Abstract
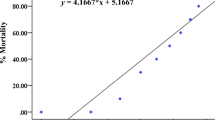
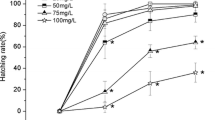
Cyhalofop-butyl is an aryloxyphenoxypropionate post-emergence herbicide widely used around the world in agriculture. The acute toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl to embryos, larvae (12 and 72 h post-hatching), and adult zebrafish, as well as the short-term developmental toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl to embryo and sac-fry stages, was tested. The results showed that the 96-h LC50 values of cyhalofop-butyl to embryos, 12 h post-hatching larvae, 72 h post-hatching larvae, and adult fish were 2.03, 0.58, 1.42, and 3.49 mg/L, respectively, suggesting zebrafish early life stages were more sensitive to cyhalofop-butyl than adult stage. Cyhalofop-butyl would inhibit the spontaneous movement, heartbeat, hatching rate of embryos, and the body length of surviving larvae of zebrafish at 1.00 mg/L or higher concentrations. Morphological abnormalities, including pericardial edema, yolk sac edema, deformation of tail, and deformation of spine, were induced by cyhalofop-butyl. The results indicated that cyhalofop-butyl had significant negative impacts on zebrafish at different life stages, and spontaneous movement and hatching rate were sensitive endpoints for assessing short-term developmental toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- APP:
-
aryloxyphenoxypropionate
- DAD:
-
diode array detector
- FET:
-
Fish Embryo Toxicity
- hpf:
-
h post-fertilization
- GR:
-
growth retardation
- GST:
-
glutathione-S-transferases
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- IUPAC:
-
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
- LOEC:
-
the lowest observed effect concentration
- NOEC:
-
the no observed effect concentration
- OECD:
-
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development
- PE:
-
pericardial edema
- SD:
-
spine deformation
- TD:
-
tail deformation
- UV:
-
ultraviolet
- YSE:
-
yolk sac edema
References
Bleau H, Daniel C, Chevalier G, vanTra H, Hontela A (1996) Effects of acute exposure to mercury chloride and methylmercury on plasma cortisol, T3, T4, glucose and liver glycogen in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 34(3):221–235
Chen Y, Huang Y, Wen C, Wang Y, Chen W, Chen L, Tsay HJ (2008) Movement disorder and neuromuscular change in zebrafish embryos after exposure to caffeine. Neurotoxicol Teratol 30(5):440–447
Dang Z, Li K, Yin H, Hakkert B, Vermeire T (2011) Endpoint sensitivity in fish endocrine disruption assays: regulatory implications. Toxicol Lett 202(1):36–46
De Gaspar I, Blanquez MJ, Fraile B, Paniagua R, Arenas MI (1999) The hatching gland cells of trout embryos: characterisation of N- and O-linked oligosaccharides. J Anat 194:109–118
Domingues I, Oliveira R, Lourenço J, Grisolia CK, Mendo S, Soares AMVM (2010) Biomarkers as a tool to assess effects of chromium (VI): comparison of responses in zebrafish early life stages and adults. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 152(3):338–345
Ducharme NA, Reif DM, Gustafsson JA, Bondesson M (2015) Comparison of toxicity values across zebrafish early life stages and mammalian studies: implications for chemical testing. Reprod Toxicol 55:3–10
Embry MR, Belanger SE, Braunbeck TA, Galay-Burgos M, Halder M, Hinton DE, Léonard MA, Lillicrap A, Norberg-King T, Whale G (2010) The fish embryo toxicity test as an animal alternative method in hazard and risk assessment and scientific research. Aquat Toxicol 97(2):79–87
Fako VE, Furgeson DY (2009) Zebrafish as a correlative and predictive model for assessing biomaterial nanotoxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(6):478–486
Fent K (2003) Ecotoxicological problems associated with contaminated sites. Toxicol Lett 140:353–365
Fent K, Meier W (1992) Tributyltin-induced effects on early life stages of minnows Phoxinus phoxinus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22(4):428–438
Fraysse B, Mons R, Garric J (2006) Development of a zebrafish 4-day embryo-larval bioassay to assess toxicity of chemicals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63(2):253–267
Guo Z, Huang F, Xu Z (2008) Residue dynamics of 10% fenoxaprop-p-ethyl cyhalofop-butyl EC in rice. J Ecol Rural Environ 24:51–54 (in Chinese)
Huang F, Guo ZY, Xu Z, Yang RB (2006) Toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl and fenoxaprop-ethyl to tadpole. J 327 Agro-Environ Sci 26(3):1063–1066 (in Chinese)
ISO (1996) Water quality-determination of the acute lethal toxicity of substances to a freshwater fiss [Brachydanio rerio Hamiltone-Buchanan (Teleostei, Cyprinidae)]. In: Part 3: Flow-through Method
Ito M, Kawahara H, Asai M (1998) Selectivity of cyhalofop-butyl in Poaceae species. J Weed Sci Technol 43(2):122–128
Jin M, Zhang X, Wang L, Huang C, Zhang Y, Zhao M (2009a) Developmental toxicity of bifenthrin in embryo-larval stages of zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 95(4):347–354
Jin Y, Chen R, Sun L, Qian H, Liu W, Fu Z (2009b) Induction of estrogen-responsive gene transcription in the embryo, larval, juvenile and adult life stages of zebrafish as biomarkers of short-term exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 150(3):414–420
Kimmel CB, Patterson J, Kimmel RO (1974) The development and behavioral characteristics of the startle response in the zebrafish. Dev Psychobiol 7:47–60
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203(3):253–310
Kumar B, Sharma R, Singh S (2012) Evaluation of harvest residues of cyhalofop-butyl in paddy soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89(2):344–347
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T (2009a) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 149(2):196–209
