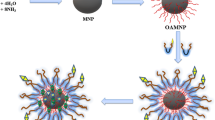
Abstract
This study aimed to prepared a dual-stimuli-responsive delivery system based on iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) and Pluronic F127—Folic acid conjugation (F127-FA) for poorly water-soluble drugs. Oleic acid-coated IONPs were prepared and modified with F127-FA using ultrasonic treatment to form IONPs/F127-FA meanwhile Quercetin (QCT)—a poorly water-soluble drug was encapsulated into the nano-system. The results illustrated the successful preparation of IONPs/F127-FA and its saturation magnetization value was found to be 25.6 emu/g. Moreover, QCT was effectively entrapped into the synthesized IONPs/F127-FA and showed 23.45 ± 7.23% loading capacity and 89.87 ± 2.05% entrapment efficiency. Additionally, the MTT assay revealed that loaded QCT in IONPs/F127-FA showed high inhibition against the human breast cancer cells compared to the free one, which was attributed to the ability to bind to folate receptor α of IONPs/F127-FA. These results suggested that the IONPs/F127-FA system would be a promising dual-stimuli-responsive drug delivery system in cancer treatment.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request.
References
A. Tewabe, A. Abate, M. Tamrie, A. Seyfu, E.A. Siraj, Targeted drug delivery—from magic bullet to nanomedicine: principles, challenges, and future perspectives. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 14, 1711 (2021)
A. Mansour, M. Romani, A.B. Acharya, B. Rahman, E. Verron, Z. Badran, Drug delivery systems in regenerative medicine: an updated review. Pharmaceutics 15(2), 695 (2023)
R. Liu, C. Luo, Z. Pang, J. Zhang, S. Ruan, M. Wu, L. Wang, T. Sun, N. Li, L. Han, Advances of nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for disease diagnosis and treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 34(2), 107518 (2023)
P. Kundu, S. Das, N. Chattopadhyay, Switching from endogenous to exogenous delivery of a model drug to DNA through micellar engineering. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 203, 111765 (2020)
X. Lin, J. Wu, Y. Liu, N. Lin, J. Hu, B. Zhang, Stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems for the diagnosis and therapy of lung cancer. Molecules 27(3), 948 (2022)
M. Zhang, W. Hu, C. Cai, Y. Wu, J. Li, S. Dong, Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment. Mater. Today Bio. 14, 100223 (2022)
J. Zhang, Y. Lin, Z. Lin, Q. Wei, J. Qian, R. Ruan, X. Jiang, L. Hou, J. Song, J. Ding, Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery in synergistic cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 9(5), 2103444 (2022)
F. Reyes-Ortega, Á.V. Delgado, E.K. Schneider, B.L. Checa Fernández, G.R. Iglesias, Magnetic nanoparticles coated with a thermosensitive polymer with hyperthermia properties. Polymers 10(1), 10 (2018)
D. Stanicki, T. Vangijzegem, I. Ternad, S. Laurent, An update on the applications and characteristics of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 19(3), 321–335 (2022)
H. Aslam, S. Shukrullah, M.Y. Naz, H. Fatima, H. Hussain, S. Ullah, M.A. Assiri, Current and future perspectives of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles based controlled drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 67, 102946 (2022)
T.N. Le Thi, T.H. Nguyen, D.Q. Hoang, T.V. Tran, N.T. Nguyen, D.H. Nguyen, Development of new magnetic nanoparticles: Oligochitosan obtained by γ-rays and –coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 422, 863–868 (2017)
K. McNamara, S.A.M. Tofail, Nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Adv. Phys.: X 2(1), 54–88 (2016)
Y.A. Koksharov, S. Gubin, I. Taranov, G. Khomutov, Y.V. Gulyaev, Magnetic nanoparticles in medicine: progress, problems, and advances. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 67(2), 101–116 (2022)
J. Yoo, C. Park, G. Yi, D. Lee, H. Koo, Active targeting strategies using biological ligands for nanoparticle drug delivery systems. Cancers 11(5), 640 (2019)
N. Kang, S. Son, S. Min, H. Hong, C. Kim, J. An, J.S. Kim, H. Kang, Stimuli-responsive ferroptosis for cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 4006 (2023)
