Abstract
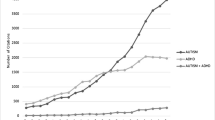
Consistent with well-documented structural and microstructural abnormalities in prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE), recent studies suggest that functional connectivity (FC) may also be disrupted. We evaluated whole-brain FC in a large multi-site sample, examined its cognitive correlates, and explored its potential to objectively identify neurodevelopmental abnormality in individuals without definitive dysmorphic features. Included were 75 children with PAE and 68 controls from four sites. All participants had documented heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. All underwent a formal evaluation of physical anomalies and dysmorphic facial features. MRI data were collected using modified matched protocols on three platforms (Siemens, GE, and Philips). Resting-state FC was examined using whole-brain graph theory metrics to characterize each individual’s connectivity. Although whole-brain FC metrics did not discriminate prenatally-exposed from unexposed overall, atypical FC (> 1 standard deviation from the grand mean) was significantly more common (2.7 times) in the PAE group vs. controls. In a subset of 55 individuals (PAE and controls) whose dysmorphology examination could not definitively characterize them as either Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) or non-FAS, atypical FC was seen in 27 % of the PAE group, but 0 % of controls. Across participants, a 1 % difference in local network efficiency was associated with a 36 point difference in global cognitive functioning. Whole-brain FC metrics have potential to identify individuals with objective neurodevelopmental abnormalities from prenatal alcohol exposure. When applied to individuals unable to be classified as FAS or non-FAS from dysmorphology alone, these measures separate prenatally-exposed from non-exposed with high specificity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., & Bullmore, E. (2007). Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol, 3(2), e17. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030017.
Archibald, S. L., Fennema-Notestine, C., Gamst, A., Riley, E. P., Mattson, S. N., & Jernigan, T. L. (2001). Brain dysmorphology in individuals with severe prenatal alcohol exposure. Dev Med Child Neurol, 43(3), 148–154.
Bassett, D. S., & Bullmore, E. (2006). Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist, 12(6), 512–523.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 57(1), 289–300.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med, 34(4), 537–541.
Bookstein, F. L., Sampson, P. D., Streissguth, A. P., & Connor, P. D. (2001). Geometric morphometrics of corpus callosum and subcortical structures in the fetal-alcohol-affected brain. Teratology, 64(1), 4–32.
Bookstein, F. L., Sampson, P. D., Connor, P. D., & Streissguth, A. P. (2002). Midline corpus callosum is a neuroanatomical focus of fetal alcohol damage. Anat Rec, 269(3), 162–174.
Bookstein, F. L., Connor, P. D., Covell, K. D., Barr, H. M., Gleason, C. A., Sze, R. W., et al. (2005). Preliminary evidence that prenatal alcohol damage may be visible in averaged ultrasound images of the neonatal human corpus callosum. Alcohol, 36(3), 151–160. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2005.07.007.
Bookstein, F. L., Connor, P. D., Huggins, J. E., Barr, H. M., Pimentel, K. D., & Streissguth, A. P. (2007). Many infants prenatally exposed to high levels of alcohol show one particular anomaly of the corpus callosum. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 31(5), 868–879. doi:10.1111/j.1530–0277.2007.00367.x.
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2009). Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci, 10(3), 186–198. doi:10.1038/nrn2575.
Cao, W., Li, W., Han, H., O’Leary-Moore, S. K., Sulik, K. K., Allan Johnson, G., et al. (2014). Prenatal alcohol exposure reduces magnetic susceptibility contrast and anisotropy in the white matter of mouse brains. Neuroimage, 102(Pt 2), 748–755. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.08.035.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155–159.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage, 9(2), 179–194.
Delis, D. C., Kramer, J. H., Kaplan, E., & Ober, B. A. (1994). California Verbal Learning Test Manual, Children’s Version. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation.
Delis, D. C., Kaplan, E., & Kramer, J. H. (2001). Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS). San Antonio, TX: Harcourt Assessment, Inc..
