Abstract
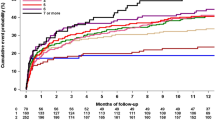
The CHA2DS2–VASc score is a validated tool to assess the thromboembolic risk in patients with atrial fibrillation. Pre-stroke CHA2DS2–VASc score may predict outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) without atrial fibrillation. The aim of this study was to investigate if the pre-stroke CHA2DS2–VASc score is able to predict short- and long-term outcomes in AIS patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis (IVT). The study group consisted of 256 consecutive patients admitted to the Udine University Hospital with AIS and underwent IVT between January 2015 to March 2017. The pre-stroke CHA2DS2–VASc score for each patient was calculated from the collected baseline data. Patients were classified into three groups according to their pre-stroke CHA2DS2–VASc score: a score of 0 of 1, a score of 2 or 3 and a score above 3. Primary outcome measures were: rate of favorable outcome at 90-days and at 1-year, and mortality at 90-days and at 1-year. Data on functional outcome and mortality 1 year after stroke were collected in 165 patients (65% of the entire sample). Favorable outcome was defined as a modified Rankin Scale score ≤ 2. Compared with the CHA2DS2–VASc score 0–1 group, patients with higher CHA2DS2–VASc scores had a worse outcome and a higher mortality 3 months and 1 year after stroke. The diagnostic performance of the CHA2DS2–VASc score as judged with AUC-ROC was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.64–0.76; p < 0.001) for favorable outcome at 90-days, 0.78 (95% CI, 0.71–0.85; p < 0.001) for favorable outcome at 1-year, 0.71 (95% CI 0.61–0.79) for mortality at 90-days, 0.73 (95% CI 0.64–0.80; p < 0.001) for mortality at 1-year. Pre-stroke CHA2DS2–VASc score represents a good predictor for short- and long-term outcomes in AIS patients treated with IVT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines-CPG; Document Reviewers (2012) 2012 Focused update of the ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation-developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 14:1385–1413
Hong HJ, Kim YD, Cha MJ, Kim J, Lee DH, Lee HS, Nam CM, Nam HS, Heo JH (2012) Early neurological outcomes according to CHADS2 score in stroke patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Eur J Neurol 19:284–290
Giralt-Steinhauer E, Cuadrado-Godia E, Ois Á, Jiménez-Conde J, Rodríguez-Campello A, Planellas L, Jimena-García S, Rubio MÁ, Roquer-González J (2012) CHA2DS2-VASc score and prognosis in ischemic strokes with atrial fibrillation. J Neurol 259:745–751
Deguchi I, Hayashi T, Ohe Y, Kato Y, Nagoya H, Fukuoka T, Maruyama H, Horiuchi Y, Tanahashi N (2013) The CHA2DS2–VASc score reflects clinical outcomes in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients with an initial cardioembolic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 22:e343-346
Acciarresi M, Paciaroni M, Agnelli G et al (2017) Prestroke CHA2DS2–VASc score and severity of acute stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation: findings from RAF Study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26:1363–1368
Ntaios G, Lip GY, Makaritsis K, Papavasileiou V, Vemmou A, Koroboki E, Savvari P, Manios E, Milionis H, Vemmos K (2013) CHADS2, CHA2S2DS2–VASc, and long-term stroke outcome in patients without atrial fibrillation. Neurology 80:1009–1017
Tu HT, Campbell BC, Meretoja A, Churilov L, Lees KR, Donnan GA, Davis SM (2013) Pre-stroke CHADS2 and CHA2DS2–VASc scores are useful in stratifying three-month outcomes in patients with and without atrial fibrillation. Cerebrovasc Dis 36:273–280
Topaz G, Pereg D, Shuvy M, Mausbach S, Kimiagar I, Telman G, Kitay-Cohen Y, Vorobeichik D, Shlomo N, Tanne D (2017) Pre-admission CHA2DS2–VASc score and outcome of patients with acute cerebrovascular events. Int J Cardiol 244:277–281
Cappellari M, Bovi P, Micheletti N, Tomelleri G, Moretto G (2013) The risk stratification based on the CHA2DS2–VASc may predict the response to intravenous thrombolysis after stroke. J Neurol 260:2681–2683
Steiner T, Salman RA, Ntaios G (2014) The European Stroke Organization (ESO) guidelines. Int J Stroke 9:838–839
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW Jr, Qureshi AI, Rosenfield K, Scott PA, Summers DR, Wang DZ, Wintermark M, Yonas H (2013) American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, Council on Clinical Cardiology: guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:870–947
