Abstract
Background
Placenta growth factor (PlGF) is an important co-factor in retinal neovascularization. To examine whether retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells may represent a source for PlGF during retinopathy, we determined whether human RPE cells in vitro produce and respond to PlGF. In addition, we determined whether the cells express receptors for PlGF, i.e. flt-1 and neuropilins.
Methods
Cultured human RPE cells of passages 3–5 were used. The regulation of the PlGF gene and protein expression by growth factors and cytokines was evaluated by quantitative PCR and ELISA. Proliferation rates and chemotaxis were determined by a bromodeoxyuridine and a Boyden chamber assay.
Results
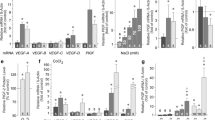
Human RPE cells express mRNAs for various members of the vascular endothelial growth factor family and for their receptors, including mRNAs for PlGF, flt-1, KDR, and neuropilins-1 and -2. The expression levels of the mRNAs for neuropilins-1 and -2 were significantly higher than those for flt-1 and KDR. Members of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β superfamily of growth factors (BMP-4, TGF-β1, and β2) were strong inducers of PlGF gene expression, and evoked secretion of PlGF-2 protein by RPE cells. Exogenous PlGF-2 induced chemotaxis in RPE cells and reduced slightly the cell proliferation at high concentrations.
Conclusion
The findings that RPE cells produce and respond to PlGF indicate that the factor exerts an autocrine/paracrine action on these cells. It is suggested that increased expression of TGF-β-related growth factors during diabetic retinopathy may cause PlGF secretion by RPE cells contributing to the stimulation of cell migration as a critical component of the progression of fibrovascular membranes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bFGF:
-
basic fibroblast growth factor
- BMP:
-
bone morphogenetic protein
- BrdU:
-
bromodeoxyuridine
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- flt:
-
FMS-related tyrosine kinase1 (VEGF-R1)
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HB-EGF:
-
heparin-binding epridermal growth factor-like growth factor
- HGF:
-
hepatocyte growth factor
- IL:
-
interleukin
- KDR:
-
kinase insert domain receptor (VEGF-R2)
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PDGF:
-
platelet-derived growth factor
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- PlGF:
-
placenta growth factor
- RPE:
-
retinal pigment epithelium
- TGF:
-
transforming growth factor
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGF-R:
-
VEGF receptor
References
Autiero M, Waltenberger J, Communi D, Kranz A, Moons L, Lambrechts D, Kroll J, Plaisance S, De Mol M, Bono F, Kliche S, Fellbrich G et al. (2003) Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors flt1 and flk1. Nat Med 9:936–943
Baird A, Durkin T (1986) Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by type beta-transforming growth factor: interactions with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 138:476–482
Blaauwgeers HG, Holtkamp GM, Rutten H, Witmer AN, Koolwijk P, Partanen TA, Alitalo K, Kroon ME, Kijlstra A, van Hinsbergh VW, Schlingemann RO (1999) Polarized vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by human retinal pigment epithelium and localization of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors on the inner choriocapillaris. Evidence for a trophic paracrine relation. Am J Pathol 155:421–428
Cao Y, Ji WR, Qi P, Rosin A, Cao Y (1997) Placenta growth factor: identification and characterization of a novel isoform generated by RNA alternative splicing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235:493–498
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A, Vincenti V, Compernolle V, De Mol M, Wu Y, Bono F, Devy L, Beck H, Scholz D, Acker T et al. (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7:575–583
Castellon R, Hamdi HK, Sacerio I, Aoki AM, Kenney MC, Ljubimov AV (2002) Effects of angiogenic growth factor combinations on retinal endothelial cells. Exp Eye Res 74:523–535
Cui JZ, Hinz BJ, Greve MD, Potter MJ, Hornan D, Samad A, To E, Matsubara JA (2003) Expression of neuropilin-1 in choroidal neovascular membranes. Can J Ophthalmol 38:41–45
Dull RO, Yuan J, Chang YS, Tarbell J, Jain RK, Munn LL (2001) Kinetics of placenta growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor synergy in endothelial hydraulic conductivity and proliferation. Microvasc Res 61:203–210
Enzmann V, Kaufmann A, Hollborn M, Wiedemann P, Gemsa D, Kohen L (1999) Effective chemokines and cytokines in the rejection of human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell grafts. Transpl Immunol 7:9–14
Frank RN, Amin RH, Eliott D, Puklin JE, Abrams GW (1996) Basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are present in epiretinal and choroidal neovascular membranes. Am J Ophthalmol 122:393–403
Fuh G, Li B, Crowley C, Cunningham B, Wells JA (1998) Requirements for binding and signaling of the kinase domain receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem 273:11197–11204
Fujisawa H (2004) Discovery of semaphorin receptors, neuropilin and plexin, and their functions in neural development. J Neurobiol 59:24–33
Heimark RL, Twardzik DR, Schwartz SM (1986) Inhibition of endothelial regeneration by type-beta transforming growth factor from platelets. Science 233:1078–1080
Hinton DR, He S, Graf K, Yang D, Hsueh WA, Ryan SJ, Law RE (1998) Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation mediates PDGF-directed migration of RPE cells. Exp Cell Res 239:11–15