F. Xie, M. Wang, Q. Chen, T. Chi, S. Zhu, P. Wei, Y. Yang, L. Zhang, X. Li, Z. Liao, Endogenous stimuli-responsive nanoparticles for cancer therapy: from bench to bedside. Pharmacol. Research (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106522
P.S. Ginter, P.J. McIntire, X. Cui, L. Irshaid, Y. Liu, Z. Chen, S.J. Shin, Folate receptor alpha expression is associated with increased risk of recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 17(7), 544–549 (2017)
P. Ebrahimnejad, A.S. Taleghani, K. Asare-Addo, A. Nokhodchi, An updated review of folate-functionalized nanocarriers: a promising ligand in cancer. Drug Discov. Today 27(2), 471–489 (2022)
S.A. Kularatne, P.S. Low, Targeting of nanoparticles: folate receptor. Methods Mol. Biol. 624, 249–265 (2010)
N. Kaur, P. Popli, N. Tiwary, R. Swami, Small molecules as cancer targeting ligands: shifting the paradigm. J. Control. Release 355, 417–433 (2023)
M. Narvekar, H.Y. Xue, J.Y. Eoh, H.L. Wong, Nanocarrier for poorly water-soluble anticancer drugs—barriers of translation and solutions. AAPS PharmSciTech 15(4), 822–833 (2014)
K.U. Khan, M.U. Minhas, S.F. Badshah, M. Suhail, A. Ahmad, S. Ijaz, Overview of nanoparticulate strategies for solubility enhancement of poorly soluble drugs. Life Sci. 291, 120301 (2022)
Z. Warnken, H.D. Smyth, R.O. Williams, Route-specific challenges in the delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs, in Formulating poorly water soluble drugs. ed. by R.O. Williams, D.A. Davis, D.A. Miller (Springer, Cham, 2022)
T.T.C. Nguyen, C.K. Nguyen, T.H. Nguyen, N.Q. Tran, Highly lipophilic pluronics-conjugated polyamidoamine dendrimer nanocarriers as potential delivery system for hydrophobic drugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 70, 992–999 (2017)
PJ, R.J., O.S. Oluwafemi, S. Thomas, and A.O. Oyedeji, Recent advances in drug delivery nanocarriers incorporated in temperature-sensitive Pluronic F-127–A critical review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 72, 103390 (2022)
C. Rossi, A. Donati, S. Ulgiati, M. Sansoni, Structural investigation of folic acid by nmr proton relaxation and molecular mechanics analysis. J. Magn. Reson 14, 181–185 (1992)
C. Guo, Y. Hu, H. Qian, J. Ning, S. Xu, Magnetite (Fe3O4) tetrakaidecahedral microcrystals: synthesis, characterization, and micro-Raman study. Mater. Charact. 62(1), 148–151 (2011)
T.T. Hoang Thi, D.H. Nguyen Tran, L.G. Bach, H. Vu-Quang, D.C. Nguyen, K.D. Park, D.H. Nguyen, Functional magnetic core-shell system-based iron oxide nanoparticle coated with biocompatible copolymer for anticancer drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 11(3), 120 (2019)
C. Guo, H. Liu, J. Wang, J. Chen, Conformational structure of triblock copolymers by FT-raman and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 209(2), 368–373 (1999)
Y.-L. Su, J. Wang, H.-Z. Liu, FTIR Spectroscopic study on effects of temperature and polymer composition on the structural properties of PEO−PPO−PEO block copolymer micelles. Langmuir 18(14), 5370–5374 (2002)
E.M.K.A.D. Mohammed, Qualitative and quantitative determination of folic acid in tablets by FTIR spectroscopy. IJAPBC 2014, 3 (2014)
D.-H. Zhang, G.-D. Li, J.-X. Li, J.-S. Chen, One-pot synthesis of Ag–Fe3O4 nanocomposite: a magnetically recyclable and efficient catalyst for epoxidation of styrene. Chem. Commun. 29, 3414–3416 (2008)
S.A. Gómez-Lopera, P.R.F. Delgado, A.V. Delgado, Synthesis and characterization of spherical magnetite/biodegradable polymer composite particles. J. Colloid Interface sci. 240(1), 40–47 (2001)
F. Li, J. Sun, H. Zhu, X. Wen, C. Lin, D. Shi, Preparation and characterization novel polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles as carriers for doxorubicin. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 88(1), 58–62 (2011)
P. Wang, J. Jiang, The Volatility Asymmetry of Rate of Return on CSI 300 Index at Different Stages, in Advances in Information Technology and Industry Applications. ed. by D. Zeng (Springer, Berlin, 2012)
H. Patir, S.K.S. Sarada, S. Singh, T. Mathew, B. Singh, A. Bansal, Quercetin as a prophylactic measure against high altitude cerebral edema. Free Radical Biol. Med. 53(4), 659–668 (2012)
