Abstract
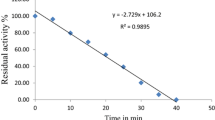
Bael (Aegle marmelos) is considered as a holy fruit comprised of vast number of phytonutrients. Whole bael tree including all its parts has medicinal significance. Lack of awareness and seasonal nature makes its processing rather challenging. Conventional heat processing may lead to inactivation of quality hampering enzymes such as peroxidase, but at the cost of loss in essential phytonutrients. In the present work it was observed that thermal inactivation of bael peroxidase obeyed first order kinetics with enzyme activation energy of 7.7 kJ mol−1. Complete inactivation of bael peroxidase was achieved within 11 min at 85 °C while ultrasound treatment attained in lesser time of 4 min at 64.07 W cm−2 ultrasonic intensity. Loss of marmelosin a well-known phytonutrient in bael fruit was found to be 83.29 % by heat (11 min, 85 °C) and only 50.20 % by ultrasonication (4 min, 64.07 W cm−2 ultrasonic intensity). Ultrasonication has potential to overcome harmful effects of heat processing with retention of phyto-constituents and hence has promising future in various food processing applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Badam, S.S. Bedekar, K.B. Sonawane, S.P. Joshi, In vitro antiviral activity of bael (Aegle marmelos Corr) upon human coxsackie viruses B1–B6. J. Commun. Dis. 34, 88 (2002)
A.K. Gupta, N. Tandon, Reviews on Indian Medicinal Plants, vol. 1 (Indian Council of Medicinal Research, New Delhi). 312 (2004)
P.K. Hajra, V.J. Nair, P. Daniel, Flora of India, vol. 4 (Botanical Survey of India Calcutta, Calcutta, 1997), p. 264
H. Takase, K. Yamamoto, H. Hirano, Y. Saito, A. Yamashita, Pharmacological profile of gastric mucosal protection by marminutes and nobiletin from a traditional herbal medicine. Aurantii fructus immaturus. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 66, 139 (1994)
G.C. Jagetia, P. Venkatesh, M.S. Baliga, Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa inhibits the proliferation of transplanted Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28, 58 (2005)
R. Chopra, Indigenous drugs of India Calcutta (Academic publishers, Calcutta, 1982)
S. Pitre, S.K. Srivastava, Two new anthraquinones from the seeds of Peganum harmala. Planta Med. 53, 106–107 (1987)
D.U. Lee, V. Heinz, D. Knorr, Effects of combination treatments of nisin and high-intensity ultrasonication with high pressure on the microbial inactivation in liquid whole egg. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 4, 387–393 (2003)
T.J. Mason, L. Paniwnyk, J.P. Lorimer, The uses of ultrasonication in food technology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 3, 253–260 (1996)
H. Feng, G.V. Barbosa-Canovas, J. Weiss, Ultrasonication Technologies for Food and Bioprocessing (Springer, New York, 2011)
J.Y. Ciou, H.H. Linb, P.Y. Chiang, C.C. Wang, A.L. Charles, The role of polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase in the browning of water caltrop pericarp during heat treatment. Food Chem. 34, 523–527 (2011)
G.E. Anthon, D.M. Barrett, Kinetic parameters for the thermal inactivation of quality-related enzymes in carrots and potatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 4119–4125 (2002)
P.B. Shinde, S.D. Katekhaye, M.B. Mulik, K.S. Laddha, Rapid simultaneous determination of marmelosin, umbelliferone and scopoletin from Aegle marmelos fruit by RP-HPLC. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 2251–2255 (2014)
V. Sciancalepore, V. Longone, F.S. Alviti, Partial purification and some properties of peroxidase from malvasi grapes. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 36, 105–110 (1985)
E.P. Troiani, C.T. Tropiani, E. Clemente, Peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in grape. Cienc. Agrotecnologia, 27, 2003, 635–642. DOI:10.1590/S1413-70542003000300019.
P. Cano, M.A. Marin, C. Fuster, Effects of some thermal treatments on polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase activities of banana (Musa cavendishii, var. enana). J. Sci. Food Agric. 51, 223–231 (1990)
S.S. Ercan, C. Soysal, Effect of ultrasound and temperature on tomato peroxidase. Ultrason. Sonochem. 18, 689–695 (2011)
V. Bifani, J. Inostroza, M.J. Cabezas, M. Ihl, Determination of kinetic parameters of peroxidase and chlorophyll in green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Win) and their stability when frozen. Rev. Quim. Teor. Apl. 467, 57–64 (2002)
F.E. Morales-Blancas, C.E. Chandia, L. Cisneros-Zevallos, Thermal inactivation kinetics of peroxidase and lipoxygenase from broccoli, green asparagus and carrots. J. Food Sci. 67, 146–154 (2002)
C. Soysal, Z. Soylemez, Kinetics and inactivation of carrot peroxidase by heat treatment. J. Food Eng. 68, 349–356 (2005)
R.M.S. Cruz, C.M. Vieira, C.L.M. Silva, Effect of heat and thermosonication treatments on peroxidase inactivation kinetics in watercress (Nasturtium officinale). J. Food Eng. 72, 8–15 (2006)
S.O. Eze, F.C. Chilaka, Kinetics and thermodynamics of heat inactivation of sorghum peroxidase. Ital. J. Food Sci. 19, 5 (2007)
M.V. Aguero, M.R. Ansorena, S.I. Roura, C.E. Del Valle, Thermal inactivation of peroxidase during blanching of butternut squash. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 41, 401–407 (2008)
C. Ganthavorn, C.W. Nagel, J.R. Powers, Thermal inactivation of asparagus lipoxygenase and peroxidase. J. Food Sci. 56, 47–49 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabir, M.P., Ananthanarayan, L. Comparative inactivation studies of Aegle marmelos (bael) peroxidase in crude extract of fruit by heat processing and ultrasonication treatment. Food Measure 11, 417–422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-016-9409-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-016-9409-x