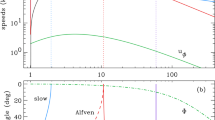
Abstract
By comparing a magneto-frictional model of the low-coronal magnetic-field to a potential-field source-surface model, we investigate the possible impact of non-potential magnetic structure on empirical solar-wind models. These empirical models (such as Wang–Sheeley–Arge) estimate the distribution of solar-wind speed solely from the magnetic-field structure in the low corona. Our models are computed in a domain between the solar surface and 2.5 solar radii, and they are extended to 0.1 AU using a Schatten current-sheet model. The non-potential field has a more complex magnetic skeleton and quasi-separatrix structures than the potential field, leading to different sub-structure in the solar-wind speed proxies. It contains twisted magnetic structures that can perturb the separatrix surfaces traced down from the base of the heliospheric current sheet. A significant difference between the models is the greater amount of open magnetic flux in the non-potential model. Using existing empirical formulae this leads to higher predicted wind speeds for two reasons: partly because magnetic-flux tubes expand less rapidly with height, but more importantly because more open-field lines are further from coronal-hole boundaries.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G.: 1969, Magnetic fields and the structure of the solar corona. I: Methods of calculating coronal fields. Solar Phys. 9, 131. DOI . ADS .
Antiochos, S.K., Mikić, Z., Titov, V.S., Lionello, R., Linker, J.A.: 2011, A model for the sources of the slow solar wind. Astrophys. J. 731, 112. DOI . ADS .
Arge, C.N., Pizzo, V.J.: 2000, Improvement in the prediction of solar wind conditions using near-real time solar magnetic field updates. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10465. DOI . ADS .
Arge, C.N., Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J., Mayer, L.R.: 2003, Improved method for specifying solar wind speed near the Sun. In: Velli, M., Bruno, R., Malara, F., Bucci, B. (eds.) Solar Wind Ten CS-679, Amer. Inst. Phys., 190. DOI . ADS .
Arge, C.N., Luhmann, J.G., Odstrcil, D., Schrijver, C.J., Li, Y.: 2004, Stream structure and coronal sources of the solar wind during the May 12th, 1997 CME. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 1295. DOI . ADS .
Cook, G.R., Mackay, D.H., Nandy, D.: 2009, Solar cycle variations of coronal null points: implications for the magnetic breakout model of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 704, 1021. DOI . ADS .
Craig, I.J.D., Sneyd, A.D.: 1986, A dynamic relaxation technique for determining the structure and stability of coronal magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 311, 451. DOI . ADS .
Crooker, N.U., McPherron, R.L., Owens, M.J.: 2014, Comparison of interplanetary signatures of streamers and pseudostreamers. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 4157. DOI . ADS .
Crooker, N.U., Antiochos, S.K., Zhao, X., Neugebauer, M.: 2012, Global network of slow solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 117, 4104. DOI . ADS .
Edwards, S.J., Parnell, C.E.: 2015, Null point distribution in global coronal potential field extrapolations. Solar Phys. 290, 2055. DOI . ADS .
Edwards, S.J., Parnell, C.E., Harra, L.K., Culhane, J.L., Brooks, D.H.: 2015, A comparison of global magnetic field skeletons and active region upflows. Solar Phys. (in press).
Freed, M.S., Longcope, D.W., McKenzie, D.E.: 2015, Three-year global survey of coronal null points from Potential-Field-Source-Surface (PFSS) modeling and Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) observations. Solar Phys. 290, 467. DOI . ADS .
Haynes, A.L., Parnell, C.E.: 2007, A trilinear method for finding null points in a three-dimensional vector space. Phys. Plasmas 14(8), 082107. DOI . ADS .
Haynes, A.L., Parnell, C.E.: 2010, A method for finding three-dimensional magnetic skeletons. Phys. Plasmas 17(9), 092903. DOI . ADS .
Hudson, H.S., Svalgaard, L., Hannah, I.G.: 2014, Solar sector structure. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 17. DOI . ADS .
Longcope, D.W.: 2005, Topological methods for the analysis of solar magnetic fields. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2, 7. DOI . ADS .
Mackay, D., Yeates, A.: 2012, The Sun’s global photospheric and coronal magnetic fields: observations and models. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 9, 6. DOI . ADS .
Odstrcil, D.: 2003, Modeling 3-D solar wind structure. Adv. Space Res. 32, 497. DOI . ADS .
Parnell, C.E., Maclean, R.C., Haynes, A.L.: 2010, The detection of numerous magnetic separators in a three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic model of solar emerging flux. Astrophys. J. Lett. 725, L214. DOI . ADS .
Parnell, C.E., Smith, J.M., Neukirch, T., Priest, E.R.: 1996, The structure of three-dimensional magnetic neutral points. Phys. Plasmas 3, 759. DOI . ADS .
Platten, S.J., Parnell, C.E., Haynes, A.L., Priest, E.R., Mackay, D.H.: 2014, The solar cycle variation of topological structures in the global solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 565, A44. DOI . ADS .
Poduval, B., Zhao, X.P.: 2014, Validating solar wind prediction using the current sheet source surface model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 782, L22. DOI . ADS .
Priest, E.R., Titov, V.S.: 1996, Magnetic reconnection at three-dimensional null points. Proc. Roy. Soc. London Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 354, 2951. ADS .
