Abstract
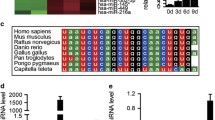
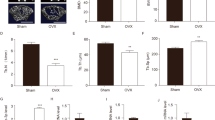
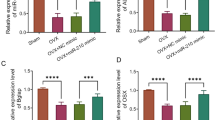
Osteoporosis is a kind of metabolic bone disorder. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) has been proven to play an important role in bone formation, whereas its role in osteoporosis is unclear. In the present study, miR-21 expression was inhibited by TNF-α in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). TNF-α induced cell apoptosis, and inhibited cell proliferation and differentiation of MSCs. Whereas the effect was reversed by miR-21 mimics. Expression of reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) which is a predicted target of miR-21 was inhibited by miR-21 mimics. A luciferase reporter gene assay showed that miR-21 directly bound to RECK 3′-UTR. The effect of TNF-α on MSCs was reversed by RECK siRNA which was consistent with miR-21 mimics. The expression of MT1-MMP was inhibited by TNF-α and enhanced by RECK siRNA and miR-21 mimics. For the in vivo study, an osteoporosis model (OVX) was established by bilateral oophorectomy in mice. The expression of miR-21 decreased and RECK increased in the OVX mice. When treated with lentiviral RECK shRNA, the osteocalcin concentration and alkaline phosphate activity of the OVX mice decreased. The bone mineral density of the right femur mid-diaphysis was improved by RECK shRNA. Collectively, miR-21 modulated the osteoporosis by targeting RECK. These results emphasize the role of miR-21 during osteoporosis and suggest RECK might be a new medical target for osteoporosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- RECK:
-
Reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs
- OVX:
-
Ovariectomy
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphate
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density
References
Weinstein RS, Manolagas SC (2000) Apoptosis and osteoporosis. Am J Med 108:153–164
Rana TM (2007) Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:23–36. doi:10.1038/nrm2085
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
van Wijnen AJ, van de Peppel J, van Leeuwen JP, Lian JB, Stein GS, Westendorf JJ, Oursler MJ, Im HJ, Taipaleenmaki H, Hesse E, Riester S, Kakar S (2013) MicroRNA functions in osteogenesis and dysfunctions in osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 11:72–82. doi:10.1007/s11914-013-0143-6
Jia J, Tian Q, Ling S, Liu Y, Yang S, Shao Z (2013) miR-145 suppresses osteogenic differentiation by targeting Sp7. FEBS Lett 587:3027–3031. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.07.030
Shi K, Lu J, Zhao Y, Wang L, Li J, Qi B, Li H, Ma C (2013) MicroRNA-214 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblast cells by targeting Osterix. Bone 55:487–494. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.04.002
Li E, Zhang J, Yuan T, Ma B (2014) MiR-143 suppresses osteogenic differentiation by targeting Osterix. Mol Cell Biochem 390:69–74. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1957-3
Kang IH, Jeong BC, Hur SW, Choi H, Choi SH, Ryu JH, Hwang YC, Koh JT (2015) MicroRNA-302a stimulates osteoblastic differentiation by repressing COUP-TFII expression. J Cell Physiol 230:911–921. doi:10.1002/jcp.24822
Zhang F, Yang Z, Cao M, Xu Y, Li J, Chen X, Gao Z, Xin J, Zhou S, Zhou Z, Yang Y, Sheng W, Zeng Y (2014) MiR-203 suppresses tumor growth and invasion and down-regulates MiR-21 expression through repressing Ran in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett 342:121–129. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.037
Gong C, Nie Y, Qu S, Liao JY, Cui X, Yao H, Zeng Y, Su F, Song E, Liu Q (2014) miR-21 induces myofibroblast differentiation and promotes the malignant progression of breast phyllodes tumors. Cancer Res 74:4341–4352. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0125
Li B, Ren S, Li X, Wang Y, Garfield D, Zhou S, Chen X, Su C, Chen M, Kuang P, Gao G, He Y, Fan L, Fei K, Zhou C, Schmit-Bindert G (2014) MiR-21 overexpression is associated with acquired resistance of EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 83:146–153. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.11.003
Liu J, Zhu H, Yang X, Ge Y, Zhang C, Qin Q, Lu J, Zhan L, Cheng H, Sun X (2014) MicroRNA-21 is a novel promising target in cancer radiation therapy. Tumour Biol 35:3975–3979. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-1623-8
Yang N, Wang G, Hu C, Shi Y, Liao L, Shi S, Cai Y, Cheng S, Wang X, Liu Y, Tang L, Ding Y, Jin Y (2013) Tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis promoter miR-21 in estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 28:559–573. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1798
