Abstract
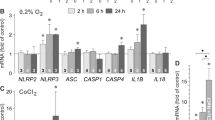
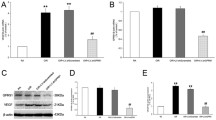
One risk factor of neovascular age-related macular degeneration is systemic hypertension; hypertension is mainly caused by extracellular hyperosmolarity after consumption of dietary salt. In retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, high extracellular osmolarity induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A (Hollborn et al. in Mol Vis 21:360–377, 2015). The aim of the present study was to determine whether extracellular hyperosmolarity and chemical hypoxia trigger the expression of further VEGF family members including placental growth factor (PlGF) in human RPE cells. Hyperosmotic media were made up by addition of 100 mM NaCl or sucrose. Chemical hypoxia was induced by CoCl2. Gene expression was quantified by real-time RT-PCR, and secretion of PlGF-2 was investigated with ELISA. Nuclear factor of activated T cell 5 (NFAT5) was depleted using siRNA. Extracellular hyperosmolarity triggered expression of VEGF-A, VEGF-D, and PlGF genes, and secretion of PlGF-2. Hypoosmolarity decreased PlGF gene expression. Hypoxia induced expression of VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-D, and PlGF genes. Extracellular hyperosmolarity and hypoxia produced additive PlGF gene expression. Both hyperosmolarity and hypoxia induced expression of KDR and FLT-4 receptor genes, while hyperosmolarity caused neuropilin-2 and hypoxia neuropilin-1 gene expression. The hyperosmotic, but not the hypoxic, PlGF gene expression was in part mediated by NFAT5. The expression of PlGF in RPE cells depends on the extracellular osmolarity. The data suggest that high consumption of dietary salt may exacerbate the angiogenic response of RPE cells in the hypoxic retina via transcriptional activation of various VEGF family member genes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klein R, Klein BE, Knudtson MD, Meuer SM, Swift M, Gangnon RE (2007) Fifteen-year cumulative incidence of age-related macular degeneration: the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology 114:253–262
Roth F, Bindewald A, Holz FG (2004) Keypathophysiologic pathways in age-related macular disease. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:710–716
Kent DL (2014) Age-related macular degeneration: beyond anti-angiogenesis. Mol Vis 20:46–55
Green WR, Enger C (1993) Age-related macular degeneration histopathologic studies. The 1992 Lorenz E. Zimmerman Lecture. Ophthalmology 100:1519–1535
Witmer AN, Vrensen GF, Van Noorden CJ, Schlingemann RO (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factors and angiogenesis in eye disease. Prog Retin Eye Res 22:1–29
Adamis AP, Shima DT, Yeo KT, Yeo TK, Brown LF, Berse B, D’Amore PA, Folkman J (1993) Synthesis and secretion of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193:631–638
Oshima Y, Oshima S, Nambu H, Kachi S, Hackett SF, Melia M, Kaleko M, Connelly S, Esumi N, Zack DJ, Campochiaro PA (2004) Increased expression of VEGF in retinal pigmented epithelial cells is not sufficient to cause choroidal neovascularization. J Cell Physiol 201:393–400
Schlingemann RO (2004) Role of growth factors and the wound healing response in age-related macular degeneration. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:91–101
De Oliveira Dias JR, Rodrigues EB, Maia M, Magalhães O Jr, Penha FM, Farah ME (2011) Cytokines in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: fundamentals of targeted combination therapy. Br J Ophthalmol 95:1631–1637
Lim LS, Mitchell P, Seddon JM, Holz FG, Wong TY (2012) Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 379:1728–1738
Martin G, Schlunck G, Hansen LL, Agostini HT (2004) Differential expression of angioregulatory factors in normal and CNV-derived human retinal pigment epithelium. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:321–326
Ikeda Y, Yonemitsu Y, Onimaru M, Nakano T, Miyazaki M, Kohno R, Nakagawa K, Ueno A, Sueishi K, Ishibashi T (2006) The regulation of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF-A, -C, and -D) expression in the retinal pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 83:1031–1040
Zhao B, Ma A, Cai J, Boulton M (2006) VEGF-A regulates the expression of VEGF-C in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Br J Ophthalmol 90:1052–1059
Hollborn M, Tenckhoff S, Seifert M, Köhler S, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2006) Human retinal epithelium produces and responds to placenta growth factor. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 244:732–741
