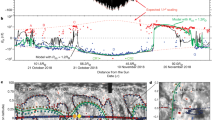
Abstract
Coronal holes can produce several types of solar wind with a variety of compositional properties, depending on the location and strength of the heating along their open magnetic field lines. High-speed wind is associated with (relatively) slowly diverging flux tubes rooted in the interiors of large holes with weak, uniform footpoint fields; heating is spread over a large radial distance, so that most of the energy is conducted outward and goes into accelerating the wind rather than increasing the mass flux. In the rapidly diverging open fields present at coronal hole boundaries and around active regions, the heating is concentrated at low heights and the temperature maximum is located near the coronal base, resulting in high oxygen freezing-in temperatures and low asymptotic wind speeds. Polar plumes have a strong additional source of heating at their bases, which generates a large downward conductive flux, raising the densities and enhancing the radiative losses. The relative constancy of the solar wind mass flux at Earth reflects the tendency for the heating rate in coronal holes to increase monotonically with the footpoint field strength, with very high mass fluxes at the Sun offsetting the enormous flux-tube expansion in active region holes. Although coronal holes are its main source, slow wind is also released continually from helmet streamer loops by reconnection processes, giving rise to plasma blobs (small flux ropes) and the heliospheric plasma sheet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Abramenko, V. Yurchyshyn, H. Watanabe, Sol. Phys. 260, 43 (2009)
M.R. Aellig, A.J. Lazarus, J.T. Steinberg, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 2767 (2001)
E. Antonucci, L. Abbo, D. Telloni, Astrophys. J. 643, 1239 (2006)
C.N. Arge, V.J. Pizzo, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10465 (2000)
J.R. Asbridge, S.J. Bame, W.C. Feldman, M.D. Montgomery, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 2719 (1976)
S.J. Bame, J.R. Asbridge, W.C. Feldman, J.T. Gosling, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 1487 (1977)
G. Borrini, J.T. Gosling, S.J. Bame, W.C. Feldman, J.M. Wilcox, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4565 (1981)
A. Bürgi, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 3137 (1992)
Y. Chen, X. Li, H.Q. Song, Q.Q. Shi, S.W. Feng, L.D. Xia, Astrophys. J. 691, 1936 (2009)
S.R. Cranmer, Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 6, 3 (2009)
S.R. Cranmer, A.A. van Ballegooijen, Astrophys. J. 720, 824 (2010)
S.R. Cranmer et al., Astrophys. J. 511, 481 (1999)
S.R. Cranmer, A.A. van Ballegooijen, R.J. Edgar, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 171, 520 (2007)
N.U. Crooker, J.T. Gosling, S.W. Kahler, J. Geophys. Res. 107, A2 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA000236
N.U. Crooker, C.-L. Huang, S.M. Lamassa, D.E. Larson, S.W. Kahler, H.E. Spence, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A03107 (2004)
C.E. DeForest, P.L. Lamy, A. Llebaria, Astrophys. J. 560, 490 (2001)
E. Endeve, T.E. Holzer, E. Leer, Astrophys. J. 603, 307 (2004)
V.G. Eselevich, V.G. Fainshtein, G.V. Rudenko, Sol. Phys. 188, 277 (1999)
U. Feldman, E. Landi, N.A. Schwadron, J. Geophys. Res. 110, A07109 (2005)
L.A. Fisk, N.A. Schwadron, Astrophys. J. 560, 425 (2001)
A. Gabriel, F. Bely-Dubau, E. Tison, K. Wilhelm, Astrophys. J. 700, 551 (2009)
J. Geiss, G. Gloeckler, R. von Steiger, Space Sci. Rev. 72, 49 (1995)
S. Giordano, E. Antonucci, G. Noci, M. Romoli, J.L. Kohl, Astrophys. J. 531, L79 (2000)
B.E. Goldstein et al., Astron. Astrophys. 316, 296 (1996)
R. Hammer, Astrophys. J. 259, 767 (1982)
V.H. Hansteen, E. Leer, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 21577 (1995)
J.V. Hollweg, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 4111 (1986)
J.V. Hollweg, J.M. Turner, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 97 (1978)
J.C. Kasper, M.L. Stevens, A.J. Lazarus, J.T. Steinberg, K.W. Ogilvie, Astrophys. J. 660, 901 (2007)
Y.-K. Ko, L.A. Fisk, J. Geiss, G. Gloeckler, M. Guhathakurta, Sol. Phys. 171, 345 (1997)
E. Leer, T.E. Holzer, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 4681 (1980)
R.H. Levine, Sol. Phys. 79, 203 (1982)
