Abstract
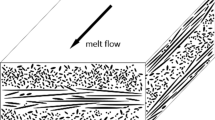
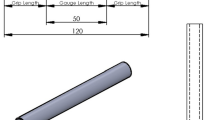
Flexural fatigue tests were conducted on injection molded glass fiber reinforced a blend of polyphenylene ether ketone and polyphenylene sulfide composite using four-point bending with different stress ratios and different frequencies. The fatigue behavior of this material was described. The constructed S-N curves shift their trends obviously at the maximum cyclic stress being about 80% of the ultimate flexural strength. Examinations of failure surfaces for various loading conditions show that the fatigue failure mechanisms appear to be matrix yielding at high stresses and crack growth at low stresses. Analyses of the fatigue data at various stress ratios reveal that the data at low stress superimpose to form a single curve which is nearly linear when they are plotted as stress range versus number of cycles to failure in bilogarithmic axes, while the data at high stresses also converge to yield a single curve when they are plotted as (S max S range)1/2 against specimen lifetimes (S max is the maximum stress andS range is the stress range). These results show that for the studied material the main factor influencing the lifetime is the stress range at low stresses and the parameter (S max S range)1/2 at high stresses. Comparison of fatigue data in the frequency range of 0.89–7.0 Hz was made, no significant effect of frequency on the fatigue behavior is found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, S. S., and Chim, E. S.-M., ‘Fatigue damage and degradation in random short-fiber SMC composite’,Journal of Composite Materials 17, 1983, 114–134.
Kundrat, R., Joneja, S. and Broutman, L. J., ‘Fatigue damage studies in high strength sheetmolding compound fiberglass composites’,Polymer Composites 3, 1982, 105–112.
Riegner, D. A., and Hsu, J. C., ‘Fatigue considerations for FRP composites’, inProceedings of the SAE Fatigue Conference, P-109, Society of Automotive Engineers, Detroit, MI, 1982, pp. 237–247.
Chim, E. S.-M., and Wang, S. S., ‘Residual strength and residual fracture toughness of random short-fiber composites during cyclic fatigue’,Journal of Composites Technology & Research 12, 1990, 223–228.
Newaz, G. M., ‘Fatigue damage growth rate in unidirectional composites in flexural loading’,Journal Materials Science Letter 4, 1985, 197–199.
Baron, Ch., Schulte, K., and Harig, H., ‘Influence of fiber and matrix failure strain on static and fatigue properties of carbon fibre-reinforced plastics’,Composite Science and Technology 29, 1987, 257–272.
Shih, G. C., and Ebert, L. J., ‘The effect of the fiber/matrix interface on the flexural fatigue performance of unidirectional fiberglass composites’,Composite Science and Technology 28, 1987, 137–161.
Newaz, G. M., ‘Influence of matrix material on flexural fatigue performance of unidirectional composites’,Composite Science and Technology 24, 1985, 199–214.
Reifsnider, K. L., Henneke, E. G., Stinchcomb, W. W., and Duke, J. C., ‘Damage mechanisms and NDE of composite laminates’, in Z. Hashin and C.T. Herakovich (eds.),Mechanics of Composite Materials, Recent Advances, Pergamon Press, New York, 1983, pp. 399–420.
Poursartip, A., Ashby, M. F., and Beaumont, P. W. R., ‘The fatigue damage mechanics of a carbon fiber composite laminate: I — development of the model’,Composite Science Technology 25, 1985, 193–218.
Mandell, J. F., McGarry, F. J., Huang, D. D., and Li, C. G., ‘Some effects of matrix and interface properties on the fatigue of short fiber-reinforced thermoplastics’,Polymer Composites 4, 1983, 32–39.
Malzahn, J. C., and Schultz, J. M., ‘Tension-tension and compression-compression fatigue behavior of an injection-molded short-glass-fiber/poly(ethylene terephthalate) composite’,Composite Science Technology 27, 1986, 253–289.
Sendeckyj, G. P., ‘Life prediction for resin-matrix composite materials’, in K. L. Reifsnider (ed.),Fatigue of Composite Materials, Vol. 4 in Composite Materials series, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1990, Chapter 10.
Mandell, J. F., ‘Fatigue behavior of short fiber composite materials’, in K. L. Reifsnider (ed.),Fatigue of Composite Materials, Vol. 4 in Composite Materials series, Elsevier, Amsterdam, Chapter 7.
Yang, Y. M., and Li, B. Y. (unpublished data).
Hertzberg, R. W., and Manson, J. A.,Fatigue in Engineering Plastics, Academic Press, New York, 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., D'Amore, A., Yang, Y. et al. Flexural fatigue of short glass fiber reinforced a blend of polyphenylene ether ketone and polyphenylene sulfide. Appl Compos Mater 1, 183–195 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00567526
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00567526