Donald, K. A., Eastman, E., Howells, F. M., Adnams, C., Riley, E. P., Woods, R. P., et al. (2015a). Neuroimaging effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the developing human brain: a magnetic resonance imaging review. Acta Neuropsychiatr, 27(5), 251–269. doi:10.1017/neu.2015.12.
Donald, K. A., Roos, A., Fouche, J. P., Koen, N., Howells, F. M., Woods, R. P., et al. (2015b). A study of the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on white matter microstructural integrity at birth. Acta Neuropsychiatr, 27(4), 197–205. doi:10.1017/neu.2015.35.
Donald, K. A., Ipser, J. C., Howells, F. M., Roos, A., Fouche, J. P., Riley, E. P., et al. (2016). Interhemispheric functional brain connectivity in neonates with prenatal alcohol exposure: preliminary findings. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 40(1), 113–121. doi:10.1111/acer.12930.
Elliott, C. D. (2007). Differential Ability Scales - Second Edition (DAS-II): Introductory and technical handbook. San Antonio, TX: PsychCorp.
Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Power, J. D., Dosenbach, N. U., Church, J. A., Miezin, F. M., et al. (2009). Functional brain networks develop from a "local to distributed" organization. PLoS Computational Biology, 5(5), e1000381. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000381.
Fan, J., Meintjes, E. M., Molteno, C. D., Spottiswoode, B. S., Dodge, N. C., Alhamud, A. A., et al. (2015). White matter integrity of the cerebellar peduncles as a mediator of effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on eyeblink conditioning. Human Brain Mapping, 36(7), 2470–2482. doi:10.1002/hbm.22785.
Fryer, S. L., Schweinsburg, B. C., Bjorkquist, O. A., Frank, L. R., Mattson, S. N., Spadoni, A. D., et al. (2009). Characterization of white matter microstructure in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(3), 514–521. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00864.x.
Green, C. R., Mihic, A. M., Nikkel, S. M., Stade, B. C., Rasmussen, C., Munoz, D. P., et al. (2009). Executive function deficits in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) measured using the Cambridge neuropsychological tests automated battery (CANTAB. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(6), 688–697. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01990.x.
Greve, D. N., & Fischl, B. (2009). Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration. Neuroimage, 48(1), 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.060.
Jacobson, S. W. (1998). Specificity of neurobehavioral outcomes associated with prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 22(2), 313–320.
Jones, K. L., Robinson, L. K., Bakhireva, L. N., Marintcheva, G., Storojev, V., Strahova, A., et al. (2006). Accuracy of the diagnosis of physical features of fetal alcohol syndrome by pediatricians after specialized training. Pediatrics, 118(6), E1734–E1738. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1037.
Jones, K. L., Hoyme, H. E., Robinson, L. K., Del Campo, M., Manning, M. A., Prewitt, L. M., et al. (2010). Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: extending the range of structural defects. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 152 A(11), 2731–2735. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33675.
Korkman, M., Kirk, U., & Kemp, S. (2007). NEPSY-II (Second ed.). San Antonio, TX: PsychCorp.
Latora, V., & Marchiori, M. (2001). Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett, 87(19), 198701.
Lebel, C., Rasmussen, C., Wyper, K., Walker, L., Andrew, G., Yager, J., et al. (2008). Brain diffusion abnormalities in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 32(10), 1732–1740. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00750.x.
Lebel, C., Rasmussen, C., Wyper, K., Andrew, G., & Beaulieu, C. (2010). Brain microstructure is related to math ability in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 34(2), 354–363. doi:10.1111/j.1530–0277.2009.01097.x.
Li, L., Coles, C. D., Lynch, M. E., & Hu, X. (2009). Voxelwise and skeleton-based region of interest analysis of fetal alcohol syndrome and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in young adults. Hum Brain Mapp, 30(10), 3265–3274.
