Abstract
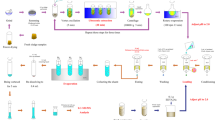
Extraction and analysis methods have been developed for the detection of the following four antibacterial agents and two natural estrogens in treated municipal wastewater sludge and commercial compost: sulfamethoxazole (SMX), sulfadimethoxine (SDM), tetracycline (TET), oxytetracycline (OXY), estrone (E1), and 17β-estradiol (E2). The antibiotics and estrogens were extracted from secondary sludge and mixed compost using ultrasonic solvent extraction. Citric acid (pH 4.7) and methanol were used as extraction buffer, followed by tandem-solid-phase extraction cleanup, strong anion exchange + hydrophilic–lipophilic balance for antibiotics and CarboPrep/NAX for estrogens. For quantification, two different methods were employed, using HPLC–MS/MS, with an electrospray ionization source for antibiotics and an atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization source for estrogens. Recoveries were 11–31% for the sulfonamides (SMX and SDM) and tetracyclines (TET and OXY) and 30–59% for the estrogens (E1 and E2) over the entire method. Limits of detection for the extraction method were in the nanogram per gram range for dry weight sludge and compost samples. Neither of the two sulfonamide antibiotics was detected in secondary sludge or mixed compost samples. Estrogens were found in compost in amounts of 160 ± 65 ng/g (E1) and 21 ± 3 ng/g (E2), but not in sludge. The tetracyclines, as well as what is believed to be the 4-epimer of OXY, were found in both sludge and compost in amounts of 1.57 ± 0.67 and 2.95 ± 0.42 μg/g (TET), 0.56 ± 0.12 and 6.51 ± 0.52 μg/g (OXY), and 7.60 ± 1.68 and 1.35 ± 0.24 μg/g (4-epi-OXY), respectively. These results indicate that sorption-prone compounds are not removed during the wastewater treatment process and can persist through sludge digestion and that the composting process does not sufficiently eliminate these particular contaminants. Thus, biosolids (even composted) are an additional source of drug residues leaching into the environment, and it must be considered while using biosolids as fertilizer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, H., Siegrist, H., Halling-Sørensen, B., & Ternes, T. A. (2003). Fate of estrogens in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 4021–4026.
Anderson, C. R., Rupp, H. S., & Wu, W.-H. (2005). Complexities in tetracycline analysis–chemistry, matrix extraction, cleanup, and liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1075, 23–32.
Andreu, V., Vazquez-Roig, P., Blasco, C., & Picó, Y. (2009). Determination of tetracycline residues in soil by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anals of Bioanalytical Chemistry, 394, 1329–1339.
Avisar, D., Lester, Y., & Ronen, D. (2009a). Sulfamethoxazole detected in a deep phreatic aquifer beneath effluent irrigated land. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 4278–4282.
Avisar, D., Levin, G., & Gozlan, I. (2009b). The occurrence of oxytetracycline (OTC) in local groundwater beneath fish pond. Earth and environmental sciences. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0088-3.
Avisar, D., Primor, O., & Mamane, H. (2009c). Sorption of sulfonamides and tetracyclines to montmorillonite clay. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0212-8.
Babić, S., Petrović, M., & Kaštelan-Macan, M. (1998). Ultrasonic solvent extraction of pesticides from soil. Journal of Chromatography. A, 823, 3–9.
Barber, L. B., Keefe, S. H., Leblanc, D. R., Bradley, P. M., Chapelle, F. H., Meyer, M. T., Loftin, K. A., Kolpin, D. W., & Rubio, F. (2009). Fate of sulfamethoxazole, 4-nonylphenol, and 17β-estradiol in groundwater contaminated by wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 4843–4850.
Baronti, C., Curini, R., D’Ascenzo, G., Di Corcia, A., Gentili, A., & Samperi, R. (2000). Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 5059–5066.
Batt, A. L., Snow, D. D., & Aga, D. S. (2006). Occurrence of sulfonamide antimicrobials in private water wells in Washington County, Idaho, USA. Chemosphere, 64, 1963–1971.
Belfroid, A. C., Van der Horst, A., Vethaak, A. D., Schäfer, A. J., Rijs, G. B. J., Wegener, J., & Cofino, W. P. (1999). Analysis and occurrence of estrogenic hormones and their glucuronides in surface water and waste water in the Netherlands. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 101–108.
