Abstract
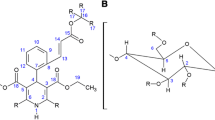
Telmisartan (TEL) is a poorly bioavailable antihypertensive drug candidate owing to its low solubility in all the biofluids. The present study is aimed to enhance the solubility of TEL by forming an inclusion complex with sulfobutylether beta-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD), discover its mode of inclusion and predict the bioavailability of the prepared complexes. The formation of the inclusion complex is explained based on the hydrogen bond propensities and molecular dynamics simulations. Freeze-drying method was employed for the preparation of inclusion complexes. These complexes were subsequently characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy. The spatial configuration of the drug inside the cyclodextrin cavity is probed using 1H and 13C NMR. The in silico docking results are in good agreement with the experimental data and reveal that the hydrogen bond is formed as a part of the guest molecule enters from the broader end of the ring and the protons at the interior portion of the molecule interact with the carboxylic acid (–COOH) group of TEL leading to the formation of a hydrogen bond. The phenyl moiety of TEL occupies the central core and forms multiple Van-der-Waals interactions with the glucopyranose units of the SBE-β-CD. The inclusion complex demonstrates significantly higher in vitro dissolution profile as compared with plain TEL. The GastroPlus™ simulation software generated parameters of inclusion complex in comparison to plain TEL show a seven fold increase in Cmax and 18 fold increase in bioavailability.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wienen, W., Entzeroth, M., Meel, J.C.A., Stangier, J., Busch, U., Ebner, T., Schmid, J., Lehmann, H., Matzek, K., Kempthorne-Rawson, J., Gladigau, V., Hauel, H.N.: A review on telmisartan: a novel, long-acting angiotensin II-receptor antagonist. Cardiovasc. Drug. Rev. 18, 127–154 (2006)
Kaur, M., Bhatia, R.K., Pissurlenkar, R.R.S., Coutinho, E.C., Jain, U.K., Katare, O.P., Chandra, R., Madan, J.: Telmisartan complex augments solubility, dissolution and drug delivery in prostate cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 101, 614–622 (2014)
Abali, H., Güllü, I.H., Engin, H., Haznedaroğlu, I.C., Erman, M., Tekuzman, G.: Old antihypertensives as novel antineoplastics: angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Med. Hypotheses 59, 344–348 (2002)
Sharpe, M., Jarvis, B., Goa, K.L.: Telmisartan: a review of its use in hypertension. Drugs 61(10), 1501–1529 (2001)
McClellan, K.J., Markham, A.: Telmisartan. Drugs 56(6), 1039–1044 (1998)
Park, J., Park, H.J., Cho, W., Cha, K.-H., Yeon, W., Kim, M.S., Kim, J.S., Hwang, S.: Comparative study of telmisartan tablets prepared via the wet granulation method and prior? Prepared using the spray-drying method. J. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 463–468 (2011)
Tran, P.H.L., Tran, H.T.T., Lee, B.J.: Modulation of microenvironmental pH and crystallinity of ionizable telmisartan using alkalizers in solid dispersions for controlled release. J. Control. Rel. 129, 59–65 (2008)
Sangwai, M., Vavia, P.: Amorphous ternary cyclodextrin nanocomposites of telmisartan for oral drug delivery: improved solubility and reduced pharmacokinetic variability. Int. J. Pharm. 453, 423–432 (2013)
Van Hoogevest, P., Liu, X., Fahr, A.: Drug delivery strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs: the industrial perspective Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 8(11), 1481–1500 (2011)
Singh, A., Worku., Z.A., Van den Mooter, G.: Oral formulation strategies to improve solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 8(10), 1361–1378 (2011)
Davis, M.E., Brewster, M.E.: Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 1023–1035 (2004)
Zia, V., Rajewski, R.A., Stella, V.: Effect of cyclodextrin charge on complexation of neutral and charged substrates: comparison of (SBE)7M-beta-CD to HP-beta-CD. J. Pharm. Res. 18, 667–673 (2001)
Irie, T., Uekama, K.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: III: toxicological issues and safety evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci. 86, 147–162 (1997)
Thompson, D.O.: Cyclodextrins-enabling excipients: their present and future use in pharmaceuticals. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 14, 1–104 (1997)
Dinnebier, R.E., Sieger, P., Nar, H., Shankland, K., David, W.I.F.: Structure characterization of three crystalline modifications of telmisartan by single crystal and high-resolution X-ray powder diffraction. J. Pharm. Sci. 89, 1465–1479 (2000)
Wang, J., Pham, D., Kee, T.W., Clafton, S.N., Guo, X., Clements, P., Lincoln, S.F., Prud’homme, R.K., Easton, C.J.: Aggregation and host–guest interactions in dansyl-substituted poly(acrylate)s in the presence of β-cyclodextrin and a β-cyclodextrin dimer in aqueous solution: a UV-Vis, fluorescence, 1H NMR, and rheological study. Macromolecules 44, 9782–9791 (2011)
Kiwon, O.K., Jung, Y.W., Jee, J., Byun, Y.: Facile docking and scoring studies of carborane ligands with estrogen receptor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 34, 1051–1054 (2013)
