Abstract
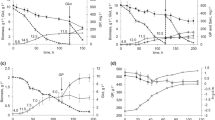
Heavy metal-contaminated soil derived from a former uranium mining site in Ronneburg, Germany, was used for sterile mesocosms inoculated with the extremely metal-resistant Streptomyces mirabilis P16B-1 or the sensitive control strain Streptomyces lividans TK24. The production and fate of bacterial hydroxamate siderophores in soil was analyzed, and the presence of ferrioxamines E, B, D, and G was shown. While total ferrioxamine concentrations decreased in water-treated controls after 30 days of incubation, the sustained production by the bacteria was seen. For the individual molecules, alteration between neutral and cationic forms and linearization of hydroxamates was observed for the first time. Mesocosms inoculated with biomass of either strain showed changes of siderophore contents compared with the non-treated control indicating for auto-alteration and consumption, respectively, depending on the vital bacteria present. Heat stability and structural consistency of siderophores obtained from sterile culture filtrate were shown. In addition, low recovery (32 %) from soil was shown, indicating adsorption to soil particles or soil organic matter. Fate and behavior of hydroxamate siderophores in metal-contaminated soils may affect soil properties as well as conditions for its inhabiting (micro)organisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adgent MA, Squadrito GL, Ballinger CA, Krzywanski DM, Lancaster JR, Postlethwait EM (2012) Desferrioxamine inhibits protein tyrosine nitration: mechanisms and implications. Free Radic Biol Med 53:951–961
Ahmed E, Holmström SJM (2014a) The effect of soil horizon and mineral type on the distribution of siderophores in soil. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 131:184–195
Ahmed E, Holmström SJM (2014b) Siderophores in environmental research: roles and applications. Microb Biotechnol 7:196–208
Alexander DB, Zuberer DA (1991) Use of chrome azurol S reagents to evaluate siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria. Biol Fertil Soils 12:39–45
Amoroso MJ, Oliver G, Castro GR (2002) Estimation of growth inhibition by copper and cadmium in heavy metal tolerant actinomycetes. J Basic Microbiol 42:231–237
Bank TL, Kukkadapu RK, Madden AS, Ginder-Vogel MA, Baldwin ME, Jardine PM (2008) Effects of gamma-sterilization on the physico-chemical properties of natural sediments. Chem Geol 251:1–7
Barriopedro D, Fischer EM, Luterbacher J, Trigo RM, García-Herreram R (2011) The hot summer of 2010: redrawing the temperature record map of Europe. Sci 332:220–224
Bossier P, Verstraete W (1986) Detection of siderophores in soil by a direct bioassay. Soil Biol Biochem 18:481–486
Boukhalfa H, Crumbliss AL (2002) Chemical aspects of siderophore mediated iron transport. Biometals 15:325–339
Cappellen PV (2003) Biomineralization and global biogeochemical cycles. In Dove PM. et al. (eds). Biomineralization, vol. 54
Castignetti D, Siddiqui AS (1990) The catabolism and heterotrophic nitrification of the siderophore deferrioxamine B. Biol Met 3:197–203
Chater KF, Biro S, Lee KJ, Palmer T, Schrempf H (2010) The complex extracellular biology of Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:171–198
Cocozza C, Tsao CCG, Cheah S-F, Kraemer SM, Raymond KN, Miano TM, Sposito G (2002) Temperature dependence of goethite dissolution promoted by trihydroxamate siderophores. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:431–438
Dean RB, Dixon WJ (1951) Simplified statistics for small numbers of observations. Anal Chem 23:636–638
Dhungana S, Ratledge C, Crumbliss AL (2004) Iron chelation properties of an extracellular siderophore exochelin. Inorg Chem 43:6274–6283
Dimkpa CO, Svatoš A, Dabrowska P, Schmidt A, Boland W, Kothe E (2008a) Involvement of siderophores in the reduction of metal-induced inhibition of auxin synthesis in Streptomyces spp. Chemosphere 74:19–25
Dimkpa C, Svatoš A, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E (2008b) Hydroxamate siderophores produced by Streptomyces acidiscabies E13 bind nickel and promote growth in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) under nickel stress. Can J Microbiol 54:163–172