Mei Y, Bian C, Li J, Du Z, Zhou H, Yang Z, Zhao RC (2013) miR-21 modulates the ERK-MAPK signaling pathway by regulating SPRY2 expression during human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J Cell Biochem 114:1374–1384. doi:10.1002/jcb.24479
Fan X, Wang E, Wang X, Cong X, Chen X (2014) MicroRNA-21 is a unique signature associated with coronary plaque instability in humans by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 via reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs. Exp Mol Pathol 96:242–249. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2014.02.009
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W, Xiaoyun L (2011) MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration. Med Oncol 28:1469–1474. doi:10.1007/s12032-010-9563-7
Mannello F, Tonti GA, Bagnara GP, Papa S (2006) Role and function of matrix metalloproteinases in the differentiation and biological characterization of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 24:475–481. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0333
Oh J, Takahashi R, Kondo S, Mizoguchi A, Adachi E, Sasahara RM, Nishimura S, Imamura Y, Kitayama H, Alexander DB, Ide C, Horan TP, Arakawa T, Yoshida H, Nishikawa S, Itoh Y, Seiki M, Itohara S, Takahashi C, Noda M (2001) The membrane-anchored MMP inhibitor RECK is a key regulator of extracellular matrix integrity and angiogenesis. Cell 107:789–800
Wu T, Xie M, Wang X, Jiang X, Li J, Huang H (2012) miR-155 modulates TNF-alpha-inhibited osteogenic differentiation by targeting SOCS1 expression. Bone 51:498–505. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.05.013
Raisz LG (2005) Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Investig 115:3318–3325. doi:10.1172/JCI27071
Clowes JA, Riggs BL, Khosla S (2005) The role of the immune system in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. Immunol Rev 208:207–227. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00334.x
Nanes MS (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: molecular and cellular mechanisms in skeletal pathology. Gene 321:1–15
Dong J, Cui X, Jiang Z, Sun J (2013) MicroRNA-23a modulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced osteoblasts apoptosis by directly targeting Fas. J Cell Biochem 114:2738–2745. doi:10.1002/jcb.24622
Wang Y, Gao X, Wei F, Zhang X, Yu J, Zhao H, Sun Q, Yan F, Yan C, Li H, Ren X (2014) Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-21 for cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene 533:389–397. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.038
Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, Zhu QS, Hamidi S, Navab R (2014) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One 9:e103698. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103698
Wang N, Zhang CQ, He JH, Duan XF, Wang YY, Ji X, Zang WQ, Li M, Ma YY, Wang T, Zhao GQ (2013) MiR-21 down-regulation suppresses cell growth, invasion and induces cell apoptosis by targeting FASL, TIMP3, and RECK genes in esophageal carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 58:1863–1870. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2612-2
Ren W, Wang X, Gao L, Li S, Yan X, Zhang J, Huang C, Zhang Y, Zhi K (2014) MiR-21 modulates chemosensitivity of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin by targeting PDCD4. Mol Cell Biochem 390:253–262. doi:10.1007/s11010-014-1976-8
Li C, Li C, Yue J, Huang X, Chen M, Gao J, Wu B (2012) miR-21 and miR-101 regulate PLAP-1 expression in periodontal ligament cells. Mol Med Rep 5:1340–1346. doi:10.3892/mmr.2012.797
Holmbeck K, Bianco P, Pidoux I, Inoue S, Billinghurst RC, Wu W, Chrysovergis K, Yamada S, Birkedal-Hansen H, Poole AR (2005) The metalloproteinase MT1-MMP is required for normal development and maintenance of osteocyte processes in bone. J Cell Sci 118:147–156. doi:10.1242/jcs.01581
Toth M, Chvyrkova I, Bernardo MM, Hernandez-Barrantes S, Fridman R (2003) Pro-MMP-9 activation by the MT1-MMP/MMP-2 axis and MMP-3: role of TIMP-2 and plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:386–395
Manduca P, Castagnino A, Lombardini D, Marchisio S, Soldano S, Ulivi V, Zanotti S, Garbi C, Ferrari N, Palmieri D (2009) Role of MT1-MMP in the osteogenic differentiation. Bone 44:251–265. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2008.10.046
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Dong, Y., Wu, C. et al. MiR-21 overexpression improves osteoporosis by targeting RECK. Mol Cell Biochem 405, 125–133 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2404-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2404-4