Hoffmann S, Masood R, Zhang Y, He S, Ryan SJ, Gill P, Hinton DR (2000) Selective killing of RPE with a vascular endothelial growth factor chimeric toxin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:2389–2393
Ishida S, Shinoda K, Kawashima S, Oguchi Y, Okada Y, Ikeda E (2000) Coexpression of VEGF receptors VEGF-R2 and neuropilin-1 in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:1649–1656
Khaliq A, Foreman D, Ahmed A, Weich H, Gregor Z, McLeod D, Boulton M (1998) Increased expression of placenta growth factor in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Lab Invest 78:109–116
Maglione D, Guerriero V, Viglietto G, Ferraro MG, Aprelikova O, Alitalo K, Del Vecchio S, Lei KJ, Chou JY, Persico MG (1993) Two alternative mRNAs coding for the angiogenic factor, placenta growth factor (PlGF), are transcribed from a single gene of chromosome 14. Oncogene 8:925–931
Migdal M, Huppertz B, Tessler S, Comforti A, Shibuya M, Reich R, Baumann H, Neufeld G (1998) Neuropilin-1 is a placenta growth factor-2 receptor. J Biol Chem 273:22272–22278
Miller JW, Adamis AP, Shima DT, D’Amore PA, Moulton RS, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J, Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Berse B et al. (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor is temporally and spatially correlated with ocular angiogenesis in a primate model. Am J Pathol 145:574–584
Mitamura Y, Tashimo A, Nakamura Y, Tagawa H, Ohtsuka K, Mizue Y, Nishihira J (2002) Vitreous levels of placenta growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 25:2352
Nagineni CN, Samuel W, Nagineni S, Pardhasaradhi K, Wiggert B, Detrick B, Hooks JJ (2003) Transforming growth factor-β induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Cell Physiol 197:453–462
Nakamura F, Goshima Y (2002) Structural and functional relation of neuropilins. Adv Exp Med Biol 515:55–69
Neufeld G, Kessler O, Herzog Y (2002) The interaction of neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 with tyrosine-kinase receptors for VEGF. Adv Exp Med Biol 515:81–90
Oh H, Takagi H, Otani A, Koyama S, Kemmochi S, Uemura A, Honda Y (2002) Selective induction of neuropilin-1 by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a mechanism contributing to VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:383–388
Park JE, Chen HH, Winer J, Houck KA, Ferrara N (1994) Placenta growth factor. Potentiation of vascular endothelial growth factor bioactivity, in vitro and in vivo, and high affinity binding to Flt-1 but not to Flk-1/KDR. J Biol Chem 269:25646–25654
Pe’er J, Folberg R, Itin A, Gnessin H, Hemo I, Keshet E (1996) Upregulated expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 80:241–245
Pertovaara L, Kaipainen A, Mustonen T, Orpana A, Ferrara N, Saksela O, Alitalo K (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 269:6271–6274
Pfaffl M (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2002–2007
Rakic JM, Lambert V, Devy L, Luttun A, Carmeliet P, Claes C, Nguyen L, Foidart, JM, Noel A, Munaut C (2003) Placental growth factor, a member of the VEGF family, contributes to the development of choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3186–3193
Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Assoian RK, Smith JM, Roche NS, Wakefield LM, Heine UI, Liotta LA, Falanga V, Kehrl JH et al. (1986) Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4167–4171
Saika S, Okada Y, Miyamoto T, Yamanaka O, Ohnishi Y, Ooshima A, Liu CY, Weng D, Kao WW (2004) Role of p38 MAP kinase in regulation of cell migration and proliferation in healing corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:100–109
Sharma GD, He J, Bazan HE (2003) p38 and ERK1/2 coordinate cellular migration and proliferation in epithelial wound healing: evidence of cross-talk activation between MAP kinase cascades. J Biol Chem 278:21989–21997
Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G, Klagsbrun M (1998) Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 92:735–745
Soker S, Miao HQ, Nomi M, Takashima S, Klagsbrun M (2002) VEGF165 mediates formation of complexes containing VEGFR-2 and neuropilin-1 that enhance VEGF165-receptopr binding. J Cell Biochem 85:357–368
Spirin KS, Saghizadeh M, Lewin SL, Zardi L, Kenney MC, Ljubimov AV (1999) Basement membrane and growth factor gene expression in normal and diabetic human retinas. Curr Eye Res 18:490–499
Surapisitchat J, Hoefen RJ, Pi X, Yoshizumi M, Yan C, Berk BC (2001) Fluid shear stress inhibits TNF-alpha activation of JNK but not ERK1/2 or p38 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Inhibitory crosstalk among MAPK family members. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6476–6481
Tamagnone L, Comoglio PM (2004) To move or not to move? Semaphorin signalling in cell migration. EMBO Rep 5:356–361
Wang L, Zeng H, Wang P, Soker S, Mukhopadhyay D (2003) Neuropilin-1-mediated vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent endothelial cell migration. J Biol Chem 278:48848–48860
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ute Weinbrecht for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KO 1547/4-1; BR 1249/2-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollborn, M., Tenckhoff, S., Seifert, M. et al. Human retinal epithelium produces and responds to placenta growth factor. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmo 244, 732–741 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-005-0154-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-005-0154-9