Abstract
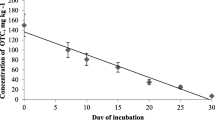
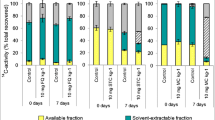
Tetracyclines used in veterinary therapy invariably will find their way as parent compound and degradation products to the agricultural field. Major degradation products formed due to the limited stability of parent tetracyclines (tetracycline, chlortetracycline, and oxytetracycline) in aqueous solution were theoretically identified at various environmental conditions, such as pH, presence of chelating metals, and light. Their potency was assessed on sludge bacteria, tetracycline-sensitive soil bacteria, and tetracycline-resistant strains. Several of the degradation products had potency at the same concentration level as tetracycline, chlortetracycline, and oxytetracycline on both the sludge and the tetracycline-sensitive soil bacteria. Further, both 5a,6-anhydrotetracycline and 5a,6-anhydrochlortetracycline had potency on tetracycline-resistant bacteria supporting a mode of action different from that of the parent compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 June 2001/Accepted: 22 October 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halling-Sørensen, B., Sengeløv, G. & Tjørnelund, J. Toxicity of Tetracyclines and Tetracycline Degradation Products to Environmentally Relevant Bacteria, Including Selected Tetracycline-Resistant Bacteria. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 42, 263–271 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-001-0017-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-001-0017-2