org/10.5352/JLS.2021.31.2.115
Kim KH, Kim JY (2021b) Understanding wheat starch metabolism in properties, environmental stress condition, and molecular approaches for value-added utilization. Plants 10:c2282
Kumar RR, Goswami S, Sharma SK et al (2015) Harnessing next generation sequencing in climate change: RNA-Seq analysis of heat stress-responsive genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Omi A J Integr Biol. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2015.0097
Kumar RR, Goswami S, Singh K, Dubey K, Singh S, Sharma R, Verma N, Kala YK, Rai GK, Grover M, Mishra DC (2016) Identification of putative RuBisCo Activase (TaRca1)—the catalytic chaperone regulating carbon assimilatory pathway in wheat (Triticum aestivum) under the heat stress. Front Plant Sci 7:986
Kumar RR, Singh K, Ahuja S et al (2018) Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals novel stress-associated active proteins (SAAPs) and pathways involved in modulating tolerance of wheat under terminal heat. Funct Integr Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0648-2
Kumar RR, Tasleem M, Jain M et al (2019) Nitric oxide triggered defense network in wheat: augmenting tolerance and grain-quality related traits under heat-induced oxidative damage. Environ Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.11.016
Kumar RR, Goswami S, Rai GK et al (2020) Protection from terminal heat stress: a trade-off between heat-responsive transcription factors (HSFs) and stress-associated genes (SAGs) under changing environment. Cereal Res Commun. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-020-00097-y
Kumar RR, Dubey K, Arora K et al (2021) Characterizing the putative mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and their protective role in oxidative stress tolerance and carbon assimilation in wheat under terminal heat stress. Biotechnol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00597
Kumar RR, Ahuja S, Rai GK et al (2022) Silicon triggers the signalling molecules and stress-associated genes for alleviating the adverse effect of terminal heat stress in wheat with improved grain quality. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03365-y
Kumari A, Kumar RR, Singh JP, Verma P, Singh GP, Chinnusamy V et al (2020) Characterization of the starch synthase under terminal heat stress and its effect on grain quality of wheat. 3 Biotech 10:1
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lakaew K, Akeprathumchai S, Thiravetyan P (2021) Foliar spraying of calcium acetate alleviates yield loss in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by induced anti-oxidative defence system under ozone and heat stresses. Ann Appl Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12653
Large EC (1954) Growth stages in cereals illustration of the Feekes scale. Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.1954.tb00716.x
Lemi T (2019) Effects of climate change variability on agricultural productivity. Int J Environ Sci Nat Resour. https://doi.org/10.19080/ijesnr.2019.17.555953
Li A, Wang X, Leseberg CH et al (2008a) Biotic and abiotic stress responses through calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) signaling in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Signal Behav. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.3.9.5757
Li AL, Zhu YF, Tan XM et al (2008b) Evolutionary and functional study of the CDPK gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9281-5
Li X, Zhao L, Zhang H et al (2022) Genome-wide identification and characterization of CDPK family reveal their involvements in growth and development and abiotic stress in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063088
Li Y, Wei ZZ, Sela H, Govta L, Klymiuk V et al (2023) Dissection of a rapidly evolving wheat resistance gene cluster by long-read genome sequencing accelerated the cloning of Pm69. Plant Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100646
Liu F, Si H, Wang C et al (2016) Molecular evolution of Wcor15 gene enhanced our understanding of the origin of A, B and D genomes in Triticum aestivum. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31706
Marcussen T, Sandve SR, Heier L et al (2014) A chromosome-based draft sequence of the hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome. Science 345:1250092–1250092
Medina E, Kim SH, Yun M, Choi WG (2021) Recapitulation of the function and role of ros generated in response to heat stress in plants. Plants 10(2):371
Mittal S, Mallikarjuna MG, Rao AR et al (2017) Comparative analysis of CDPK family in maize, Arabidopsis, rice, and sorghum revealed potential targets for drought tolerance improvement. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00115
Moeder W, Phan V, Yoshioka K (2019) Ca2+ to the rescue – Ca2+channels and signaling in plant immunity. Plant Sci 279:19–26
Narendra MC, Roy C, Kumar S et al (2021) Effect of terminal heat stress on physiological traits, grain zinc and iron content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Czech J Genet Plant Breed. https://doi.org/10.17221/63/2020-CJGPB
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36
Rose TJ, Raymond CA, Bloomfield C, King GJ (2015) Perturbation of nutrient source-sink relationships by post-anthesis stresses results in differential accumulation of nutrients in wheat grain. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400272
Scott MF, Fradgley N, Bentley AR et al (2021) Limited haplotype diversity underlies polygenic trait architecture across 70 years of wheat breeding. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-021-02354-7
Sehgal D, Dhakate P, Ambreen H, Shaik KH, Rathan ND, Anusha NM, Deshmukh R, Vikram P (2023) Wheat omics: advancements and opportunities. Plants 12(3):426
Shi S, Li S, Asim M et al (2018) The arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) and their roles in plant growth regulation and abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 19:1900
Singh A, Sagar S, Biswas DK (2017) Calcium dependent protein kinase, a versatile player in plant stress management and development. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2018.1428438
