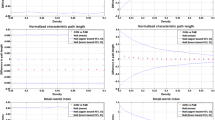
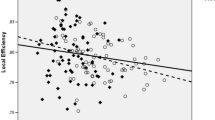
Abstract
Functional neuroimaging offers the opportunity to understand the effect of prenatal alcohol exposure on the activities of the brain as well as providing a window into the relationship between neural activation and the behavioral outcomes that have been described in affected individuals. Several different methodologies have been used to examine the neurophysiological signal changes associated with different brain functions in prenatally exposed individuals and those diagnosed with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) or other fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD). These include electroencephalography (EEG), positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). These studies demonstrate that it is feasible to use these technologies with this clinical population and that the damage to the central nervous system associated with prenatal alcohol exposure has widespread functional implications; however, currently, the literature in these areas is limited and unsystematic. Functional MRI with this clinical population has just begun to explore the implications of prenatal alcohol exposure with the first paper published in 2005. Other methodologies are similarly limited in scope. Nonetheless, these functional neuroimaging studies suggest that prenatal alcohol exposure, or a diagnosis of FAS, may lead to restrictions in neural efficiency or a global decrement in processing resources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre, G. K., Detre, J. A., & Wang, J. (2005). Perfusion fMRI for functional neuroimaging. International Review of Neurobiology, 66, 213–236.
Amaro, E., & Barker, G. J. (2006). Study design in fMRI: basic principles. Brain and Cognition, 60, 220–232.
Archibald, S. L., Fennema-Notestine, C., Gamst, A., Riley, E. P., Mattson, S. N., & Jernigan, T. L. (2001). Brain dysmorphology in individuals with severe prenatal alcohol exposure. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 43(3), 148–154.
Astley, S. J., Aylward, E. H., Olson, H. C., Kerns, K., Brooks, A., Coggins, T. E., et al. (2009). Functional magnetic resonance imaging outcomes from a comprehensive magnetic resonance study of children with fatal alcohol spectrum disorders. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 1(1), 61–80.
Bhatara, V. S., Lovrein, F., Kirkeby, J., Swayze, V., Unruh, E., & Johnson, V. (2002). Brain function in fetal alcohol syndrome assessed by single photon emission computed tomography. South Dakota Journal of Medicine, 55(2), 59–62.
Bookheimer, S. Y., & Sowell, E. R. (2005). Brain imaging in FAS commentary on the article by Malisza et al. Pediatric Research, 58(6), 1148–1149.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain’s default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Science, 1124, 1–38.
Burden, M. J., Andrew, C., Saint-Amour, D., Meintjes, E. M., Molteno, C. D., Hoyme, H. E., et al. (2009). The effects of fetal alcohol syndrome on response execution and inhibition: an event-related potential study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(11), 1994–2004.
Burden, M. J., Jacobson, J. L., Westerlund, A., Lundahl, L. H., Morrison, A., Dodge, N. C., et al. (2010). An event-related potential study of response inhibition in ADHD with and without prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 34(4), 617–627.
Burden, M. J., Westerlund, A., Muckle, G., Dodge, N., Dewailly, E., Nelson, C. A., et al. (2011). The effects of maternal binge drinking during pregnancy on neural correlates of response inhibition and memory in childhood. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 35(1), 69–82.
Chen, X., Coles, C. D., Lynch, M. E., & Hu, X. (2011). Understanding specific effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on brain structure in young adults. Human Bran Mapping, In press.
Chernick, V., Childiaeva, R., & Ioffe, S. (1983). Effects of maternal alcohol intake and smoking on neonatal electroencephalogram and anthropometric measurements. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 146(1), 41–47.
Church, M. W., & Gerkin, K. P. (1988). Hearing disorders in children with fetal alcohol syndrome: findings from case reports. Pediatrics, 82(2), 147–154.
Clark, C. M., Li, D., Conry, J., Conry, R., & Loock, C. (2000). Structural and functional brain integrity of fetal alcohol syndrome in nonretarded cases. Pediatrics, 105(5), 1096–1099.
Cohen, M. S., & Bookheimer, S. Y. (1994). Localization of brain function using magnetic resonance imaging. Trends in Neurosciences, 17(7), 268–277.
D’Angiulli, A., Grunau, P., Maggi, S., & Herdman, A. (2006). Electroencephalographic correlates of prenatal exposure to alcohol in infants and children: a review of findings and implications for neurocognitive development. Alcohol Research & Health, 40(2), 127–133.
Dehaene, S., Molko, N., Cohen, L., & Wilson, A. J. (2004). Arithmetic and the brain. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 14, 218–224.
Derauf, C., Kekatpure, M., Neyzi, N., Lester, B., & Kosofsky, B. (2009). Neuroimaging of children following prenatal drug exposure. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 20, 441–454.