Blackwood, R. K., Boothe, J. H., Chopra, I., Cunha, B. A., Goodman, J. J., Gustafson, R. H., Hlavka, J. J., Hostálek, Z., Kiser, J. S., Rogalski, W., & Vanek, Z. (Eds.). (1985). The tetracyclines (p. 59). Berlin: Springer.
Boxall, A. B. A., Blackwell, P., Cavallo, R., Kay, P., & Tolls, J. (2002). The sorption and transport of a sulphonamide antibiotic in soil systems. Toxicology Letters, 131, 19–28.
Braga, O., Smythe, G. A., Schafer, A. I., & Feitz, A. J. (2005). Steroid estrogens in primary and tertiary wastewater treatment plants. Water Science and Technology, 38, 3047–3055.
Capolongo, F., Santi, A., Tomasi, L., Anfossi, P., Missagia, M., & Montesissa, C. (2002). Residues of oxytetracycline and its 4′-epimer in edible tissues from turkeys. Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, 85, 8–14.
Castiglioni, S., Bagnati, R., Calamari, D., Fanelli, R., & Zuccato, E. (2005). A multiresidue analytical method using solid-phase estraction and high-pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to measure pharmaceuticals of different therapeutic classes in urban wastewaters. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1092, 206–215.
Christian, T., Schneider, R., Färber, H., Skutlarek, D., Meyer, M., & Goldbach, H. (2003). Determination of antibiotic residues in manure, soil, and surface waters. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 36–44.
Christiansen, L.B., Winther-Nielsen, M., Helweg, C. (2002). Feminisation of fish: the effect of estrogenic compounds and their fate in sewage treatment plant and nature. Danish Environmental Protection Agency, Danish Ministry of the Environment. Environmental Project (Miljøprojekt) No. 729.
Colucci, M. S., Bork, H., & Topp, E. (2001). Persistence of estrogenic hormones in agricultural soils. I. 17β-Estradiol and estrone. Journal of Environmenal Quality, 30, 2070–2076.
De Liguoro, M., Cibin, V., Capolongo, F., Halling-Sørensen, B., & Montesissa, C. (2003). Use of oxytetracycline and tylosin in intensive calf farming: evaluation of transfer to manure and soil. Chemosphere, 52, 203–212.
Desbrow, C., Routledge, E. J., Brighty, G. C., Sumpter, J. P., & Waldock, M. (1998). Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 1549–1558.
Drillia, P., Stamatelatou, K., & Lyberatos, G. (2005). Fate and mobility of pharmaceuticals in solid matrices. Chemosphere, 60, 1034–1044.
Feitosa-Felizzola, J., & Chiron, S. (2009). Occurrence and distribution of selected antibiotics in a small Mediterranean stream (Arc River, Southern France). Journal of Hydrology, 364, 50–57.
Filby, A. L., Neuparth, T., Thorpe, K. L., Owen, R., Galloway, T. S., & Tyler, C. R. (2007). Health impacts of estrogens in the environment, considering complex mixture effects. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115, 1704–1710.
Gu, C., Karthikeyan, K. G., Sibley, S. D., & Pedersen, J. A. (2007). Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere, 66, 1494–1501.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Nors Nielsen, S., Lanzky, P. F., Ingerslev, F., Holten Lutzhoft, H. C., & Jorgensen, S. E. (1998). Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere, 36, 357–393.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Sengeløv, G., & Tjørnelund, J. (2002). Toxicity of tetracyclines and tetracycline degradation products to environmentally relevant bacteria, including selected tetracycline-resistant bacteria. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 42, 263–271.
Hamscher, G., Sczesny, S., Höper, H., & Nau, H. (2002). Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 1509–1518.
Hanselman, T. A., Graetz, D. A., & Wilkie, A. C. (2003). Manure-borne estrogens as potential environmental contaminants: a review. Environmental Science & Technology, 23, 5471–5478.
Hartig, C., Storm, T., & Jekel, M. (1999). Detection and identification of sulphonamide drugs in municipal waste water by liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 854, 163–173.
Hirsch, R., Ternes, T., Haberer, K., & Kratz, K.-L. (1999). Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 109–188.
Holm, J. V., Ruggc, K., Bjerg, P. L., & Christensen, T. H. (1995). Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical organic compounds in the groundwater downgradient of a landfill (Grinsted, Denmark). Environmental Science & Technology, 29, 1415–1420.
Huang, C. H., & Sedlak, D. L. (2001). Analysis of estrogenic hormones in municipal wastewater effluent and surface water using enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay and gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 133–139.
