Abstract
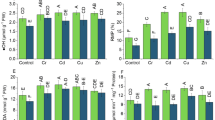
Brassica juncea L. plants were subjected to cobalt (Co) ion (0, 5 × 10−4, 10−3, 1.5 × 10−3 and 2 × 10−3 M) toxicity and were sprayed with different concentrations of 24-epibrassinolide (24-EBL) (0, 10−10, 10−8 and 10−6 M) at 15-day stage after sowing. They were sampled at 30 and 60 days after sowing and analyzed for growth parameters in terms of shoot length and number of leaves. Thereafter, leaves were excised and content of proteins and the activities of antioxidative enzymes (superoxide dismutase (SOD) (EC 1.15.1.1) catalase (CAT) (EC 1.11.1.6), ascorbate peroxidase (APOX) (EC 1.11.1.11), guaiacol peroxidase (POD) (EC 1.11.1.7) glutathione reductase (GR) (EC 1.6.4.2), monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR) (EC 1.1.5.4) and dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) (EC 1.8.5.1)) were analyzed. The plants exposed to cobalt ion exhibited a significant decline in growth in terms of shoot length and number of leaves. However, foliar spray treatment with 24-EBL was able to alleviate the stress generated by cobalt ion and significantly improved the above parameters. The activities of antioxidative enzymes (SOD, CAT, POD, GR, APOX, MDHAR and DHAR) and protein content were also regulated considerably in leaves of plants treated with 24-EBL alone, 10−8 M concentration being the most effective. The activities of antioxidative enzymes also increased in leaves of B. juncea plants by the application of cobalt ion to soil and consequently sprayed with 24-EBL. Similarly, the protein content was also regulated in leaves of B. juncea plants treated with 24-EBL as compared to untreated control plants, thereby revealing stress-protective properties of 24-EBL.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 24-EBL:
-
24-Epibrassinolide
- 28-HBL:
-
28-Homobrassinolide
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- APOX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- Cont.:
-
Control
- DAS:
-
Days after sowing
- DHAR:
-
Dehydroascorbate reductase
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- MDHAR:
-
Monodehydroascorbate reductase
- POD:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
Specific activity
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- UA:
-
Unit activity
References
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinhan, pp 673–684
Agarwal S, Shaheen R (2007) Stimulation of antioxidant system and lipid peroxidation by abiotic stresses in leaves of Momordica charantia. Braz J Plant Physiol 19(2):149–161
Ali B, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2007) 28-Homobrassinolide ameliorates the saline stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Environ Exp Bot 59:217–223
Arora A, Sairam RK, Srivastava GC (2002) Oxidative stress and antioxidative system in plants. Curr Sci 82:1227–1238
Arora P, Bhardwaj R, Kanwar MK (2010a) Presoaking seed treatment of 24-epiBL modulates Cr stress in Brassica juncea L. plants. Terr Aquatic Environ Toxicol 5:14–18
Arora P, Bhardwaj R, Kanwar MK (2010b) Seed presoaking treatment of 28-homobrassinolide modulates antioxidative defense system of Brassica Juncea L. under zinc metal stress. Seed Sci Biotech 4(1):23–27
Arora P, Bhardwaj R, Kanwar MK (2010c) 24-Epibrassinolide regulated antioxidative defense system of Brassica juncea L. under Zn metal stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16(3):285–293
Ashraf M, Akram NA, Arteca RN, Foolad MR (2010) The physiological, biochemical and molecular roles of brassinosteroids and salicylic acid in plant processes and salt tolerance. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29(3):162–190
Bajguz (2000) Effect of brassinosteroids on nucleic acids and protein content in cultured cells of Chlorella vulgaris. Plant Physiol Biochem 38(3):209–215
Bajguz A, Tretyn A (2003) The chemical characteristic and distribution of brassinosteroids in plants. Phytochemistry 62:1027–1046
Bakkaus E, Gouget B, Gallien JP, Khodja H, Carrot F, Morel JL, Collins R (2005) Concentration and distribution of cobalt in higher plants: the use of micro-PIXE spectroscopy. Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res B 231:350–356
Baryla A, Laborde C, Montillet JL, Triantaphylides C, Chagvardieff P (2000) Evaluation of lipid peroxidation as a toxicity bioassay for plants exposed to copper. Environ Pollut 109:131–135
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1975) Purification of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 250:5475–5480
Choudhary SP, Bhardwaj R, Gupta BD, Dutt P, Kanwar M, Arora P (2009a) Epibrassinolide regulated synthesis of polyamines and auxins in Raphanus sativus L. seedlings under Cu metal stress. Braz J Plant Physiol 21(1):25–32
Choudhary SP, Bhardwaj R, Gupta BD, Dutt P, Arora P (2009b) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on polyamines titers, antioxidative enzymes and seedling growth of Raphnus sativus L. under copper stress. Plant stress 3(1):7–12
Collins RN, Bakkaus E, Carriere M, Khodja H, Proux O, Morel J-L, Gouget B (2010) Uptake, localization, and speciation of cobalt in Triticum aestivum L. (Wheat) and Lycopersicon esculentum M. (Tomato). Environ Sci Technol 44(8):2904–2910
Dalton DA, Russell SA, Hanus FJ, Pascoe GA, Evans HJ (1986) Enzymatic reactions of ascorbate and glutathione that prevent peroxide damage in soybean root nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (PNAS) 83:3811–3815