Galek, P.T.A., Fabian, L., Allen, F.H.: Universal prediction of intramolecular hydrogen bonds in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. B 66, 237–252 (2010)
Wood, P.A., Feeder, N., Furlow, M., Galek, P.T.A., Groom, C.R., Pidcock, E.: Knowledge-based approaches to co-crystal design. CrystEngComm 16, 5839–5848 (2014)
Martiny, V.Y., Martz, F., Selwa, E., Lorga, B.I.: Blind pose prediction, scoring, and affinity ranking of the CSAR 2014 dataset. J. Chem. Inf. Model. S6, 996–1003 (2016)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Williams, R.O., Mahaguna, V., Sriwongjanya, M.: Characterization of an inclusion complex of cholesterol and hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 46, 355–360 (1998)
Klein, S.: The use of biorelevant dissolution media to forecast the in vivo performance of a drug. AAPS J. 12, 397–406 (2010)
Zoeller, T., Dressman, J.B., Klein, S.: Application of a ternary HP-β-CD-complex approach to improve the dissolution performance of a poorly soluble weak acid under biorelevant conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 430, 176–183 (2012)
Fagerberg, J.H., Tsinman, O., Sun, N., Tsinman, K., Avdeef, A., Bergstrom, C.A.S.: Dissolution rate and apparent solubility of poorly soluble drugs in biorelevant dissolution media. Mol. Pharm. 7, 1419–1430 (2010)
George, J.K., Singh, S.K., Verma, P.R.P.: In vivo in silico pharmacokinetic simulation studies of carvedilol-loaded nanocapsules using GastroPlus. Ther. Deliv. 7, 305–318 (2016)
Ishiguro, N., Maeda, K., Kishimoto, W., Saito, A., Harada, A., Ebner, T., Roth, W., Igarashi, T., Sugiyama, Y.: Predominant contribution of OATP1b3 to the hepatic uptake of telmisartan, an angiotensin ii receptor antagonist, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 34, 1109–1115 (2006)
Stangier, J., Schmid, J., Türck, D., Switek, H., Verhagen, A., Peeters, P.A., van Marle, S.P., Tamminga, W.J., Sollie, F.A., Jonkman, J.H.: Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of intravenously and orally administered [14C] telmisartan in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 40, 1312–1322 (2000)
Li, R., Barton, H.A., Maurer.:, T.S.: A Mechanistic Pharmacokinetic model for liver transporter substrates under liver cirrhosis conditions. CPT 4, 338–349 (2015)
Stangier, J., Su, C.P.F., Schöndorfer, G., Roth, W.: Pharmacokinetics and safety of intravenous and oral telmisartan 20 mg and 120 mg in subjects with hepatic impairment compared with healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 40, 1355–1364 (2000)
De Buck, S.S., Sinha, V.K., Fenu, L.A., Nijsen, M.J., Mackie, C.E., Gilissen, R.A.H.J.: Prediction of human pharmacokinetics using physiologically based modeling: a retrospective analysis of 26 clinically tested drugs. Drug Metab. Dispos. 35, 1766–1780 (2007)
Grandelli, H.E., Stickle, B., Whittington, A., Kiran, E.: Inclusion complex formation of β-cyclodextrin and naproxen: a study on exothermic complex formation by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 77, 269–277 (2013)
Bisson-Boutelliez, C., Fontanay, S., Finance, C., Kedzierewicz, F.: Preparation and physicochemical characterization of amoxicillin beta-cyclodextrin complexes. AAPS PharmSciTech 11, 574–581 (2010)
Ge, X., Huang, Z., Tian, S., Huang, Y., Zeng, C.: Complexation of carbendazim with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin to improve solubility and fungicidal activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 89, 208–212 (2012)
Zhang, Y., Zhi, Z., Jiang, T., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Wang, S.: Spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles for loading and release of the poorly water-soluble drug telmisartan. J. Control. Release 145, 257–263 (2010)
Chella, N., Narra, N., Rama Rao, T.: Preparation and characterization of liquisolid compacts for improved dissolution of telmisartan. J. Drug Deliv. 2014, 692793 (2014)
Zhao, R., Tan, T., Sandstrorm, C.: NMR studies on puerarin and its interaction with beta-cyclodextrin. J. Biol. Phys. 37, 387–400 (2011)
Ieiri, I., Nishimura, C., Maeda, K., Sasaki, T., Kimura, M., Chiyoda, T., Hirota, T., Irie, S., Shimizu, H., Noguchi, T., Yoshida, K., Sugiyama, Y.: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenomic profiles of telmisartan after the oral microdose and therapeutic dose. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 21, 495–505 (2011)
Yamada, A., Maeda, K., Ishiguro, N., Tsuda, Y., Igarashi, T., Ebner, T., Roth, W., Ikushiro, S., Sugiyama, Y.: The impact of pharmacogenetics of metabolic enzymes and transporters on the pharmacokinetics of telmisartan in healthy volunteers. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 21, 523–530 (2011)
Fagerholm, U.: Prediction of human pharmacokinetics-biliary and intestinal clearance and enterohepatic circulation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 60, 535–542 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, A., Ghate, M.V., Aithal, K.S. et al. In silico prediction coupled with in vitro experiments and absorption modeling to study the inclusion complex of telmisartan with modified beta-cyclodextrin. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 91, 47–60 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0797-x