Jacobsen, A. M., Halling-Sørensen, B., Ingerslev, F., & Hansen, S. H. (2004). Simultaneous extraction of tetracycline, macrolide and sulfonamide antibiotics from agricultural soils using pressurized liquid extraction, followed by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1038, 157–170.
Jobling, S., Nolan, M., Tyler, C. R., Brighty, G., & Sumpter, J. P. (1998). Widespread sexual disruption in wild fish. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 2498–2506.
Johnson, A. C., Belfroid, A., & Di Corcia, A. (2000). Estimating estrogen input to activated sludge treatment works and observations on their removal from effluent. Science of the Total Environment, 256, 163–173.
Jørgensen, S. E., & Halling-Sørensen, B. (2000). Drugs in the environment. Chemosphere, 40, 691–699.
Joss, A., Andersen, H., Ternes, T., Richie, P. R., & Siegrist, H. (2004). Removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater treatment under aerobic and anaerobic conditions: consequences for plant optimization. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 3047–3055.
Joss, A., Keller, E., Alder, A. C., Göbel, A., McArdell, C. S., Ternes, T., & Siegrist, H. (2005). Removal of pharmaceuticals and fragrances in biological wastewater treatment. Water Research, 39, 3139–3152.
Kim, S., Eichhorn, P., Jensen, J. N., Weber, A. S., & Aga, D. S. (2005). Removal of antibiotics in wastewater: effect of hydraulic and solid retention times on the fate of tetracycline in the activated sludge process. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 5816–5823.
Körner, W., Spengler, P., Bolz, U., Schueller, W., Hanf, V., & Metzger, J. W. (2001). Substances with estrogenic activity in effluents of sewage treatment plants in South-Western Germany. 2. Biological analysis. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 2142–2151.
Kühne, M., Ihnen, D., Möller, G., & Agthe, O. (2000). Stability of tetracycline in water and liquid manure. Journal of Veterinary Medicine Series A, 47, 379–384.
Kumar, K., Gupta, S. C., Chander, Y., & Singh, A. K. (2005). Antibiotic use in agriculture and its impact on the terrestrial environment. Advances in Agronomy, 87, 1–57.
Lewis, K. M. & Archer, R. D. (1979). pKa values of estrone, 17 beta-estradiol and 2-methoxyestrone. Steroids, 34, 485–499.
Lindberg, R. H., Wennberg, P., Johansson, M. I., Tysklind, M., & Andersson, B. A. V. (2005). Screening of human antibiotic substances and determination of weekly mass flows in five sewage treatment plants in Sweden. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 3421–3429.
Lindsey, M. E., Meyer, M., & Thurman, E. M. (2001). Analysis of trace levels of sulfonamide and tetracycline antimicrobials in groundwater and surface water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 4640–4646.
Loke, M. L., Tjørnelund, J., & Halling-Sørensen, B. (2002). Determination of the distribution coefficient (log Kd) of oxytetracycline, tylosin A, olaquindox and metronidazole in manure. Chemosphere, 48, 351–361.
Lopez de Alda, M., Díaz-Cruz, S., Petrovic, M., & Barceló, D. (2003). Liquid chromatography-(tandem) mass spectrometry of selected emerging pollutants (steroid sex hormones, drugs and alkylphenolic surfactants) in the aquatic environment. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1000, 503–526.
Martinez, E. E., & Shimoda, W. (1988). Liquid chromatographic determination of tetracycline residues in animal feeds. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 71, 477–480.
Mitscher, L. A. (1978). The chemistry of the tetracycline antibiotics. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Oberdörster, E., & Cheek, A. O. (2000). Gender benders at the beach: endocrine disruption in marine and estuarine organisms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 23–36.
Onji, Y., & Tanigawa, K. (1984). Liquid-chromatographic determination of tetracycline residues in meat and fish. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 67, 1135–1137.
Pena, A. L. S., Lino, C. M. & Silveira, I. N. (1999). Determination of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and chlortetracycline in milk by liquid chromatography with post column derivatization and fluorescence detection. The Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, 82, 55–59.
Peng, X., Wang, Z., Kuang, W., Tan, J., & Li, K. (2006). A preliminary study on the occurrence and behaviour of sulfonamides, ofloxacin and chloramphenicol antimicrobials in wastewaters of two sewage treatment plants in Guangzhou, China. Science of the Total Environment, 371, 314–322.
Pérez, S., Eichhorn, P., & Aga, D. S. (2005). Evaluating the biodegradability of sulfamethazine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfathiazole, and trimethoprim at different stages of sewage treatment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 1361–1367.