Rachmeler, L.A., Platten, S.J., Bethge, C., Seaton, D.B., Yeates, A.R.: 2014, Observations of a hybrid double-streamer/pseudostreamer in the solar corona. Astrophys. J. Lett. 787, L3. DOI . ADS .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Arge, C.N.: 2015, On the role played by magnetic expansion factor in the prediction of solar wind speed. Space Weather 13, 154. DOI . ADS .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z.: 2001, An empirically-driven global MHD model of the solar corona and inner heliosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15889. DOI . ADS .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z., Lionello, R., Ledvina, S.A., Luhmann, J.G.: 2006, A comparison between global solar magnetohydrodynamic and potential field source surface model results. Astrophys. J. 653, 1510. DOI . ADS .
Riley, P., Lionello, R., Linker, J.A., Mikic, Z., Luhmann, J., Wijaya, J.: 2011, Global MHD modeling of the solar corona and inner heliosphere for the whole heliosphere interval. Solar Phys. 274, 361. DOI . ADS .
Riley, P., Ben-Nun, M., Linker, J.A., Mikic, Z., Svalgaard, L., Harvey, J., Bertello, L., Hoeksema, T., Liu, Y., Ulrich, R.: 2014, A multi-observatory inter-comparison of line-of-sight synoptic solar magnetograms. Solar Phys. 289, 769. DOI . ADS .
Schatten, K.H.: 1971, Current sheet magnetic model for the solar corona. Cosm. Electrodyn. 2, 232. ADS .
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 6, 442. DOI . ADS .
Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 2005, Surface evolution of the Sun’s magnetic field: a historical review of the flux-transport mechanism. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2, 5. DOI . ADS .
Smith, E.J., Balogh, A., Forsyth, R.J., McComas, D.J.: 2001, Ulysses in the South polar cap at solar maximum: heliospheric magnetic field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 4159. DOI . ADS .
Tadesse, T., Pevtsov, A.A., Wiegelmann, T., MacNeice, P.J., Gosain, S.: 2014, Global solar free magnetic energy and electric current density distribution of Carrington rotation 2124. Solar Phys. 289, 4031. DOI . ADS .
Titov, V.S.: 2007, Generalized squashing factors for covariant description of magnetic connectivity in the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 660, 863. DOI . ADS .
Titov, V.S., Hornig, G., Démoulin, P.: 2002, Theory of magnetic connectivity in the solar corona. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1164. DOI . ADS .
Titov, V.S., Mikić, Z., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Antiochos, S.K.: 2011, Magnetic topology of coronal hole linkages. Astrophys. J. 731, 111. DOI . ADS .
van Ballegooijen, A.A., Cranmer, S.R.: 2008, Hyperdiffusion as a mechanism for solar coronal heating. Astrophys. J. 682, 644. DOI . ADS .
van Ballegooijen, A.A., Priest, E.R., Mackay, D.H.: 2000, Mean field model for the formation of filament channels on the Sun. Astrophys. J. 539, 983. DOI . ADS .
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Culhane, J.L., Baker, D., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H., DeRosa, M.L., Rouillard, A.P., Opitz, A., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Brooks, D.H.: 2012, Magnetic topology of active regions and coronal holes: implications for coronal outflows and the solar wind. Solar Phys. 281, 237. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M.: 2009, Coronal holes and open magnetic flux. Space Sci. Rev. 144, 383. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1990, Solar wind speed and coronal flux-tube expansion. Astrophys. J. 355, 726. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Young, P.R., Muglach, K.: 2014, Evidence for two separate heliospheric current sheets of cylindrical shape during mid-2012. Astrophys. J. 780, 103. DOI . ADS .
Yang, W.H., Sturrock, P.A., Antiochos, S.K.: 1986, Force-free magnetic fields – the magneto-frictional method. Astrophys. J. 309, 383. DOI . ADS .
Yeates, A.R.: 2014, Coronal magnetic field evolution from 1996 to 2012: continuous non-potential simulations. Solar Phys. 289, 631. DOI . ADS .
Yeates, A.R., Mackay, D.H.: 2012, Chirality of high-latitude filaments over solar cycle 23. Astrophys. J. Lett. 753, L34. DOI . ADS .
Yeates, A.R., Mackay, D.H., van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2008, Evolution and distribution of current helicity in full-Sun simulations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 680, L165. DOI . ADS .
Yeates, A.R., Mackay, D.H., van Ballegooijen, A.A., Constable, J.A.: 2010, A nonpotential model for the Sun’s open magnetic flux. J. Geophys. Res. 115, 9112. DOI . ADS .
Zhao, X., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, Predicting the heliospheric magnetic field using the current sheet-source surface model. Adv. Space Res. 16, 181. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
A.R. Yeates and S.J. Edwards were supported by STFC through consortium grant ST/K001043/1 and the Durham University Impact Acceleration Account, as well as by the US Air Force Office for Scientific Research. D.H. Mackay would like to thank the Leverhulme Trust and STFC for financial support. The authors thank Andrew L. Haynes for the use of his separatrix surface and null-point finding codes. Numerical simulations used the SRIF and STFC funded HPC cluster at the University of St Andrews.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below are the links to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edwards, S.J., Yeates, A.R., Bocquet, FX. et al. Influence of Non-Potential Coronal Magnetic Topology on Solar-Wind Models. Sol Phys 290, 2791–2808 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0795-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0795-8