Abstract
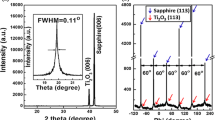
Gallium-doped ZnO (1.2 at. %) thin films with various thicknesses were deposited on sapphire (001) substrates at 500∘C using a pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technique. The thin films with different thicknesses (20, 40, 100, 200, 400, and 600 nm, respectively) were obtained by changing the deposition time. An x-ray diffractometer (XRD) was used to investigate the structural properties of the thin films. All of the thin films had a preferred (002) orientation. However, the thin films with 20 and 40 nm thicknesses were of low crystallinity. With increasing thickness the (002) peak increased greatly, and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) values were calculated by using omega scans. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM) were used to investigate the nanoscale phenomena and the surface morphologies of the thin films. The surface roughness increased as the thickness increased. The thin film with 20 nm thickness was very smooth, and no nucleation center could be observed. However, the thin film with thickness over 100 nm showed nucleation. The nucleation center varied with increasing thickness. A spectrometer was used to investigate the luminescent properties of the thin films. It was found that all of the thin films showed near band edge emissions and no deep-level emissions were observed. A blueshift was also observed due to the Burstein-Moss effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Y. Liang and A. D. Yoffe, Phys. Rev. Lett. 20, 59 (1968).
T.L. Yang, D.H. Zhang, J. Ma, H.L. Ma, and Y. Chen, Thin Solid Films, 326, 60 (1998).
B. Sang, A. Yamada, and M. Konagai, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 37(Part 2), L206 (1998).
P. Verardi, N. Nastase, C. Gherasim, C. Ghica, M. Dinescu, R. Dinu, and C. Flueraru, J. Crystal Growth 197, 523 (1999).
J.F. Cordaro, Y. Shim, and J.E. May, J. Appl. Phys., 60, 4186 (1986).
Y.R. Ryu, S. Zhu, J.D. Budai, H.R. Chandrasekhar, P.F. Miceli, and H.W. White, J. Appl. Phys., 88, 201 (2000).
D.C. Look, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 80, 383 (2001).
F.K. Shan, B.C. Shin, S.C. Kim, and Y.S. Yu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 24, 1861 (2004).
J. Song, I. Pak, K. Yoon, W. Cho, and K. Lim, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 29, 219 (1996).
F. K. Shan and Y. S. Yu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1869 (2004).
F.K. Shan, G.X. Liu, B.I. Kim, B.C. Shin, S.C. Kim, and Y.S. Yu, J. Korean Phys. Soc., 42, S1157 (2003).
S. So and C. Park, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 40, 925 (2002).
Y.F. Lu, H.Q. Ni, Z.H. Ni, Z.H. Mai, and Z.M. Ren, J. Appl. Phys., 88, 498 (2000).
F.K. Shan, B.I. Kim, G.X. Liu, Z.F. Liu, J.Y. Sohn, W.J. Lee, B.C. Shin, and Y.S. Yu, J. Appl. Phys., 95, 4772 (2004).
S. Bethke, H. Pan, and B.W. Wessels, Appl. Phys. Lett., 52, 138 (1988).
H.T. Ng, B. Chen, J. Li, J. Han, and M. Meyyappan, Appl. Phys. Lett., 82, 2023 (2003).
B. Guo, Z. R. Qiu, and K. S. Wong, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2290 (2003).
S.H. Jeong, B.S. Kim, and B.T. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett., 82, 2625 (2003).
F.K. Shan, Z.F. Liu, G.X. Liu, W.J. Lee, G.H. Lee, I.S. Kim, B.C. Shin, and Y.S. Yu, J. Electroceram., 13, 195 (2004).
H.J. Ko, T. Yao, Y.F. Chen, and S.K. Hong, Appl. Phys. Lett., 76, 1905 (2000).
F.K. Shan, B.C. Shin, S.W. Jang, and Y.S. Yu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 24, 1015 (2004).
F.K. Shan, G.X. Liu, W.J. Lee, G.H. Lee, I.S. Kim, B.C. Shin, and Y.C. Kim, J. Crystal Growth, 277, 284 (2005).
F.K. Shan, G.X. Liu, W.J. Lee, G.H. Lee, I.S. Kim, and B.C. Shin, Appl. Phys. Lett., 86, 221910 (2005).
Z. F. Liu, F. K. Shan, Y. X. Li, B. C. Shin, and Y. S. Yu, J. Crystal Growth 259, 130 (2003).
Z. F. Liu, F. K. Shan, J. Y. Sohn, S. C. Kim, G. Y. Kim, Y. X. Li, and Y. S. Yu, J. Electroceram. 13, 183 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, F.K., Liu, G.X., Lee, W.J. et al. Nanoscale phenomena of gallium-doped ZnO thin films on sapphire substrates. J Electroceram 17, 287–292 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-006-9436-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-006-9436-9