Rooklidge, S. J. (2004). Environmental antimicrobial contamination from terraccumulation and diffuse pollution pathways. Science of the Total Environment, 325, 1–13.
Rose, J., Holbech, H., Lindholst, C., Nørum, U., Povlsen, A., Korsgaard, B., & Bjerregaard, P. (2002). Vitellogenin induction by 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 131, 531–539.
Sacher, F., Lange, F. T. H., Brauch, H. J., & Blankenhorn, I. (2001). Pharmaceuticals in groundwaters. Analytical methods and results of a monitoring program in Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany. Journal of Chromatography. A, 938, 199–210.
Sassman, S.A., & Lee, L.S. (2005). Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 7452–7459.
Shareef, A., Angove, M. J., Wells, J. D., & Johnson, B. B. (2006). Aqueous solubilities of estrone, 17β-estradiol, 17α-ethynylestradiol, and bisphenol A. Journal of Chemical Engineering Data, 51, 879–881.
Shore, L., Kapulnik, Y., Ben-Dov, B., Fridman, Y., Wininger, S., & Shemesh, M. (1992). Effects of estrone and 17β-estradiol on vegetative growth of Medicago sativa. Physiology of Plants, 84, 217–222.
Shore, L. S., Gurevitz, M., & Shemesh, M. (1993). Estrogen as an environmental pollutant. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 51, 361–366.
Sithole, B. B., & Guy, R. D. (1987). Models for tetracycline in aquatic environments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 32, 315–321.
Snyder, S. A., Villeneuve, D. L., Snyder, E. M., & Giesy, J. P. (2001). Identification and quantification of oestrogen receptor agonists in wastewater effluents. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3620–3625.
Ternes, T. A., Stumpf, M., Mueller, J., Haberer, K., Wilken, R.-D., & Servos, M. (1999). Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants-I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 81–90.
Ternes, T. A., Kreckel, P., & Mueller, J. (1999). Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants-II. Aerobic batch experiments with activated sludge. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 91–99.
Ternes, T. A., Andersen, H., Gilberg, D., & Bonerz, M. (2002). Determination of estrogens in sludge and sediments by liquid extraction and GC/MS/MS. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 3498–3504.
Ternes, T. A., Herrmann, N., Bonerz, M., Knacker, T., Siegrist, H., & Joss, A. (2004). A rapid method to measure the solid-water distribution coefficient (K d) for pharmaceuticals and musk fragrances in sewage sludge. Water Research, 38, 4075–4084.
Ternes, T. A., Bonerz, M., Herrmann, N., Löffler, D., Keller, E., Lacida, B. B., & Alder, A. C. (2005). Determination of pharmaceuticals, iodinated contrast media and musk fragrances in sludge by LC tandem MS and GC/MS. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1067, 213–223.
Thiele-Bruhn, S. (2003). Pharmaceutical antibiotics compounds in soils a review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 166, 145–167.
Thorpe, K. L., Maack, G., Benstead, R., & Tyler, C. R. (2009). Estrogenic wastewater treatment works effluents reduce egg production in fish. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 2976–2982.
Tolls, J. (2001). Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3397–3406.
Tor, A., Aydin, M. E., & Özcan, S. (2006). Ultrasonic solvent extraction of organochlorine pesticides from soil. Analytica Chimica Acta, 559, 173–180.
Tzadikov, I. (2010) Ministry of Environmental Protection report, “סילוק בוצות מטש” עירוניים – 2009" (in Hebrew).
Vogel, J. R., Verstraeten, I. M., Coplen, T. B., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., & Barber, L. B. (2005). Occurrence of selected pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical compounds and stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in a Riverbank filtration study, Platte River, Nebraska. US Geological Survey Data Series (2001–2003), 117, 1–39.
Wang, Y., Hu, W., Cao, Z., Fu, X., & Zhu, T. (2005). Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting compounds in reclaimed water from Tianjin, China. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 383, 857–863.
Yalkowsky, S. H. & Dannenfelser, R. M. (1992). The AQUASOL dATAbASE of Aqueous Solubility. Fifth Ed, Univ Az, College of Pharmacy, Tucson, AZ.
Zhu, J., Snow, D. D., Cassade, D. A., Monson, S. J., & Spalding, R. F. (2001). Analysis of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and chlortetracycline in water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 928, 177–186.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Israel Ministry of the Environment and the Winikow Fund for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafrir, M., Avisar, D. Development Method for Extracting and Analyzing Antibiotic and Hormone Residues from Treated Wastewater Sludge and Composted Biosolids. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 2571–2587 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1049-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1049-5