Abstract
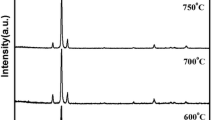
Ga-doped (5 wt%) zinc oxide (GZO) thin films were fabricated on corning 1737 substrates at a fixed oxygen pressure of 200 mTorr at various substrate temperatures (100–300 °C) by using pulsed laser deposition (PLD) in order to investigate the microstructure, optical, and electrical properties of the GZO thin films. It was observed that all the thin films exhibit c-axis orientation and exhibit only a (002) diffraction peak. The GZO thin film, which was fabricated at 200 mTorr and 300 °C, showed the highest (002) orientation, and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the (002) diffraction peak was 0.38°. The position of the XRD peak shifted to a higher angle with increase in the substrate temperature. The optical transmittance in the visible region was greater than 85%. The Burstein-Moss effect, which causes a shift toward a high photon energy level, was observed. The electrical property indicated that the highest carrier concentration (2.33 × 1021 cm−3) and the lowest resistivity (3.72 × 10−4 Ωcm) were obtained in the GZO thin film fabricated at 200 mTorr and 300 °C.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Berry, D.S. Ginley, P.E. Burrows, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 193304 (2008). doi:10.1063/1.2917565
B.D. Ann, S.H. Oh, D.U. Hong, D.H. Shin, A. Moujoud, H.J. Kim, Cryst. Growth 310, 3303–3307 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2008.04.014
T. Nakada, Y. Ohkubo, A. Kunioka, D.B. Chrisey, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 3344–3348 (1991). doi:10.1143/JJAP.30.3344
Q.B. Ma, Z.Z. Ye, H.P. He, S.H. Hu, J.R. Wang, L.P. Zhu et al., J. Cryst. Growth 304, 64–68 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2007.01.037
S.M. Park, T. Ikegami, K. Ebihara, P.K. Shin, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 1522–1527 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.02.046
R.B.H. Tahar, N.B.H. Tahar, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 5285–5289 (2005). doi:10.1007/s10853-005-0522-1
P. Nunes, E. Fortunato, P. Tonello, F. Braz-Fernandes, P. Vilarinho, R. Martins, Vacuum 64, 281–285 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0042-207X(01)00322-0
F.K. Shan, G.X. Liu, W.J. Lee, B.C. Shin, Y.C. Kim, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 50, 626–631 (2007)
B.T. Lee, T.H. Kim, S.H. Jeong, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. (Berl.) 39, 957–961 (2006)
V. Assunção, E. Fortunato, A. Marques, H. Águas, I. Ferreira, M.E.V. Costa et al., Thin Solid Films 427, 401–405 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(02)01184-7
K.Y. Cheong, N. Muti, S. Roy Ramanan, Thin Solid Films 410, 142–146 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(02)00286-9
K.T. Ramakrishna Reddy, R.W. Miles, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 17, 279–281 (1998). doi:10.1023/A:1006569203107
Q.B. Ma, Z.Z. Ye, H.P. He, J.R. Wang, L.P. Zhu, B.H. Zhao, Vacuum 82, 9–14 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.vacuum.2006.12.010
F.K. Shan, G.X. Liu, W.J. Lee, B.C. Shin, S.C. Kim, J. Electroceram. 17, 287–292 (2006). doi:10.1007/s10832-006-9436-9
J.L. Zhao, X.M. Li, J.M. Bian, W.D. Yu, X.D. Gao, J. Cryst. Growth 276, 507–512 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2004.11.407
N. Fujimura, T. Nishihara, S. Goto, J. Xu, T. Ito, J. Cryst. Growth 130, 269–279 (1993). doi:10.1016/0022-0248(93)90861-P
X. Chen, W. Guan, G. Fang, X.Z. Zhao, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 1561–1567 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.02.137
Z.F. Liu, F.K. Shan, J.Y. Sohn, S.C. Kim, G.Y. Kim, Y.X. Li et al., J. Electroceram. 13, 183–187 (2004). doi:10.1007/s10832-004-5096-9
F.K. Shan, B.I. Kim, G.X. Liu, Z.F. Liu, J.Y. Sohn, W.J. Lee et al., J. Appl. Phys. 95, 4772–4775 (2004). doi:10.1063/1.1690091
E. Burstein, Phys. Rev. 93, 632–633 (1954). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.93.632
R.E. Dietz, J.J. Hopfield, D.G. Thomas, J. Appl. Phys. 32, 2282–2286 (1961). doi:10.1063/1.1777060
Z.C. Jin, I. Hamberg, C.G. Granqvist, J. Appl. Phys. 17, 279 (1998)
S.M. Park, T. Ikegami, K. Ebihara, Thin Solid Films 513, 90–94 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2006.01.051
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, H.H., Joung, Y.H. & Kang, S.J. Influence of the substrate temperature on the optical and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films fabricated by pulsed laser deposition. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 20, 704–708 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9788-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9788-9