Dimkpa CO, Merten D, Svatoš A, Büchel G, Kothe E (2009a) Siderophores mediate reduced and increased uptake of cadmium by Streptomyces tendae F4 and sunflower (Helianthus annuus), respectively. J Appl Microbiol 107:1687–1696
Dimkpa CO, Merten D, Svatoš A, Büchel G, Kothe E (2009b) Metal-induced oxidative stress impacting plant growth in contaminated soil is alleviated by microbial siderophores. Soil Biol Biochem 41:154–162
Escarré J, Lefèbvr C, Raboyeau S, Dossantos A, Gruber W, Cleyet Marel J, Frérot H, Noret N, Mahieu S, Collin C, van Oort F (2011) Heavy metal concentration survey in soils and plants of the les malines mining district (Southern France): implications for soil restoration. Water Air Soil Pollut 216:485–504
Fischer EM, Seneviratne SI, Lüthi D, Schär C (2007) Contribution of land-atmosphere coupling to recent European summer heat waves. Geophys Res Lett 34:L06707
Galhaut L, de Lespinay A, Walker D, Bernal M, Correal E, Lutts S (2014) Seed priming of Trifolium repens L. improved germination and early seedling growth on heavy metal-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–15
Grawunde A, Merten D, Büchel G (2014) Origin of middle rare earth element enrichment in acid mine drainage-impacted areas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6812–6823
Guo T, DeLaune RD, Patrick WH Jr (1997) The influence of sediment redox chemistry on chemically active forms of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and zinc in estuarine sediment. Environ Int 23:05–316
Haack EA, Johnston CT, Maurice PA (2008) Mechanisms of siderophore sorption to smectite and siderophore-enhanced release of structural Fe3+. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:3381–3397
Haferburg G, Reinicke M, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E (2007) Microbes adapted to acid mine drainage as source for strains active in retention of aluminum or uranium. J Geochem Explor 92:196–204
Havlicek E (2012) Soil biodiversity and bioindication: from complex thinking to simple acting. Eur J Soil Biol 49:80–84
Hernlem BJ, Vane LM, Sayles GD (1999) The application of siderophores for metal recovery and waste water remediation: examination of correlations for predictions of metal affinities. Water Res 33:951–960
Hider RC, Kong XL (2010) Chemistry and biology of siderophores. Nat Prod Rep 27:637–657
Huang P-M, Wang M-K, Chiu C-Y (2005) Soil mineral–organic matter–microbe interactions: impacts on biogeochemical processes and biodiversity in soils. Pedobiologia 49:609–635
Kothe E, Dimkpa C, Haferburg G, Schmidt A, Schmidt A, Schütze E (2010) Streptomycete heavy metal resistance: extracellular and intracellular mechanisms. In: Sherameti I, Varma A (eds) Soil heavy metals, vol. 19. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 225–235
Langella F, Grawunder A, Stark R, Weist A, Merten D, Haferburg G, Büchel G, Kothe E (2014) Microbially assisted phytoremediation approaches for two multi-element contaminated sites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6845–6858
Matsumoto K, Ozawa T, Jitsukawa K, Masuda H (2004) Synthesis, solution behavior, thermal stability, and biological activity of an Fe (III) complex of an artificial siderophore with intramolecular hydrogen bonding networks. Inorg Chem 43:8538–8546
Mawji E, Gledhill M, Milton JA, Tarran GA, Ussher S, Thompson A, Wolff GA, Worsfold PJ, Achterberg EP (2008) Hydroxamate siderophores: occurrence and importance in the Atlantic Ocean. Environ Sci Technol 42:8675–8680
McNamara NP, Black HIJ, Beresford NA, Parekh NR (2003) Effects of acute gamma irradiation on chemical, physical and biological properties of soils. Appl Soil Ecol 24:117–132
Miltner A, Bombach P, Schmidt-Brücken B, Kästner M (2011) SOM genesis: microbial biomass as a significant source. Biogeochemistry:1–15
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
O’Kane G (2012) What is the real cost of our food? Implications for the environment, society and public health nutrition. Public Health Nutr 15:268–276
Pattus F, Abdallah MA (2000) Siderophores and iron-transport in microorganisms. J Chin Chem Soc 47:1–20
Phieler R, Voit A, Kothe E (2013) Microbially supported phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: strategies and applications. In Scheper T et al. (eds). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 1–25
