Abstract
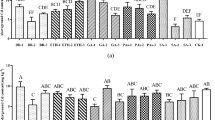
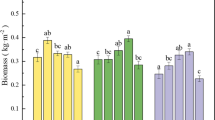
The efficiency of phytoremediation is mainly dependent on the capacity of plants in absorption, translocation, and accumulation of Cd. This study was designed to investigate whether Cd translocation and accumulation in tall fescue plants was regulated by foliar application of KH2PO4. The results showed that the foliar application of KH2PO4 significantly increased Cd concentration and total Cd accumulated in leaves and the capacity of Cd extraction, compared to the root application. The water-soluble organic acid complexes and the pectate- and protein-integrated Cd were the two major Cd chemical forms deposited in leaves. The foliar application increased Cd in the pectate- and protein-integrated forms and decreased the water-soluble forms in leaves. Cd phosphates were not the major chemical forms deposited in leaves in both foliar and root applications. The results indicated that the foliar application of KH2PO4 enhanced Cd accumulation in leaves of tall fescue, which might be associated with the leaf deposit of the pectate- and protein-integrated Cd forms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awad, M. A., Ismail, S. M., & Al-Qurashi, A. D. (2014). Effect of potassium soil and foliar spray fertilization on yield, fruit quality and nutrient uptake of ‘Seweda’ date palm grown in sandy loam soil. Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment, 12, 305–311.
Boyanov, M. I., Kelly, S. D., Kemner, K. M., Bunker, B. A., Fein, J. B., & Fowle, D. A. (2003). Adsorption of cadmium to Bacillus subtilis bacterial cell walls: a pH-dependent X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy study. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 67, 3299–3311.
Brennan, R. F., & Bolland, M. D. A. (2014). Cadmium concentration in yellow lupin grain is decreased by zinc applications to soil but is increased by phosphorus applications to soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 37, 850–868.
Chang, Z. H., Jin, X., & Li, D. Y. (2014). Phosphorus responses vary among cool-season turfgrasses during establishment from seed. Agronomy Journal, 106, 1975–1980.
Chen, S. B., Xu, M. G., Ma, Y. B., & Yang, J. C. (2007). Evaluation of different phosphate amendments on availability of metals in contaminated soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 67, 278–285.
Choppala, G., Saifullah Bolan, N., Bibi, S., Iqbal, M., Rengel, Z., Kunhikrishnan, A., Ashwath, N., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance to cadmium toxicity. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 33, 374–391.
Du, J. N., Yan, C. L., & Li, Z. D. (2014). Phosphorus and cadmium interactions in Kandelia obovata (S. L.) in relation to cadmium tolerance. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 355–365.
Fan, L., & Moshe, S. (2002). Response of maize to foliar vs soil application of nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 25, 2333–2342.
Fernandez, V., Guzman, P., Peirce, C. A. E., McBeath, T. M., Khayet, M., & McLaughlin, M. J. (2014). Effect of wheat phosphorus status on leaf surface properties and permeability to foliar-applied phosphorus. Plant and Soil, 384, 7–20.
Hasan, M. K., Ahammed, G. J., Yin, L. L., Shi, K., Xia, X. J., Zhou, Y. H., Yu, J. Q., & Zhou, J. (2015). Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 601.
He, B., Yun, Z. L., Shi, J. B., & Jiang, G. B. (2012). Research progress of heavy metal pollution in China: sources, analytical methods, status, and toxicity. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58, 134–140.
Huang, H. G., Li, T. Q., Gupta, D. K., He, Z. L., Yang, X. E., Ni, B. N., & Li, M. (2012). Heavy metal phytoextraction by Sedum alfredii is affected by continual clipping and phosphorus fertilization amendment. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 24, 376–386.
Jemo, M., Nwoke, C., Pypers, P., & Vanlauwe, B. (2015). Response of maize (Zea mays) to the application of foliar fertilizers in the Sudan and Guinea savanna zone of Nigeria. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 178, 374–383.
Jin, D. F., & West, C. A. (1984). Characteristics of galacturonate oligomers as elicitors of casbenesynthetase activity in castor bean seedlings. Plant Physiololy, 74, 989–992.
Leopold, I., Gunther, D., Schmidt, J., & Neumann, D. (1999). Phytochelatins and heavy metal tolerance. Phytochemistry, 50, 1323–1328.
Levi-Minzi, R., & Petruzzelli, G. (1984). The influence of phosphate fertilizers on Cd solubility in soil. Water Air Soil Pollution., 23, 423–429.
Li, C. C., Dang, F., Cang, L., Zhou, C. F., & Zhou, D. M. (2014). Integration of metal chemical forms and subcellular partitioning to understand metal toxicity in two lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivars. Plant and Soil, 384, 201–212.
Liu, Y., Zhuang, P., Li, Z. A., Zou, B., Wang, G., Li, N. Y., & Qiu, J. (2013). Effects of fertiliser and intercropping on cadmium uptake by maize. Chemistry and Ecology, 29, 489–500.
Matusik, J., Bajda, T., & Manecki, M. (2008). Immobilization of aqueous cadmium by addition of phosphates. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 1332–1339.
McGowen, S. L., Basta, N. T., & Brown, G. O. (2001). Use of diammonium phosphate to reduce heavy metal solubility and transport in smelter-contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 493–500.
McLaughlin, M. J., Whatmuff, M., Warne, M., Heemsbergen, D., Barry, G., Bell, M., Nash, D., & Pritchard, D. (2006). A field investigation of solubility and food chain accumulation of biosolid-cadmium across diverse soil types. Environmental Chemistry, 3, 428–432.