Fabiani, M., Gratton, G., & Coles, M. G. H. (2000). Event-related brain potentials methods, theory, and applications. In J. T. Cacioppo, L. G. Tassinary, & G. G. Berntson (Eds.), Handbook of psychophysiology (pp. 53–84). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Feng, C.-M., Narayana, S., Lancaster, J. L., Jerabek, P. A., Arnow, T. L., Zhu, F., et al. (2004). CBF changes during brain activation: fMRI vs. PET. Neuroimage, 22, 443–446.
Frankel, F., Paley, B., Marquardt, R., & O’Connor, M. (2006). Stimulants, neuroleptics, and children’s friendship training for children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 16(6), 777–789.
Friston, K. J., Ashburner, J., Frith, C. D., Poline, J.-B., Heather, J. D., & Frackowiak, R. S. J. (1995). Spatial registration and normalization of images. Human Brain Mapping, 3(3), 165–189.
Fryer, S. L., Tapert, S. F., Mattson, S. N., Paulus, M. P., Spadoni, A. D., & Riley, E. P. (2007). Prenatal alcohol exposure affects frontal-striatal BOLD response during inhibitory control. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 31(8), 1415–1424.
Grabner, R. H., Ansari, D., Reishofer, G., Stern, E., Ebner, F., & Neuper, C. (2007). Individual differences in mathematical competence predict parietal brain activation during mental calculation. Neuroimage, 38, 346–356.
Havlicek, V., Childiaeva, R., & Chernick, V. (1977). EEG frequency spectrum characteristics of sleep states in infants of alcoholic mothers. Neuropädiatrie, 8(4), 360–373.
Ioffe, S., & Chernick, V. (1990). Prediction of subsequent motor and mental retardation in newborn infants exposed to alcohol in utero by computerized EEG analysis. Neuropediatrics, 21(1), 11–17.
Ioffe, S., Childiaeva, R., & Chernick, V. (1984). Prolonged effects of maternal alcohol ingestion on the neonatal electroencephalogram. Pediatrics, 74(3), 330–335.
Jones, K. L., & Smith, D. W. (1973). Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet, 302(7836), 999–1001.
Kable, J. A., & Coles, C. D. (2004). Teratology of alcohol: Implications for school settings. In R. T. Brown (Ed.), Handbook of pediatric psychology in school settings. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Kable, J. A., Coles, C. D., Lynch, M. E., & Carroll, J. (2009). The impact of maternal smoking on fast auditory brainstem responses. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 31(4), 216–224.
Kaneko, W. M., Phillips, E. L., Riley, E. P., & Ehlers, C. L. (1996). EEG findings in fetal alcohol syndrome and Down syndrome children. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 98, 20–28.
Kotsoni, E., Byrd, D., & Casey, B. J. (2006). Special considerations for functional magnetic resonance imaging of pediatric populations. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 23, 877–886.
Li, Z., Coles, C. D., Lynch, M. E., Ma, X., Peltier, S., & Hu, X. (2008). Occipital-temporal reduction and sustained visual attention deficit in prenatal alcohol exposed adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 2, 39–48.
Li, Z., Santhanam, P., Coles, C. D., Lynch, M. E., Hamann, S., Peltier, S., et al. (2010). Increased default mode activity in adolescents prenatally exposed to cocaine. Human Bran Mapping, In press, doi:10.1002/hbm.21059.
Liddle, E. B., Hollis, C., Batty, M. J., Groom, M. J., Totman, J. J., Liotti, M., et al. (2010). Task-related default mode network modulation and inhibitory control in ADHD: effects of motivation and methylphenidate. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, In press, doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02333.x.
Logothetis, N. K. (2008). What we can do and what we cannot do with fMRI. Nature, 453, 869–878.
Malisza, K. L., Allman, A.-A., Shiloff, D., Jakobson, L., Longstaffe, S., & Chudley, A. E. (2005). Evaluation of spatial working memory function in children and adults with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Pediatric Research, 58, 1150–1157.
Mattson, S. N., Riley, E. P., Jernigan, T. L., Ehlers, C. L., Delis, D. C., Jones, K. L., et al. (1992). Fetal alcohol syndrome: a case report of neuropsychological, MRI and EEG assessment of two children. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 16(5), 1001–1003.
Mattson, S. N., Calarco, K. E., & Lang, A. R. (2006). Focused and shifting attention in children with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Neuropsychology, 20(3), 361–369.
Meintjes, E. M., Jacobson, J. L., Molteno, C. D., Gatenby, J. C., Warton, C., Cannistraci, C. J., et al. (2010). An fMRI study of number processing in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 34(8), 1450–1464.
Norman, A. L., Crocker, N., Mattson, S. N., & Riley, E. P. (2009). Neuroimaging and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 15(3), 209–217.