Deng Z, Zhang X, Tang W, Oses-Prieto JA, Suzuki N, Gendron JM, Chen H, Guan S, Chalkley RJ, Peterman TK, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2007) A proteomics study of brassinosteroid response in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(12):2058–2071
Fariduddin Q, Hasan SA, Ali B, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2008) Effect of modes of application of 28-homobrassinolide on mung bean. Turk J Biol 32:17–21
Foyer CH, Lopez-Delgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signaling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Grove MD, Spencer GF, Rohwedder WK, Mandava N, Worley JF, Warthen JD, Steffens GL, Flippen-Anderson JL, Cook JC (1979) Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica napus pollen. Nature 281:216–217
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanism for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53(366):1–11
Hall JL, Williams LE (2003) Transition metal transporters in plants. J Exp Bot 54:2601–2613
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 4th edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Hasan SA, Hayat S, Ali B, Ahmad A (2008) 28-Homobrassinolide protects chickpea (Cicer arietinum) from cadmium toxicity by stimulating antioxidant. Environ Poll 151:60–66
Haubrick LL, Assmann SM (2006) Brassinosteroids and plant function: some clues, more puzzles. Plant Cell Environ 29:446–457
Hayat S, Ali B, Hassan SA, Ahmad A (2007) Brassinosteroids enhanced antioxidants under cadmium stress in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot 60(1):33–41
Hayat S, Ali B, Hassan SA, Hayat Q, Ahmad A (2009) Brassinosteroids protect Lycopersicon esculentum from cadmium toxicity applied as shotgun approach. Protoplasma 239(1–4):3–14
Hossain MA, Nakano Y, Asada K (1984) Monodehydroascorbate reductase in spinach chloroplasts and its participation in regeneration of ascorbate for scavenging hydrogen peroxide. Plant Cell Physiol 25:385–395
Kasprzak KS (2002) Oxidative DNA and protein damage in metal-induced toxicity and carcinogenesis. Free Rad Biol Med 32:958–967
Khripach VA, Zhabinskii VN, de-Groot AE (2000) Twenty years of brassinosteroids: steroidal plant hormones warrant better crops for the XXI century. Ann Bot 86:441–447
Kobayashi M, Shimizu S (1999) Cobalt proteins. Eur J Biochem 261(1):1–9
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autooxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 186:189–195
Lowry OH, Resbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mittler RS, Vanderauwera M, Gollery F, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22(5):867–880
Nemhauser JL, Chory J (2004) BRing it on: new insights into the mechanism of brassinosteroid action. J Exp Bot 55:265–270
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279
NRC (1999) Metals and radionuclides: technologies for characterization, remediation, and containment. In: Groundwater and soil cleanup: improving management of persistent contaminants, National Academy Press, Washington DC, pp 72–128
Nunez M, Mazzafera P, Mazorra LM, Siqueira WJ, Zullo MAT (2003) Influence of brassinosteroid analogue on antioxidant enzymes in rice grown in culture medium with NaCl. Biol Plant 47:67–70
Ogweno JO, Song XS, Shi K, Hu WH, Mao WH, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Nogue′s S (2008) Brassinosteroids alleviate heat-induced inhibition of photosynthesis by increasing carboxylation efficiency and enhancing antioxidant systems in Lycopersicon esculentum. J Plant Growth Regul 27:49–57
Palit S, Sharma A, Talukder G (1994) Effect of cobalt on plants. Bot Rev 60(2):149–181
Pullman GS, Zhang Y, Phan BH (2003) Brassinolide improves embryogenic tissue initiation in conifers and rice. Plant Physiol 22:96–104
Putter J (1974) Peroxidase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinhan, pp 685–690
Teisseire H, Guy V (2000) Copper-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes activities in fronds of duckweed (Lemna minor). Plant Sci 153:65–72
Vangronsveld JH, Clijsters (1994) Toxic effects of metals. In: Farago ME (ed) Plants and the chemical elements. Biochemistry, uptake, tolerance and toxicity. VCH Publishers, Weinheim, pp 150–177
Vardhini BV, Rao SSR (2003) Amelioration of osmotic stress by brassinosteroids on seed germination and seedling growth of three varieties of sorghum. Plant Growth Regul 41:25–31
Xue LW, Du JB, Yang H, Xu F, Yuan S, Lin HH (2009) Brassinosteroids counteract abscisic acid in germination and growth of Arabidopsis. Z Naturforsch C 64(3–4):225–230
Ye Q, Zhu W, Li L, Zhang S, Yin Y, Ma H, Wang X (2010) Brassinosteroids control male fertility by regulating the expression of key genes involved in Arabidopsis anther and pollen development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (PNAS) 107(13):6100–6105
Zhou B, Guo Z, Liu Z (2005) Effects of abscisic acid on antioxidant systems of Stylosanthes guianensis (Aublet) Sw. under chilling stress. Crop Sci 45:599–605
Acknowledgments
Financial assistance from University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India is duly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Lewak.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, P., Bhardwaj, R. & Kanwar, M.K. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on growth, protein content and antioxidative defense system of Brassica juncea L. subjected to cobalt ion toxicity. Acta Physiol Plant 34, 2007–2017 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1002-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1002-2