M.-Y. Wong, G.N.C. Chiu, Liposome formulation of co-encapsulated vincristine and quercetin enhanced antitumor activity in a trastuzumab-insensitive breast tumor xenograft model. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 7(6), 834–840 (2011)
M. Kakran, N.G. Sahoo, L. Li, Dissolution enhancement of quercetin through nanofabrication, complexation, and solid dispersion. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 88(1), 121–130 (2011)
Y. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Ma, A. Yu, F. Cai, W. Shao, G. Zhai, Formulation optimization and in situ absorption in rat intestinal tract of quercetin-loaded microemulsion. Colloids Surf., B 71(2), 306–314 (2009)
S. Khan, S. Setua, S. Kumari, N. Dan, A. Massey, B.B. Hafeez, M.M. Yallapu, Z.E. Stiles, A. Alabkaa, J. Yue, A. Ganju, S. Behrman, M. Jaggi, S.C. Chauhan, Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles of curcumin enhance gemcitabine therapeutic response in pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials 208, 83–97 (2019)
A. Granja, C. Nunes, C.T. Sousa, S. Reis, Folate receptor-mediated delivery of mitoxantrone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles to breast cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 154, 113525 (2022)
N.L. Chaves, I. Estrela-Lopis, J. Böttner, C.A. Lopes, B.C. Guido, A.R. de Sousa, S.N. Báo, Exploring cellular uptake of iron oxide nanoparticles associated with rhodium citrate in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 5511–5523 (2017)
M. Kaksonen, A. Roux, Mechanisms of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19(5), 313–326 (2018)
T. Kirchhausen, Clathrin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69(1), 699–727 (2000)
A. Rauf, M. Imran, I.A. Khan, M. Ur-Rehman, S.A. Gilani, Z. Mehmood, M.S. Mubarak, Anticancer potential of quercetin: a comprehensive review. Phytother Res 32(11), 2109–2130 (2018)
R. Vakili-Ghartavol, A.A. Momtazi-Borojeni, Z. Vakili-Ghartavol, H.T. Aiyelabegan, M.R. Jaafari, S.M. Rezayat, S. Arbabi Bidgoli, Toxicity assessment of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in different tissues. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 48(1), 443–451 (2020)
N. Fernandez-Bertolez, C. Costa, F. Brandao, J.A. Duarte, J.P. Teixeira, E. Pasaro, V. Valdiglesias, B. Laffon, Evaluation of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity induced by oleic acid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in human astrocytes. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 60(9), 816–829 (2019)
J. Varshosaz, S. Taymouri, F. Hassanzadeh, S.H. Javanmard, M. Rostami, Folated synperonic-cholesteryl hemisuccinate polymeric micelles for the targeted delivery of docetaxel in melanoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 746093 (2015)
U.V. Vo, C.K. Nguyen, V.C. Nguyen, T.V. Tran, B.Y.T. Thi, D.H. Nguyen, Gelatin-poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether-functionalized porous Nanosilica for efficient doxorubicin delivery. J. Polym. Res. 26(1), 6 (2018)
Funding
This research is funded by the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST) under grant number NVCC19.04/22–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Author notes
Tien-Dung Nguyen-Dinh and Nhu-Thuan Nguyen-Phuoc have contributed equally to this work.
Contributions
T-DN-D contributed to methodology, software, conceiving and designing the analysis, and data curation. N-TN-P contributed to methodology, conceiving and designing the analysis, data curation, and software. NTTL contributed to visualization, validation, collection the data, and performing the analysis. NHN contributed to conceiving and designing the analysis, contributing the data or analysis tools, and writing and original draft preparation. DHN contributed to investigation, conceptualization, supervision, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen-Dinh, TD., Nguyen-Phuoc, NT., Le, N.T.T. et al. A dual-stimuli-responsive delivery system for poorly water-soluble drug based on iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Research 38, 4057–4067 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01120-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01120-8