Lammer E, Kamp HG, Hisgen V, Koch M, Reinhard D, Salinas ER, Wendler K, Zok S, Braunbeck T (2009b) Development of a flow-through system for the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol In Vitro 23(7):1436–1442
Manjunatha B, Peng W, Liu K, Marigoudar SR, Chen X, Wang X, Wang X (2014) The effects of henna (hair dye) on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(17):10361–10367
Mu X, Pang S, Sun X, Gao J, Chen J, Chen X, Li X, Wang C (2013) Evaluation of acute and developmental effects of difenoconazole via multiple stage zebrafish assays. Environ Pollut 175:147–157
Nagel R (2002) DarT: the embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio—a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 19:38–48
Newman MC, Unger MA (2002) Fundamentals of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Nguyen TD, Han EM, Seo MS, Kim SR, Yun MY, Lee DM, Lee GH (2008) A multi-residue method for the determination of 203 pesticides in rice paddies using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 619(1):67–74
Niell S, Pareja L, Geis Asteggiante L, Cesio MV, Heinzen H (2010) Comparison of extraction solvents and conditions for herbicide residues in milled rice with liquid chromatography-diode array detection analysis (LC-DAD). Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 27(2):206–211
OECD 203 (1992) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. In: Section 2: effects on biotic systems test no. 203: fish, acute toxicity (FET) test. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
OECD 212 (1998) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. In: Section 2: effects on biotic systems test no. 212: fish, short-term toxicity test on embryo and sac-fry stage. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
OECD 236 (2013) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. In: Section 2: effects on biotic systems test no. 236: fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Oliveira R, Domingues I, Koppe Grisolia C, Soares AM (2009) Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 16(6):679–688
Ottis BV, Mattice JD, Talbert RE (2005) Determination of antagonism between cyhalofop-butyl and other rice (Oryza sativa) herbicides in barnyard grass (Echinochloa crusgalli). J Agric Food Chem 53:4064–4068
Pareja L, Fernández-Alba AR, Cesio V, Heinzen H (2011) Analytical methods for pesticide residues in rice. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30(2):270–291
Perrichon P, Le Bihanic F, Bustamante P, Le Menach K, Budzinski H, Cachot J, Cousin X (2014) Influence of sediment composition on PAH toxicity using zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryo-larval assays. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(24):13703–13719
Phong TK, Yoshino K, Hiramatsu K, Harada M, Inoue T (2010) Pesticide discharge and water management in a paddy catchment in Japan. Paddy Water Environ 8(4):361–369
Qin L, Liu F, Liu H, Wei Z, Sun P, Wang Z (2014) Evaluation of HODE-15, FDE-15, CDE-15, and BDE-15 toxicity on adult and embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(24):14047–14057
Strähle U, Scholz S, Geisler R, Greiner P, Hollert H, Rastegar S, Schumacher A, Selderslaghs I, Weiss C, Witters H et al (2012) Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod Toxicol 33(2):128–132
Wang SF, Liu KC, Wang XM, He QX, Chen XQ (2011) Toxic effects of celastrol on embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Drug Chem Toxicol 34(1):61–65
Wu C, Zhao X, Wu S, Cheng L, Wang Y, Chang T, Yu R, Ping L (2011) Toxicity and risk of herbicide cyhalofop-butyl on Rana limnocharis. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis 23(4):771–775
Wu J, Wang K, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014) Determination and study on dissipation and residue determination of cyhalofop-butyl and its metabolite using HPLC-MS/MS in a rice ecosystem. Environ Monit Assess 186(10):6959–6967
Xu C, Wang J, Liu W, Sheng GD, Tu Y, Ma Y (2008) Separation and aquatic toxicity of enantiomers of the pyrethroid insecticide lambdacyhalothrin. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:174–181
Yan X, Ning B, Wang L (2007) The problems and development and application of cyhalofop-butyl. World Pestic 29(2):43–45 (in Chinese)
Yang L, Ho NY, Alshut R, Legradi J, Weiss C, Reischl M, Mikut R, Liebel U, Müller F, Strähle U (2009) Zebrafish embryos as models for embryotoxic and teratological effects of chemicals. Reprod Toxicol 28(2):245–253
Zhao L, Zhu G, Jiang Z (2002) Determination of cyhalofop-butyl and its metabolites in water, soil and rice straw by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin J Anal Chem 31(2):163–166
Zhu G, Wu H, Walilino JKM, Li S (2002) Response of GSTase and liver esterase in goldfish (Carrasius auratus) and topmouth gudegon (Pseudorasbora parva) after sublethal exposure to cyhalofop-butyl and profurite-aminium. Chin J Pestic Sci 4(3):35–42
Zhu L, Mu X, Wang K, Chai T, Yang Y, Qiu L, Wang C (2015) Cyhalofop-butyl has the potential to induce developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis in early life stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Pollut 203:40–49
Acknowledgments
The present study was financially supported by National Twelfth Five-Year Plan for Science and Technology (Grant No. 2011BAE06B09) in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Fangjie Cao and Xiaoshan Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, F., Liu, X., Wang, C. et al. Acute and short-term developmental toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl to zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 10080–10089 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6236-x