R.H. Levine, M.D. Altschuler, J.W. Harvey, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 1061 (1977)
P.C. Liewer, M. Neugebauer, T. Zurbuchen, Sol. Phys. 223, 209 (2004)
R. Lionello, P. Riley, J.A. Linker, Z. Mikić, Astrophys. J. 625, 463 (2005)
J.G. Luhmann, Y. Li, C.N. Arge, P.R. Gazis, R. Ulrich, J. Geophys. Res. 107, A8 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA007550
J.G. Luhmann et al., Sol. Phys. 256, 285 (2009)
E. Marsch, K.-H. Mühlhäuser, H. Rosenbauer, R. Schwenn, F.M. Neubauer, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 35 (1982)
W.H. Matthaeus, G.P. Zank, S. Oughton, D.J. Mullan, P. Dmitruk, Astrophys. J. 523, L93 (1999)
D.J. McComas et al., Rev. Geophys. 45, RG1004 (2007)
D.J. McComas, R.W. Ebert, H.A. Elliott, B.E. Goldstein, J.T. Gosling, N.A. Schwadron, R.M. Skoug, Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L18103 (2008)
M. Neugebauer et al., J. Geophys. Res. 103, 14587 (1998)
M. Neugebauer, P.C. Liewer, E.J. Smith, R.M. Skoug, T.H. Zurbuchen, J. Geophys. Res. 107, A12 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA000306
S.P. Owocki, T.E. Holzer, A.J. Hundhausen, Astrophys. J. 275, 354 (1983)
E.N. Parker, Astrophys. J. 372, 719 (1991)
R. Pinto, R. Grappin, Y.-M. Wang, J. Léorat, Astron. Astrophys. 497, 537 (2009)
N.-E. Raouafi, J.W. Harvey, S.K. Solanki, Astrophys. J. 658, 643 (2007)
A.F. Rappazzo, M. Velli, G. Einaudi, R.B. Dahlburg, Astrophys. J. 633, 474 (2005)
A.P. Rouillard et al., Sol. Phys. 256, 307 (2009)
Ø. Sandbæk, E. Leer, V.H. Hansteen, Astrophys. J. 436, 390 (1994)
C.J. Schrijver, M.L. DeRosa, Sol. Phys. 212, 165 (2003)
C.J. Schrijver et al., Nature 394, 152 (1998)
N.A. Schwadron, L.A. Fisk, T.H. Zurbuchen, Astrophys. J. 521, 859 (1999)
N.R. Sheeley Jr. et al., Astrophys. J. 484, 472 (1997)
N.R. Sheeley Jr., D.D.-H. Lee, K.P. Casto, Y.-M. Wang, N.B. Rich, Astrophys. J. 694, 1471 (2009)
H.Q. Song, Y. Chen, K. Liu, S.W. Feng, L.D. Xia, Sol. Phys. 258, 129 (2009)
S.T. Suess, A.-H. Wang, S.T. Wu, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 19957 (1996)
L. Teriaca, G. Poletto, M. Romoli, D.A. Biesecker, Astrophys. J. 588, 566 (2003)
A.F. Timothy, A.S. Krieger, G.S. Vaiana, Sol. Phys. 42, 135 (1975)
A. Verdini, M. Velli, Astrophys. J. 662, 669 (2007)
R. von Steiger et al., J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27217 (2000)
Y.-M. Wang, Astrophys. J. 410, L123 (1993)
Y.-M. Wang, Astrophys. J. 435, L153 (1994)
Y.-M. Wang, Astrophys. J. 449, L157 (1995)
Y.-M. Wang, Astrophys. J. 464, L91 (1996)
Y.-M. Wang, Astrophys. J. 501, L145 (1998)
Y.-M. Wang, Astrophys. J. 683, 499 (2008)
Y.-M. Wang, K. Muglach, Sol. Phys. 249, 17 (2008)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Astrophys. J. 355, 726 (1990)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Astrophys. J. 452, 457 (1995)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Astrophys. J. 587, 818 (2003)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Astrophys. J. 612, 1196 (2004)
Y.-M. Wang, S.H. Hawley, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Science 271, 464 (1996)
Y.-M. Wang et al., Astrophys. J. 498, L165 (1998)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., N.B. Rich, Astrophys. J. 658, 1340 (2007)
Y.-M. Wang, Y.-K. Ko, R. Grappin, Astrophys. J. 691, 760 (2009)
Y.-M. Wang, E. Robbrecht, A.P. Rouillard, N.R. Sheeley Jr., A.F.R. Thernisien, Astrophys. J. 715, 39 (2010)
K. Wilhelm, Astron. Astrophys. 455, 697 (2006)
K. Wilhelm, E. Marsch, B.N. Dwivedi, D.M. Hassler, P. Lemaire, A.H. Gabriel, M.C.E. Huber, Astrophys. J. 500, 1023 (1998)
K. Wilhelm et al., Astron. Astrophys. Rev. (2010, in press)
G.L. Withbroe, Astrophys. J. 325, 442 (1988)
R. Woo, S.R. Habbal, U. Feldman, Astrophys. J. 612, 1171 (2004)
L.D. Xia, E. Marsch, W. Curdt, Astron. Astrophys. 399, L5 (2003)
T.H. Zurbuchen, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 45, 297 (2007)
T.H. Zurbuchen, S. Hefti, L.A. Fisk, G. Gloeckler, N.A. Schwadron, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 18327 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YM. Semiempirical Models of the Slow and Fast Solar Wind. Space Sci Rev 172, 123–143 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-010-9733-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-010-9733-0