Nunez, P. L., & Srinivasan, R. (2006). Electric fields of the brain: The neurophysis of EEG (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Oakes, T. R., Fox, A. S., Johnstone, T., Chung, M. K., Kalin, N., & Davidson, R. J. (2007). Integrating VBM into the general linear model with voxelwise anatomical covariates. Neuroimage, 34, 500–508.
O’Hare, E. D., Lu, L. H., Houston, S. M., Bookheimer, S. Y., Mattson, S. N., O’Connor, M. J., et al. (2009). Altered frontal-parietal functioning during verbal working memory in children and adolescents with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 3200–3208.
Olegård, R., Sabel, K.-G., Aronsson, M., Sandin, B., Johansson, P. R., Carlsson, C., et al. (1979). Effects on the child of alcohol abuse during pregnancy. Retrospective and prospective studies. Acta Paediatrica, 68(Supplement S275), 112–121.
O’Malley, K. D., & Nanson, J. (2002). Clinical implications of a link between fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 47(4), 349–354.
Pettigrew, A. G., & Hutchinson, I. (1984). Effects of alcohol on functional development of the auditory pathway in the brainstem of infants and chick embryos. Ciba Foundation Symposium, 105, 26–46.
Raichle, M. E., & Snyder, A. Z. (2007). A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea. Neuroimage, 37, 1083–1090.
Riikonen, R., Salonen, I., Partanen, K., & Verho, S. (1999). Brain perfusion SPECT and MRI in foetal alcohol syndrome. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 41, 652–659.
Riikonen, R. S., Nokelainen, P., Valkonen, K., Kolehmainen, A. I., Kumpulainen, K. I., Könönen, M., et al. (2005). Deep serotonergic and dopaminergic structures in fetal alcoholic syndrome: a study with nor-beta-CIT-single-photon emission computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry. Biological Psychiatry, 57, 1565–1572.
Rössig, C., Wässer, S., & Oppermann, P. (1994). Audiologic manifestations in fetal alcohol syndrome assessed by brainstem auditory-evoked potentials. Neuropediatrics, 25(5), 245–249.
Santhanam, P., Li, Z., Hu, X., Lynch, M. E., & Coles, C. D. (2009). Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on brain activation during an arithmetic task: an fMRI study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(11), 1901–1908.
Scher, M. S., Richardson, G. A., Coble, P. A., Day, N. L., & Stoffer, D. S. (1988). The effects of prenatal alcohol and marijuana exposure: disturbances in neonatal sleep cycling and arousal. Pediatric Research, 24(1), 101–105.
Scher, M. S., Richardson, G. A., Robles, N., Geva, D., Goldschmidt, L., Dahl, R. E., et al. (1998). Effects of prenatal substance exposure: altered maturation of visual evoked potentials. Pediatric Neurology, 18(3), 236–243.
Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., & Castellanos, F. X. (2007). Spontaneous attentional fluctuations in impaired states and pathological conditions: a neurobiological hypothesis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 31, 977–986.
Sowell, E. R., Lu, L. H., O’Hare, E. D., McCourt, S. T., Mattson, S. N., O’Connor, M. J., et al. (2007). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of verbal learning in children with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Neuroreport, 18(7), 635–639.
Spadoni, A. D., McGee, C. L., Fryer, S. L., & Riley, E. P. (2007). Neuroimaging and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 31(2), 239–245.
Spadoni, A. D., Bazinet, A. D., Fryer, S. L., Tapert, S. F., Mattson, S. N., & Riley, E. P. (2009). BOLD response during spatial working memory in youth with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(12), 2067–2076.
Spohr, H. L., & Steinhausen, H. C. (1987). Follow-up studies of children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Neuropediatrics, 18(1), 13–17.
Wernick, M. N., & Aarsvold, J. N. (2004). Emission tomography: The fundamentals of PET and SPECT. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press.
Whittingstall, K., Stroink, G., Gates, L., Connolly, J., & Finley, A. (2003). Effects of dipole position, orientation and noise on the accuracy of EEG source localization. Biomedical Engineering Online, 2, 14.
Wilke, M., Schmithorst, V. J., & Holland, S. K. (2002). Assessment of spatial normalization of whole-brain magnetic resonance images in children. Human Brain Mapping, 17, 48–60.
Wilke, M., Schmithorst, V. J., & Holland, S. K. (2003). Normative pediatric brain data for spatial normalization and segmentation differs from standard adult data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 50, 749–757.
Wozniak, J. R., Mueller, B. A., Muetzel, R. L., Bell, C. J., Hoecker, H. L., Nelson, M. L., et al. (2011). Inter-hemispheric functional connectivity disruption in children with prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 35(5), 1–13.
Yoon, U., Fonov, V. S., Perusse, D., & Evans, A. C. (2009). The effect of template choice on morphometric analysis of pediatric brain data. Neuroimage, 45, 769–777.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coles, C.D., Li, Z. Functional Neuroimaging in the Examination of Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Neuropsychol Rev 21, 119–132 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-011-9165-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-011-9165-y