Hollborn M, Petto C, Steffen A, Trettner S, Bendig A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2009) Effects of thrombin on RPE cells are mediated by transactivation of growth factor receptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:4452–4459
Puddu A, Sanguineti R, Durante A, Nicolò M, Viviani GL (2012) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C secretion is increased by advanced glycation end-products: possible implication in ocular neovascularization. Mol Vis 18:2509–2517
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A, Vincenti V, Compernolle V, De Mol M, Wu Y, Bono F, Devy L, Beck H, Scholz D, Acker T, DiPalma T, Dewerchin M, Noel A, Stalmans I, Barra A, Blacher S, VandenDriessche T, Ponten A, Eriksson U, Plate KH, Foidart JM, Schaper W, Charnock-Jones DS, Hicklin DJ, Herbert JM, Collen D, Persico MG (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7:575–583
Huang H, Parlier R, Shen JK, Lutty GA, Vinores SA (2013) VEGF receptor blockade markedly reduces retinal microglia/macrophage infiltration into laser-induced CNV. PLoS One 8:e71808
Tarallo V, Bogdanovich S, Hirano Y, Tudisco L, Zentilin L, Giacca M, Ambati J, De Falco S (2012) Inhibition of choroidal and corneal pathologic neovascularization by Plgf1-de gene transfer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:7989–7996
Rakic JM, Lambert V, Devy L, Luttun A, Carmeliet P, Claes C, Nguyen L, Foidart JM, Noël A, Munaut C (2003) Placental growth factor, a member of the VEGF family, contributes to the development of choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3186–3193
Park JE, Chen HH, Winer J, Houck KA, Ferrara N (1994) Placenta growth factor. Potentiation of vascular endothelial growth factor bioactivity, in vitro and in vivo, and high affinity binding to Flt-1 but not to Flk-1/KDR. J Biol Chem 269:25646–25654
Dull RO, Yuan J, Chang YS, Tarbell J, Jain RK, Munn LL (2001) Kinetics of placenta growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor synergy in endothelial hydraulic conductivity and proliferation. Microvasc Res 61:203–210
Autiero M, Waltenberger J, Communi D, Kranz A, Moons L, Lambrechts D, Kroll J, Plaisance S, De Mol M, Bono F, Kliche S, Fellbrich G, Ballmer-Hofer K, Maglione D, Mayr-Beyrle U, Dewerchin M, Dombrowski S, Stanimirovic D, Van Hummelen P, Dehio C, Hicklin DJ, Persico G, Herbert JM, Communi D, Shibuya M, Collen D, Conway EM, Carmeliet P (2003) Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors flt1 and flk1. Nat Med 9:936–943
Hyman L, Schachat AP, He Q, Leske MC (2000) Hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and age-related macular degeneration. Age-Related Macular Degeneration Risk Factors Study Group. Arch Ophthalmol 118:351–358
Fraser-Bell S, Wu J, Klein R, Azen SP, Hooper C, Foong AW, Varma R (2008) Cardiovascular risk factors and age-related macular degeneration: the Los Angeles Latino Eye Study. Am J Ophthalmol 145:308–316
Klein R, Cruickshanks KJ, Nash SD, Krantz EM, Nieto FJ, Huang GH, Pankow JS, Klein BE (2010) The prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and associated risk factors. Arch Ophthalmol 128:750–758
Lifton RP, Gharavi AG, Geller DS (2001) Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 104:545–556
Khaw KT, Barrett-Connor E (1988) The association between blood pressure, age and dietary sodium and potassium: a population study. Circulation 77:53–61
Kenney WL, Chiu P (2001) Influence of age on thirst and fluid intake. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1524–1532
Van Leeuwen R, Tomany SC, Wang JJ, Klein R, Mitchell P, Hofman A, Klein BE, Vingerling JR, Cumming RG, de Jong PT (2004) Is medication use associated with the incidence of early age-related maculopathy? Pooled findings from 3 continents. Ophthalmology 111:1169–1175
Hollborn M, Vogler S, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2015) Regulation of the hyperosmotic induction of aquaporin 5 and VEGF in retinal pigment epithelial cells: involvement of NFAT5. Mol Vis 21:360–377
Cheung CY, Ko BC (2013) NFAT5 in cellular adaptation to hypertonic stress-regulations and functional significance. J Mol Signal 8:5
Chen R, Hollborn M, Grosche A, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2014) Effects of the vegetable polyphenols epigallocatechin-3-gallate, luteolin, apigenin, myricetin, quercetin, and cyanidin in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Vis 20:242–258