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274:1017–1025
Strbian D, Meretoja A, Ahlhelm FJ, Pitkäniemi J, Lyrer P, Kaste M, Engelter S, Tatlisumak T (2012) Predicting outcome of IV thrombolysis-treated ischemic stroke patients: the DRAGON score. Neurology 78:427–432
Lou M, Safdar A, Mehdiratta M, Kumar S, Schlaug G, Caplan L, Searls D, Selim M (2008) The HAT Score: a simple grading scale for predicting hemorrhage after thrombolysis. Neurology 71(18):1417–1423
Frankel MR, Morgenstern LB, Kwiatkowski T, Lu M, Tilley BC, Broderick JP, Libman R, Levine SR, Brott T (2000) Predicting prognosis after stroke: a placebo group analysis from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Trial. Neurology 55:952–959
Asuzu D, Nyström K, Schindler J, Wira C, Greer D, Halliday J, Sheth KN (2015) TURN score predicts 90-day outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients after IV thrombolysis. Neurocrit Care 23:172–178
Ronzebaum Z, Elis A, Shuvy M, Vorobeichik D, Shlomo N, Shlezinger M, Goldenberg I, Kimhi O, Pereg D (2016) CHA2DS2–VASc score and clinical outcome of patients with acute coronary syndrome. Eur J Intern Med 36:57–61
Poçi D, Hartford M, Karlsson T, Herlitz J, Edvardsson N, Caidahl K (2012) Role of the CHA2DS2–VASc score in acute coronary syndromes: risk of subsequent death or stroke in patients with and without atrial fibrillation. Chest 141:1431–1440
Podolecki T, Lenarczyk R, Kowalczyk J, Swierad M, Swiatkowski A, jedrzejczyl E, Chodor P, Zielinska T, Kalarus Z (2015) Stroke and death prediction with CHA2DS2–VASc score after myocardial infarction in patients without atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 16:497–502
Lau KK, Chan PH, Yiu KH, Chan YH, Liu S, Chan KH, Yeung CY, Li SW, Tse HF, Siu CW (2014) Roles of the CHADS2 and CHA2DS2–VASc scores in post-myocardial infarction patients: risk of new occurrence of atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. Cardiol J 21:474–483
Naccarelli GV, Panaccio MP, Cummins G, Tu N (2012) CHADS2 and CHA2DS2–VASc risk factors to predict first cardiovascular hospitalization among atrial fibrillation /atrial flutter patients. Am J Cardiol 109:1526–1533
Paoletti Perini A, Bartolini S, Pieragnoli P, Ricciardi G, Perrotta L, Valleggi A, Vergaro G, Michelotti F, Boggian G, Sassone B, Mascioli G, Emdin M, Padeletti L (2014) CHADS2 and CHA2DS2–VASc scores to predict morbidity and mortality in heart failure patients candidates to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Europace 16:71–80
Vemmos K, Ntaios G, Savvari P, Vemmou AM, Koroboki E, Manios E, Kounali A, Lip GY (2012) Stroke aetiology and predictors of outcome in patients with heart failure and acute stroke: a 10-year follow-up study. Eur J Heart Fail 14:211–218
Weimar C, Goertler M, Röther J, Ringelstein EB, Darius H, Nabavi DG, Kim IH, Benemann J, Diener HC, SCALA Study Group (2008) Predictive value of the Essen Stroke Risk Score and ankle brachial index in acute ischaemic stroke patients from 85 German stroke units. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:1339–1343
Saposnik G, Kapral MK, Liu Y, Hall R, O’Donnell M, Raptis S, Tu JV, Mamdani M, Austin PC (2011) Investigators of the registry of the canadian stroke network; stroke outcomes research canada (sorcan) working group: IScore: a risk score to predict death early after hospitalization for an acute ischemic stroke. Circulation 123:739–749
Johnston KC, Connors AF Jr, Wagner DP, Knaus WA, Wang X, Haley EC Jr (2000) A predictive risk model for outcomes of ischemic stroke. Stroke 31:448–455
Counsell C, Dennis M, McDowall M (2004) Predicting functional outcome in acute stroke: comparison of a simple six variable model with other predictive systems and informal clinical prediction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:401–405
German Stroke Study Collaboration (2004) Predicting outcome after acute ischemic stroke: an external validation of prognostic models. Neurology 62:581–585
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merlino, G., Rana, M., Naliato, S. et al. CHA2DS2–VASc score predicts short- and long-term outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis 45, 122–129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-017-1575-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-017-1575-0