Abstract
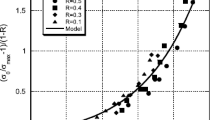
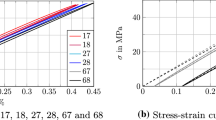
A two-parameter model explicitly accounting for the cyclic as well as the mean stress was proposed and tested on the basis of static and fatigue data obtained in four-point bending on a random continuous glass-fiber-reinforced polypropylene. The model is based on residual strength degradation and captures the effect of stress ratio (i.e. the ratio between the minimal and the maximal stress). The experimental data were in excellent agreement with the theoretical predictions, indicating that a fatigue characterization can be achieved with a minimum of experimental tests. Further, the reasonable agreement between the static strength data and the theoretical predictions highlighted the potential and reliability of the model in view of its statistical implementation





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caprino, G., D’Amore, A., Facciolo, F.: Fatigue sensitivity of random glass fibre reinforced plastics. J. Compos. Mater. 32, 1203–1220 (1998)
Chung, I., Sun, C.T., Chang, I.Y.: Modeling creep in thermoplastic composites. J. Compos. Mater. 27, 1009–1029 (1993)
D’Amore, A., Stupak, P.R., Rigale, F., Nicolais, L.: Impact and damage of polymers and composites. In: Williams, J.G., Pavan, A. (eds.) ESIS, vol. 19, pp. 413–421. Mechanical Engineering Publications, London (1995)
D’Amore, A., Caprino, G., Stupak, P., Zhou, J., Nicolais, L.: Effect of stress ratio on the flexural fatigue behaviour of continuous strand mat reinforced plastics. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 5, 1–8 (1996)
D’Amore, A., Caprino, G., Nicolais, L., Marino, G.: Long-term behaviour of PEI and PEI-based composites subjected to physical aging. Compos. Sci. Technol. 59, 1993–2003 (1999)
D’Amore, A., Caputo, F., Grassia, L., Zarrelli, M.: Numerical evaluation of structural relaxation-induced stresses in amorphous polymers. Composites, Part A, Appl. Sci. Manuf. 37, 556–564 (2006)
D’Amore, A., Grassia, L., Acierno, D.: Modelling the yield stress and the Poisson’s ratio of glassy polymers. E-Polymers, art. no. 052 (2009)
D’Amore, A., Grassia, L., Verde, P.: Modeling the fatigue behavior of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic and thermosetting matrices. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1459, pp. 372–374 (2012)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Residual stresses in amorphous polymers. Macromol. Symp. 228, 1–15 (2005)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Constitutive law describing the phenomenology of sub-yield mechanically stimulated glasses. Phys. Rev. E, Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 74, 021504 (2006)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Isobaric PVT behavior of poly(carbonate) (PC). In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1255, pp. 417–419 (2010a)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Modeling the residual stresses in reactive resins-based materials: a case study of photo-sensitive composites for dental applications. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1255, pp. 408–410 (2010b)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Thermal residual stresses in amorphous thermoplastic polymers. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1255, pp. 414–416 (2010c)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Isobaric and isothermal glass transition of PMMA: pressure-volume-temperature experiments and modelling predictions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357, 414–418 (2011)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A.: Finite element calculation of residual stress in dental restorative material. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1459, pp. 312–315 (2012)
Grassia, L., Simon, S.L.: Modeling volume relaxation of amorphous polymers: modification of the equation for the relaxation time in the KAHR model. Polymer 53, 3613–3620 (2012)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A., Simon, S.L.: On the viscoelastic Poisson’s ratio in amorphous polymers. J. Rheol. 54, 1009–1022 (2010)
Grassia, L., Pastore Carbone, M.G., Mensitieri, G., D’Amore, A.: Modeling of density evolution of PLA under ultra-high pressure/temperature histories. Polymer 52, 4011–4020 (2011a)
Grassia, L., Pastore Carbone, M.G., D’Amore, A.: Modeling of the isobaric and isothermal glass transitions of polystyrene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 122, 3752–3757 (2011b)
Grassia, L., D’Amore, A., Verde, P.: On the inter-conversion between viscoelastic material functions of polycarbonate. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1459, pp. 375–377 (2012)
Guo, J., Grassia, L., Simon, S.L.: Bulk and shear rheology of a symmetric three-arm star polystyrene. J. Polym. Sci., Part B, Polym. Phys. 50, 1233–1244 (2012)
Hour, K.Y., Sehitoglu, H.: Damage development in a short fiber reinforced composite. J. Compos. Mater. 27, 782–805 (1993)
Mandell, J.F.: In: Reifsnaide, K.L. (ed.) Fatigue of Composite Materials, pp. 231–237. Elsevier, New York (1990)
Martone, A., Grassia, L., Zarrelli, M., Giordano, M., D’Amore, A.: Enthalpy relaxation of an epoxy matrix/carbon nanotubes. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1459, pp. 347–349 (2012)
McCrum, G., Bickley, C.P., Bucknall, C.B.: Principles of Polymer Engineering. Oxford University Press, London (1989)
Netti, P., D’Amore, A., Ronca, D., Ambrosio, L., Nicolais, L.: Structure-mechanical properties relationship of natural tendons and ligaments. J. Mater. Sci., Mater. Med. 7, 525–530 (1996)
Stupak, P.R., D’Amore, A., Rigale, F., Nicolais, L.: Uniaxial and biaxial flexural fatigue of glass reinforced inter-penetrated network polymer composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 1, 19–33 (1994)
Yang, Y., D’Amore, A., Di, Y., Nicolais, L., Li, B.: Effect of physical aging on phenolphthalein polyethersulfone/poly(phenylene sulfide) blend. I. Mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 59, 1159–1166 (1996)
Zarrelli, M., Partridge, I.K., D’Amore, A.: Warpage induced in bi-material specimens: coefficient of thermal expansion, chemical shrinkage and viscoelastic modulus evolution during cure. Composites, Part A, Appl. Sci. Manuf. 37, 565–570 (2006)
Zhou, J., D’Amore, A., Yang, Y., He, T., Li, B., Nicolais, L.: Flexural fatigue of short glass fiber reinforced a blend of polyphenylene ether ketone and polyphenylene sulfide. Appl. Compos. Mater. 1, 183–195 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Amore, A., Grassia, L. & Verde, P. Modeling the flexural fatigue behavior of glass-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic matrices. Mech Time-Depend Mater 17, 15–23 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-012-9192-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-012-9192-y