Nordberg, G. F. (2004). Cadmium and health in the 21st century—historical remarks and trends for the future. Biometals, 17, 485–489.
Nothnagel, E. A., McNeil, M., & Albersheim, P. (1983). Host-pathogen interactions. XXII. A galacturonic acid oligosaccharide from plant cell walls elicits phytoalexins. Plant Physiology, 71, 916–926.
Olsson, I. M., Eriksson, J., Oborn, I., Skerfving, S., & Oskarsson, A. (2005). Cadmium in food production systems: a health risk for sensitive population groups. AMBIO, 34, 344–351.
Pande, M., Goli, M. B., & Bellaloui, N. (2014). Effect of foliar and soil application of potassium fertilizer on soybean seed protein, oil, fatty acids, and minerals. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 5, 541–548.
Pilon-Smits, E. (2005). Phytoremediation. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 56, 15–39.
Qiu, Q., Wang, Y. T., Yang, Z. Y., & Yuan, J. G. (2011). Effects of phosphorus supplied in soil on subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in two Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica parachinensis L.) cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 49, 2260–2267.
Rochayati, S., Du Laing, G., Rinklebe, J., Meissner, R., & Verloo, M. (2011). Use of reactive phosphate rocks as fertilizer on acid upland soils in Indonesia: accumulation of cadmium and zinc in soils and shoots of maize plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 186–194.
Siebers, N., Siangliw, M., & Tongcumpou, C. (2013). Cadmium uptake and subcellular distribution in rice plants as affected by phosphorus: soil and hydroponic experiments. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 13, 833–844.
Sterckeman, T., Goderniaux, M., Sirguey, C., Cornu, J. Y., & Nguyen, C. (2015). Do roots or shoots control cadmium accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens? Plant and Soil, 392, 87–99.
Tan, W. N., Li, Z. A., Qiu, J., Zou, B., Li, N. Y., Zhuang, P., & Wang, G. (2011). Lime and phosphate could reduce cadmium uptake by five vegetables commonly grown in South China. Pedosphere, 21, 223–229.
Thawornchaisit, U., & Polprasert, C. (2009). Evaluation of phosphate fertilizers for the stabilization of cadmium in highly contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 1109–1113.
Trevizam, A. R., Villanueva, F. C. A., Muraoka, T., do Nascimento, V. F., & Abreu, C. H. (2010). Phosphorus application for the chemical immobilization of cadmium in contaminated soil. Quimica Nova, 33, 1235–1241.
Vogel-Mikus, K., Arcon, I., & Kodre, A. (2010). Complexation of cadmium in seeds and vegetative tissues of the cadmium hyperaccumulator Thlaspi praecox as studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Plant and Soil, 331, 439–451.
Wang, B. L., Xie, Z. M., Chen, J. J., Jiang, J. T., & Su, Q. F. (2008). Effects of field application of phosphate fertilizers on the availability and uptake of lead, zinc and cadmium by cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) in a mining tailing contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 20, 1109–1117.
Wang, H. O., Wang, T., & Ahmad, I. (2015). Involvement of phosphate supplies in different transcriptional regulation pathway of Oryza sativa L’.s antioxidative system in response to arsenite and cadmium stress. Ecotoxicology, 24, 1259–1268.
Xu PX. 2014. Studies on cadmium tolerance and detoxification in tall fescue and Kentucky bluegrass. Ph.D. Dissertation of Shanghai JiaoTong University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, P. X., & Wang, Z. L. (2013). Physiological mechanism of hypertolerance of cadmium in Kentucky bluegrass and tall fescue: chemical forms and tissue distribution. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 96, 35–42.
Xu, P. X., & Wang, Z. L. (2014). A comparison study in cadmium tolerance and accumulation in two cool-season turfgrasses and Solanum nigrum L. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 225(5), 1938.
Xu, Q. S., Min, H. L., Cai, S. J., Fu, Y. Y., Sha, S., Xie, K. B., & Du, K. H. (2012). Subcellular distribution and toxicity of cadmium in Potamogeton crispus L. Chemosphere, 89, 114–120.
Yao, Q., Yang, R. H., Long, L. K., & Zhu, H. H. (2014). Phosphate application enhances the resistance of Arbuscular mycorrhizae in clover plants to cadmium via polyphosphate accumulation in fungal hyphae. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 108(SI), 63–70.
Yu, Z. G., & Zhou, Q. X. (2009). Growth responses and cadmium accumulation of Mirabilis jalapa L. under interaction between cadmium and phosphorus. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 38–43.
Zenk, M. H. (1996). Heavy metal detoxification in higher plants—a review. Gene, 179, 21–30.
Zhang, W., Lin, K. F., Zhou, J., Zhang, W., Liu, L. L., & Zhang, Q. Q. (2014). Cadmium accumulation, sub-cellular distribution and chemical forms in rice seedling in the presence of sulfur. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 37, 348–353.
Zhao, Y. F., Wu, J. F., Shang, D. R., Ning, J. S., Zhai, Y. X., Sheng, X. F., & Ding, H. Y. (2015). Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in the edible seaweed, Porphyra yezoensis. Food Chemistry, 168, 48–54.
Zupancic, M., Lavric, S., & Bukovec, P. (2012). Metal immobilization and phosphorus leaching after stabilization of pyrite ash contaminated soil by phosphate amendments. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14, 704–710.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for the financial support given by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31472143). The authors are indebted to Prof. Dr. Bingru Huang at Rutgers University for the great help in refining the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, D., Xu, P., Dong, Q. et al. Comparison of Foliar and Root Application of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate in Regulating Cadmium Translocation and Accumulation in Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea). Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 118 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3304-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3304-x