Singh J, Kumar R, Goswami S et al (2019) A putative heat-responsive transcription factor (TaHD97) and its targets in wheat (Triticum aestivum) providing thermotolerance. Indian J Biotechnol 18:214–223
Singh A, Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2020) Seed priming with calcium compounds abrogate fluoride-induced oxidative stress by upregulating defence pathways in an indica rice variety. Protoplasma. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-019-01460-5
Šramková Z, Gregová E, Šturdík E (2009) Chemical composition and nutritional quality of wheat grain. Acta Chim Slovaca 2:115–138
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
Wang J, Guo L, Xiao K (2007) Characterization and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Agric China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0066-z
Wang M, Li Q, Sun K et al (2018) Involvement of CsCDPK20 and CsCDPK26 in Regulation of Thermotolerance in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1068-0
Wang P, Hsu CC, Du Y et al (2020) Mapping proteome-wide targets of protein kinases in plant stress responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1919901117
Wang Y, Wang X, Wu H, Wang L, Wang H, Lu Z (2023) Characterization of Hsp17, a novel small heat shock protein, in Sphingomonas melonis TY under heat stress. Microbiol Spectrum 11(4):e01360-e1423
Wen F, Ye F, Xiao Z et al (2020) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) in grass Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6475-6
Zhang K, Han YT, Zhao FL et al (2015) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CDPK gene family in grape, vitis spp. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0552-z
Zhang H, Wei C, Yang X et al (2017) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase and its related kinase gene families in melon (Cucumis melo L.). PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176352
Zhang L, Wang L, Chen X et al (2022) The protein phosphatase 2C clade A TaPP2CA interact with calcium-dependent protein kinases, TaCDPK5/TaCDPK9–1, that phosphorylate TabZIP60 transcription factor from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci 321:111304. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLANTSCI.2022.111304
Zhao Y, Du H, Wang Y et al (2021) The calcium-dependent protein kinase ZmCDPK7 functions in heat-stress tolerance in maize. J Integr Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13056
Zou JJ, Wei FJ, Wang C, Wu JJ, Ratnasekera D, Liu WX, Wu WH (2010) Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK10 functions in abscisic acid-and Ca2+-mediated stomatal regulation in response to drought stress. Plant Physiol 154(3):1232–1243
Zuo R, Hu R, Chai G et al (2013) Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of CDPK and its closely related gene families in poplar (Populus trichocarpa). Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2351-z
Acknowledgements
We duly acknowledge the help rendered by scientists of Centre for Agricultural Bioinformatics (CABin), ICAR-Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute, New Delhi, India in executing the bioinformatics characterization of transcriptome data. We also thank the In-charge, National Phytotron Facility at ICAR-IARI, New Delhi for providing the growth chambers and other facilities for performing the experiments.
Funding
This work was funded by Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) under CABin project (sanction no. 21-56, TG3064) and National Innovations on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) project (Sanction no. TG-3079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13205_2024_3989_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 Digital gene expression (DGE) analysis of identified TaCDPKs from wheat using de novo transcriptomic approach, a) Expression pattern of TaCDPKs at various developmental stages in wheat, b) Expression pattern of TaCDPKs in different tissues of wheat; Out of 28 TaCDPKs, only 18 have their probe matching in affymetrix wheat genome array, expression analyses of putative CDPK genes were performed using Genevestigator Expression Database (TIF 1044 KB)
13205_2024_3989_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 Tissue specific expression analysis of important stress-associated genes (SAGs) in contrasting wheat cvs. under differential heat stress, a) Expression of SAGs in root tissues of contrasting wheat cvs., b) Expression of SAGs in stem tissues of contrasting wheat cvs., c) Expression of SAGs in leaves of contrasting wheat cvs., and d) Expression of SAGs in spike tissues of contrasting wheat cvs.; Wheat cvs. HD2985 (thermotolerant) and HD2329 (thermosusceptible) were used for the analysis; Root, stem, leaf and spike tissues were used for the analysis; T1 - 30±3°C, 2 h; T2 - 38±3°C, 2 h; β-Actin gene (acc. no. JQ004803) was used for normalizing the Ct value, Relative fold expression was calculated using Pfaffl method; all data are presented as mean ± SE of three replicates and different letters above each bar indicates significant difference between treatments (p ≤ 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (TIF 545 KB)
13205_2024_3989_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 Color chart depicting the expression pattern of important stress-associated genes in wheat under differential heat stress; C-22±3°C, and HS-treated (T1 - 30±3°C, 2 h; T2 - 38±3°C, 2 h), Stress-associated genes used for the expression analysis - MAPK-6 (acc. no. MN296518), CDPK-4 (acc. no. AY704446)], HSFA6e (acc. no. KU291394), HSF3 (acc. no. JQ771755)], sHSP17 (acc. no. JN572711), HSP70 (acc. no. HM209063)], SOD (acc. no. KC158224.1), CAT (acc. no. D86327); Relative fold expression has been shown on scale of 0 to +20-fold (TIF 649 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R.R., Niraj, R.K., Goswami, S. et al. Characterization of putative calcium-dependent protein kinase-1 (TaCPK-1) gene: hubs in signalling and tolerance network of wheat under terminal heat. 3 Biotech 14, 150 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03989-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03989-6