Mousa SA, Lorelli W, Campochiaro PA (1999) Role of hypoxia and extracellular matrix-integrin binding in the modulation of angiogenic growth factors secretion by retinal pigmented epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem 74:135–143
Miyamoto N, de Kozak Y, Jeanny JC, Glotin A, Mascarelli F, Massin P, BenEzra D, Behar-Cohen F (2007) Placental growth factor-1 and epithelial haemato-retinal barrier breakdown: potential implication in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 50:461–470
An WG, Kanekal M, Simon MC, Maltepe E, Blagosklonny MV, Neckers LM (1998) Stabilization of wild-type p53 by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Nature 392:405–408
Veltmann M, Hollborn M, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Kohen L, Bringmann A (2016) Osmotic induction of angiogenic growth factor expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. PLoS One 11:e0147312
Lee K, Lee JH, Boovanahalli SK, Jin Y, Lee M, Jin X, Kim JH, Hong YS, Lee JJ (2007) (Aryloxyacetylamino)benzoic acid analogues: a new class of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibitors. J Med Chem 50:1675–1684
Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, Mayer TU, Berg T (2006) Stattic: a small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem Biol 13:1235–1242
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR Jr, Grunberger D, Aggarwal BB (1996) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-κB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9090–9095
Simpson DA, Murphy GM, Bhaduri T, Gardiner TA, Archer DB, Stitt AW (1999) Expression of the VEGF gene family during retinal vaso-obliteration and hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:333–340
Yao YG, Yang HS, Cao Z, Danielsson J, Duh EJ (2005) Upregulation of placental growth factor by vascular endothelial growth factor via a post-transcriptional mechanism. FEBS Lett 579:1227–1234
Nagineni CN, Raju R, Nagineni KK, Kommineni VK, Cherukuri A, Kutty RK, Hooks JJ, Detrick B (2014) Resveratrol suppresses expression of VEGF by human retinal pigment epithelial cells: potential nutraceutical for age-related macular degeneration. Aging Dis 5:88–100
Tu HJ, Lin TH, Chiu YC, Tang CH, Yang RS, Fu WM (2013) Enhancement of placenta growth factor expression by oncostatin M in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 228:983–990
Park J, Kim H, Park SY, Lim SW, Kim YS, Lee DH, Roh GS, Kim HJ, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Jeong BY, Kwon HM, Choi WS (2014) Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein regulates the expression of aldose reductase and protein kinase Cδ in a mouse model of diabetic retinopathy. Exp Eye Res 122:13–19
Kleinewietfeld M, Manzel A, Titze J, Kvakan H, Yosef N, Linker RA, Muller DN, Hafler DA (2013) Sodium chloride drives autoimmune disease by the induction of pathogenic TH17 cells. Nature 496:518–522
Wu C, Yosef N, Thalhamer T, Zhu C, Xiao S, Kishi Y, Regev A, Kuchroo VK (2013) Induction of pathogenic TH17 cells by inducible salt-sensing kinase SGK1. Nature 496:513–517
Akrami H, Soheili ZS, Sadeghizadeh M, Ahmadieh H, Rezaeikanavi M, Samiei S, Khalooghi K (2011) PlGF gene knockdown in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 249:537–546
Kowalczuk L, Touchard E, Omri S, Jonet L, Klein C, Valamanes F, Berdugo M, Bigey P, Massin P, Jeanny JC, Behar-Cohen F (2011) Placental growth factor contributes to micro-vascular abnormalization and blood-retinal barrier breakdown in diabetic retinopathy. PLoS One 6:e17462
Englund-Johansson U, Mohlin C, Liljekvist-Soltic I, Ekström P, Johansson K (2010) Human neural progenitor cells promote photoreceptor survival in retinal explants. Exp Eye Res 90:292–299
Inoue Y, Shimazawa M, Nakamura S, Imamura T, Sugitani S, Tsuruma K, Hara H (2014) Protective effects of placental growth factor on retinal neuronal cell damage. J Neurosci Res 92:329–337
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ute Weinbrecht for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KO 1547/7-1 to L.K.) and the Geschwister Freter Stiftung (Hannover, Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Margrit Hollborn and Konrad Reichmuth have contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollborn, M., Reichmuth, K., Prager, P. et al. Osmotic induction of placental growth factor in retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro: contribution of NFAT5 activity. Mol Biol Rep 43, 803–814 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4016-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4016-9