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2010) Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol 28:142–149
Ravel J, Wellington EM, Hill RT (2000) Interspecific transfer of Streptomyces giant linear plasmids in sterile amended soil microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:529–34
Reichstein M, Ciais P, Papale D, Valentini R, Running S, Viovy N, Cramer W, Granier A, Ogée J, Allard V, Aubinet M, Bernhofer C, Buchmann N, Carrara A, Grünwald T, Heimann M, Heinesch B, Knohl A, Kutsch W, Loustau D, Manca G, Matteucci G, Miglietta F, Ourcival JM, Pilegaard K, Pumpanen J, Rambal S, Schaphoff S, Seufert G, Soussana JF, Sanz MJ, Vesala T, Zhao M (2007) Reduction of ecosystem productivity and respiration during the European summer 2003 climate anomaly: a joint flux tower, remote sensing and modelling analysis. Glob Chang Biol 13:634–651
Saha R, Saha N, Donofrio RS, Bestervelt LL (2013) Microbial siderophores: a mini review. J Basic Microbiol 53:303–317
Schalk IJ, Hannauer M, Braud A (2011) New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environ Microbiol 13:2844–2854
Schmidt A, Haferburg G, Sineriz M, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E (2005) Heavy metal resistance mechanisms in actinobacteria for survival in AMD contaminated soils. Chemie der Erde – Geochem 65:131–144
Schmidt A, Haferburg G, Schmidt A, Lischke U, Merten D, Ghergel F, Büchel G, Kothe E (2008) Heavy metal resistance to the extreme: Streptomyces strains from a former uranium mining area. Chemie Der Erde-Geochem 69:35–44
Schütze E, Weist A, Klose M, Wach T, Schumann M, Nietzsche S, Merten D, Baumert J, Majzlan J, Kothe E (2013) Taking nature into lab: biomineralization by heavy metal-resistant streptomycetes in soil. Biogeosci 10:3605–3614
Schütze E, Klose M, Merten D, Nietzsche S, Senftleben D, Roth M, Kothe E (2014) Growth of streptomycetes in soil and their impact on bioremediation. J Hazard Mater 267:128–135
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Shestivska V, Adam V, Prasek J, Macek T, Mackova M, Havel L, Diopan V, Zehnalek J, Hubalek J, Kizek R (2011) Investigation of the antioxidant properties of metallothionein in transgenic tobacco plants using voltammetry at a carbon paste electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:2869–2883
Staunton S, Barthès M, Leclerc- Cessac E, Pinel F (2002) Effect of sterilization and experimental conditions on the isotopic exchange of nickel in two contrasting soils. Eur J Soil Sci 53:655–662
Streshinskaya GM, Kozlova YI, Alferova IV, Shashkov AS, Evtushenko LI (2005) Cell wall teichoic acids from Streptomyces daghestanicus VKM Ac-1722 T and Streptomyces murinus INA-00524 T. Microbiol 74:40–45
Vassilev A, Schwitzguébel J-P, Thewys T, Van Der Lelie D, Vangronsveld J (2004) The use of plants for remediation of metal-contaminated soils. Sci World J 4:9–34
Veis, A. (2003) Mineralization in an organic matrix framework. In Dove P M et al. (eds). Biomineralization, vol. 54.
Verstraete W, Mertens B (2004) The key role of soil microbes. In: Doelman P and Eijsackers HJP (eds). Developments in soil science, vol. 29. Elsevier, p. 127–157
Wang W, Qiu Z, Tan H, Cao L (2014) Siderophore production by actinobacteria. BioMetals:1–9
Waterman KC, Adami RC, Alsante KM, Hong J, Lamdis MS, Lombardo F, Roberts CJ (2002) Stabilization of pharmaceuticals to oxidative degradation. Pharm Dev Technol 7:1–32
Zeien H, Brümmer GW (1989) Chemische extraktion zur bestimmung der schwermetallbindungsformen in böden. Mitt der Dtsch Bodenkundlichen Ges Sonderheft 59(I):505–515
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Helmholtz Interdisciplinary Graduate School for Environmental Research (HIGRADE), the Jena School for Microbial Communication (JSMC), and the Research Training Group (DFG-Gk1257) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schütze, E., Ahmed, E., Voit, A. et al. Siderophore production by streptomycetes—stability and alteration of ferrihydroxamates in heavy metal-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 19376–19383 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3842-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3842-3