Ma, X., Coles, C. D., Lynch, M. E., Laconte, S. M., Zurkiya, O., Wang, D., et al. (2005). Evaluation of corpus callosum anisotropy in young adults with fetal alcohol syndrome according to diffusion tensor imaging. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 29(7), 1214–1222.
Malisza, K. L., Buss, J. L., Bolster, R. B., de Gervai, P. D., Woods-Frohlich, L., Summers, R., et al. (2012). Comparison of spatial working memory in children with prenatal alcohol exposure and those diagnosed with ADHD; a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 4(1). doi:10.1186/1866-1955-4-12.
Mattson, S. N., Riley, E. P., Gramling, L., Delis, D. C., & Jones, K. L. (1997). Heavy prenatal alcohol exposure with or without physical features of fetal alcohol syndrome leads to IQ deficits. J Pediatr, 131(5), 718–721.
Mattson, S. N., Foroud, T., Sowell, E. R., Jones, K. L., Coles, C. D., Fagerlund, A., et al. (2010). Collaborative initiative on fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: methodology of clinical projects. Alcohol, 44(7–8), 635–641. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.08.005.
Mattson, S. N., Roesch, S. C., Glass, L., Deweese, B. N., Coles, C. D., Kable, J. A., et al. (2013). Further development of a neurobehavioral profile of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 37(3), 517–528. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01952.x.
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage, 59(3), 2142–2154. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.018.
Raichle, M. E., & Snyder, A. Z. (2007). A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea. Neuroimage, 37(4), 1083–1090 discussion 1097–1089.
Riley, E. P., Mattson, S. N., Sowell, E. R., Jernigan, T. L., Sobel, D. F., & Jones, K. L. (1995). Abnormalities of the corpus callosum in children prenatally exposed to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 19(5), 1198–1202.
Riley, E. P., McGee, C. L., & Sowell, E. R. (2004). Teratogenic effects of alcohol: a decade of brain imaging. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet, 127(1), 35–41.
Roebuck, T. M., Mattson, S. N., & Riley, E. P. (2002). Interhemispheric transfer in children with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 26(12), 1863–1871.
Roussotte, F. F., Rudie, J. D., Smith, L., O’Connor, M. J., Bookheimer, S. Y., Narr, K. L., et al. (2012). Frontostriatal connectivity in children during working memory and the effects of prenatal methamphetamine, alcohol, and Polydrug exposure. Developmental Neuroscience, 34(1), 43–57. doi:10.1159/000336242.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage, 52(3), 1059–1069. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.003.
Santhanam, P., Coles, C. D., Li, Z., Li, L., Lynch, M. E., & Hu, X. (2011). Default mode network dysfunction in adults with prenatal alcohol exposure. Psychiatry Res, 194(3), 354–362. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2011.05.004.
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., Lucas, C. P., Dulcan, M. K., & Schwab-Stone, M. E. (2000). NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children Version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 39(1), 28–38. doi:10.1097/00004583–200001000-00014.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage, 23(Suppl 1), S208–S219. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051.
Sowell, E. R., Mattson, S. N., Thompson, P. M., Jernigan, T. L., Riley, E. P., & Toga, A. W. (2001a). Mapping callosal morphology and cognitive correlates: Effects of heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Neurology, 57(2), 235–244.
Sowell, E. R., Thompson, P. M., Mattson, S. N., Tessner, K. D., Jernigan, T. L., Riley, E. P., et al. (2001b). Voxel-based morphometric analyses of the brain in children and adolescents prenatally exposed to alcohol. Neuroreport, 12(3), 515–523.
Sowell, E. R., Johnson, A., Kan, E., Lu, L. H., Van Horn, J. D., Toga, A. W., et al. (2008). Mapping white matter integrity and neurobehavioral correlates in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(6), 1313–1319. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5067-07.2008.
