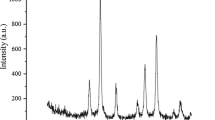
Abstract
Quercetin belongs to the chemical class of flavonoids and can be found in many common foods, such as apples, nuts, berries, etc. It has been demonstrated that quercetin has a wide array of biological effects that are considered beneficial to health treatment, mainly as anticancer. However, therapeutic applications of quercetin have been restricted to oral administration due to its sparing solubility in water and instability in physiological medium. A drug delivery methodology was proposed in this work to study a new quercetin release system in the form of magnetite–quercetin–copolymer (MQC). These materials were characterized through XRD, TEM, IR, and Thermal analysis. In addition, the magnetization curves and quercetin releasing experiments were performed. It was observed a nanoparticle average diameter of 11.5 and 32.5 nm at Fe3O4 and MQC, respectively. The presence of magnetic nanoparticles in this system offers the promise of targeting specific organs within the body. These results indicate the great potential for future applications of the MQC to be used as a new quercetin release system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexiou C et al (2006) Targeting cancer cells: Magnetic nanoparticles as drug carriers. Eur Biophys J 35:446–450
Boyer C, Whittaker MR, Bulmus V, Liu J, Davis TP (2010) The design and utility of polymer-stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles for nanomedicine applications. NPG Asia Mater 2:23–30
Braga TP, Vasconcelos IF, Sasaki JM, Fabris JD, Oliveira DQL, Valentini A (2010) Magnetic composites based on hybrid spheres of aluminum oxide and superparamagnetic nanoparticles of iron oxides. J Magn Magn Mater 322:633–637
Bukhari SB, Memon S, Tahir MM, Bhanger MI (2008) Synthesis, characterization and investigation of antioxidant activity of cobalt–quercetin complex. J Mol Struct 892:39–46
Cao H, He J, Deng L, Gao X (2009) Fabrication of cyclodextrin-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4/amino-silane core-shell nanoparticles via layer-by-layer method. Appl Surf Sci 255:7974–7980
Cheng K, Peng S, Xu C, Sun S (2009) Porous hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted delivery and controlled release of cisplatin. J Am Chem Soc 131:10637–10644
Chinnasamy CN et al (2001) Mixed spinel structure in nanocrystalline NiFe2O4. Phys Rev B 63:184108
Costa EM, Filho JMB, Nascimento TG, Macedo RO (2002) Thermal characterization of the quercetin and rutin flavonoids. Thermochim Acta 392–393:79–84
Doraiswamy PM, Finefrock AE (2004) Metals in our minds: therapeutic implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol 3:431–434
Gallo JM, Varkonyi P, Hassan EE, Groothius DR (1993) Targeting anticancer drugs to the brain: II. physiological pharmacokinetic model of oxantrazole following intraarterial administration to rat glioma-2 (RG-2) bearing rats. J Pharm Biopharm 21:575–592
Giri J et al (2008) Synthesis and characterizations of water-based ferrofluids of substituted ferrites [Fe1-xBxFe2O4, B = Mn, Co (x = 0–1)] for biomedical applications. J Magn Magn Mater 320:724–730
Gupta AK, Curtis ASG (2004) Surface modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: interaction studies with human fibroblasts in culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:493–496
Hrdina A, Lai E, Li C, Sadi B, Kramer G (2010) A comparative study of magnetic transferability of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 322:2622–2627
Hu FX, Neoh KG, Kang ET (2006) Synthesis and in vitro anti-cancer evaluation of tamoxifen-loaded magnetite/PLLA composite nanoparticles. Biomaterials 27:5725–5733
Kumari A, Yadav SK, Pakade YB, Singh B, Yadav SC (2010) Development of biodegradable nanoparticles for delivery of quercetin. Colloids Surf B 80:184–192
Laurent S et al (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110
Makris DP, Rossiter JT (2000) Heat-induced, metal-catalyzed oxidative degradation of quercetin and rutin (quercetin 3-o-rhamnosylglucoside) in aqueous model systems. J Agric Food Chem 48:3830–3838
Pinho MEN, Costa FMLL, Filho FBS, Ricardo NMPS, Yeates SG, Attwood D, Booth C (2007) Mixtures of triblock copolymers E62P39E62 and E137S18E137 potencial for drug delivery from in situ gelling micellar formulations. Int J Pharm 328:95–98
Rao BP, Rao GSN, Kumar AM, Rao KH, Murthy YLN, Hong SM, Kim CO, Kim C (2007) Soft chemical synthesis and characterization of Ni0.65Zn0.35Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 101:123902-1–123902-4
Ribeiro MENP, Vieira IGP, Cavalcante IM, Ricardo NMPS, Attowood D, Yeates SG, Booth C (2009) Solubilisation of griseofulvin, quercetin and rutin in micellar formulations of triblock copolymers E62P39E62 and E137S18E137. Int J Pharm 378:211–214
Rohn S, Buchner N, Driemel G, Rauser M, Kroh LW (2007) Thermal degradation of onion quercetin glucosides under roasting conditions. J Agric Food Chem 55:1568–1573
Shubayev VI, Pisanic TR II, Jin S (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:467–477
Slavov L et al (2010) Raman spectroscopy investigation of magnetite nanoparticles in ferrofluids. J Magn Magn Mater 322:1904–1911
Wang Z, Shen B, Aihua Z, He N (2005) Synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4 nanoparticle-based catalyst for the cross-coupling of acrylic acid with iodobenzene. Chem Eng J 113:27–34
Wang Y et al (2008) Formulation of superparamagnetic iron oxides by nanoparticles of biodegradable polymers for magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Funct Mater 18:308–318
Wei X, Gong C, Gou M, Fu S, Guo Q, Shi S, Luo F, Qiu L, Qian Z (2009) Biodegradable poly (ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers as drug delivery system. Int J Pharm 381:1–18
Yang Z, Crothers M, Ricardo NMPS, Chaibundit C, Taboada P, Mosquera V, Kelarakis A, Havredaki V, Martin L, Valder C, Collett JH, Attwood D, Heatley F, Booth C (2003) Micellisation and gelation of triblock copolymers of ethylene oxide and styrene oxide in aqueous solution. Langmuir 19:943–950
Zhao DL, Zeng XW, Xia QS, Tang JT (2009) Preparation and coercivity and saturation magnetization dependence of inductive heating property of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in an alternating current magnetic field for localized hyperthermia. J Alloys Compd 469:215–218
Zheng Y, Haworth IS, Zuo Z, Chow MSS, Chow AHL (2005) Physicochemical and structural characterization of quercetin-β-cyclodextrin complexes. J Pharm Sci 94:1079–1089
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Zhuo Yang for the preparation and characterization of copolymer E137S18E137. The study was supported by CAPES, Funcap and CNPq (Brazilian agencies). Financiamiento Basal para Centros Cientificos y Tecnologicos de Excelencia CEDENNA), Millennium Science Nucleus Basic and Applied Magnetism (P06-022F) and Fondecyt 1080164 and 3100117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barreto, A.C.H., Santiago, V.R., Mazzetto, S.E. et al. Magnetic nanoparticles for a new drug delivery system to control quercetin releasing for cancer chemotherapy. J Nanopart Res 13, 6545–6553 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0559-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0559-9