Sowell, E. R., Leow, A. D., Bookheimer, S. Y., Smith, L. M., O’Connor, M. J., Kan, E., et al. (2010). Differentiating prenatal exposure to methamphetamine and alcohol versus alcohol and not methamphetamine using tensor-based brain morphometry and discriminant analysis. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(11), 3876–3885. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4967-09.2010.
Spottiswoode, B. S., Meintjes, E. M., Anderson, A. W., Molteno, C. D., Stanton, M. E., Dodge, N. C., et al. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging of the cerebellum and eyeblink conditioning in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 35(12), 2174–2183. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01566.x.
Streissguth, A. P., & O’Malley, K. (2000). Neuropsychiatric implications and long-term consequences of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry, 5(3), 177–190.
Tambini, A., Ketz, N., & Davachi, L. (2010). Enhanced brain correlations during rest are related to memory for recent experiences. Neuron, 65(2), 280–290. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.001.
Taylor, P. A., Jacobson, S. W., van der Kouwe, A., Molteno, C. D., Chen, G., Wintermark, P., et al. (2015). A DTI-based tractography study of effects on brain structure associated with prenatal alcohol exposure in newborns. Human Brain Mapping, 36(1), 170–186. doi:10.1002/hbm.22620.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature, 393(6684), 440–442. doi:10.1038/30918.
Woolrich, M. W., Jbabdi, S., Patenaude, B., Chappell, M., Makni, S., Behrens, T., et al. (2009). Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in FSL. Neuroimage, 45(1 Suppl), S173–S186. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.055.
Wozniak, J. R., & Muetzel, R. L. (2011). What does diffusion tensor imaging reveal about the brain and cognition in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders? Neuropsychology Review, 21(2), 133–147. doi:10.1007/s11065–011–9162-1.
Wozniak, J. R., Mueller, B. A., Chang, P. N., Muetzel, R. L., Caros, L., & Lim, K. O. (2006). Diffusion tensor imaging in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 30, 1799–1806. doi:10.1111/j.1530–0277.2006.00213.x.
Wozniak, J. R., Muetzel, R. L., Mueller, B. A., McGee, C. L., Freerks, M. A., Ward, E. E., et al. (2009). Microstructural corpus callosum anomalies in children with prenatal alcohol exposure: an extension of previous diffusion tensor imaging findings. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(10), 1825–1835. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01021.x.
Wozniak, J. R., Mueller, B. A., Muetzel, R. L., Bell, C. J., Hoecker, H. L., Nelson, M. L., et al. (2011). Inter-hemispheric functional connectivity disruption in children with prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 35(5), 849–861. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01415.x.
Wozniak, J. R., Mueller, B. A., Bell, C. J., Muetzel, R. L., Hoecker, H. L., Boys, C. J., et al. (2013). Global functional connectivity abnormalities in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 37(5), 748–756. doi:10.1111/acer.12024.
Wu, K., Taki, Y., Sato, K., Hashizume, H., Sassa, Y., Takeuchi, H., et al. (2013). Topological organization of functional brain networks in healthy children: differences in relation to age, sex, and intelligence. PloS One, 8(2), e55347. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055347.
Acknowledgments
This work was performed in conjunction with the Collaborative Initiative on Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (CIFASD), which is funded by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Additional information about CIFASD can be found at www.cifasd.org.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). The following support was utilized in this work: NIAAA U01AA017122 (PI: ERS); NIAAA U01AA14834 (PI: SNM); U24AA014811 (EPR); U24AA014815 (PI: KLJ); U24AA014818 (PI: Barnett); support from the Minnesota Supercomputing Institute.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a relevant conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. All procedures were reviewed and approved by local human subject’s protection programs. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wozniak, J.R., Mueller, B.A., Mattson, S.N. et al. Functional connectivity abnormalities and associated cognitive deficits in fetal alcohol Spectrum disorders (FASD). Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1432–1445 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9624-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9624-4