Abstract
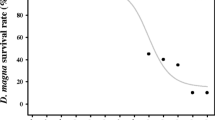
To assess the algicidal effects of the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 on the unarmored dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama and to evaluate the response of the planktonic community and the environment to this chemical, we undertook mesocosm (1,300 L) and small-scale experiments. The reduction ratio for H. circularisquama in each experiment was dependent on the concentration of TD49. At a TD49 concentration >0.4 μM, the abundance of H. circularisquama decreased by 99 % in the small-scale experiment and by 84 % in the mesocosm during the initial 2 days. At 0.2 μM TD49, the abundance of H. circularisquama decreased by up to 85 % in the small-scale experiment, whereas the abundance in the mesocosm increased, implying the absence of an algicidal effect. The decrease in planktonic organisms, including H. circularisquama, following TD49 treatment was correlated with abrupt declines in culture pH and dissolved oxygen concentration. Following addition of TD49, there was a significant increase in the abundance of diatoms and cryptophyta species, and after 8 days, the dominant species in the TD49 treatments shifted to small pennate diatoms including Cylindrotheca and Entomoneis species. The growth of some species among the zooplankton community was promoted at low TD49 concentrations (≤0.4 μM), whereas high concentrations (≥1.0 μM) had a negative effect. This study demonstrates that TD49 is an effective agent for the control for H. circularisquama blooms and that large-scale mesocosms play a crucial role in assessing the application of algicides such as TD49 in natural environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM (1997) Turning back the harmful red tide. Nature 388:513–514
Anderson DM (2009) Approaches to monitoring, control and management of harmful algal blooms (HABs). Ocean Coast Manag 52:342–347
Archambault MC, Bricelj VM, Grant J, Anderson DM (2004) Effects of suspended and sedimented clays on juvenile hard clams, Mercenaris mercenaria, within the context of harmful algal bloom mitigation. Mar Biol 144:553–565
Baek SH, Jang MC, Son MH, Joo HM, Cho H, Kim YO (2012a) Assessment of new algicidal thiazolidinedione (TD49) for the control of marine red tide organisms. “The Sea”. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 17:9–15, In Korean
Baek SH, Jang MC, Son MH, Joo HM, Cho H, Kim YO (2012b) Algicidal effects of a newly developed thiazolidinedione derivative TD49, on dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea. Ocean Polar Res 34:1–11 (In Korean)
Baek SH, Jang MC, Son MH, Kim SW, Cho H, Kim YO (2012c) Algicidal effects on Heterosigma akashiwo and Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae), and toxic effects on natural plankton assemblages by a thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 in a microcosm. J Appl Phycol. doi:10.1007/s10811-012-9905-2
Choi HG, Kim PJ, Lee WC, Yun SJ, Kim HG, Lee HJ (1998) Removal efficiency of Cochlodinium polykrikoides by yellow loess. J Korean Fish Soc 31:109–113 (In Korean)
Doucette GJ, McGovern ER, Babinchak JA (1999) Algicidal bacteria active against Gymnodinium breve (Dinophyceae). I. Bacteria isolation and characterization of killing activity. J Phycol 35:1447–1454
Han HK, Kim YM, Lim SJ, Hong SS, Jung SG, Cho H, Lee WJ, Jin ES (2011) Enhanced efficacy of TD53, a novel algicidal agent, against the harmful algae via the liposomal delivery system. Int J Pharmaceutics 405:137–141
Horiguchi T (1995) Heterocapsa circularisquama sp. nov. with pearl oyster consignments. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernandez ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae. Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Paris, pp 224–226
Imai I, Ishida Y, Hata Y (1993) Killing of marine phytoplankton by a gliding bacterium Cytophaga sp., isolated from the coastal sea of Japan. Mar Biol 116:527–532
Imai I, Ishida Y, Sakaguchi K, Hata Y (1995) Algicidal marine bacteria isolated from northern Hiroshima Bay. Japan Fish Sci 61(61):628–636
Iwataki M, Wong MW, Fukuyo Y (2002) New record of Heterocapsa circularisquama (Dinophyceae) from Hong Kong. Fish Sci 68:1161–1163
Jeong JH, Jin HJ, Sohn CH, Suh KH, Hong YK (2000) Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J Appl Phycol 12:37–43
Jeong HJ, Kim JS, Yoo YD, Kim ST, Song JY, Kim TH, Seong KA, Kang NS, Kim MS, Kim JH, Kim S, Ryu J, Lee HM, Yih WH (2008) Control of the harmful alga Cochlodinium polykrikoides by the naked ciliate Strombidinopsis jeokjo in mesocosm enclosures. Harmful Algae 7:368–377
Kang YH, Kim JD, Kim BH, Kong DS, Han MS (2005) Isolation and characterization of a bio-agent antagonistic to diatom, Stephanodiscus hantzschii. J Appl Microbiol 98:1030–1038
Kenefick SL, Se H, Peterson HG, Prepas EE (1993) Toxin release from Microcystis aeruginosa after chemical treatment. Water Sci Technol 27:433–440
Kim HG (2006) Mitigation and controls of HABs. In: Granéli E, Turner JT (eds) Ecology of harmful algae. Ecological studies. Springer, Berlin, pp 327–338
Kim YM, Wu Y, Duong TU, Ghodake GS, Kim SW, Jin ES, Cho H (2010) Thiazolidinediones as a novel class of algicides against red tide harmful algal species. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:2273–2283
Kim YM, Wu Y, Duong TU, Jung SG, Kim SW, Cho H, Jin ES (2012) Algicidal activity of thiazolidinediones derivatives against harmful algal blooming species. Mar Biotechnol 14:312–322
Kim YO, Kang J-H, Kwon OY, Jung SW, Kim SW (2011) Structural shift of planktonic communities in seawater enclosures: from autotrophic to heterotrophic communities. Aquat Ecosys Health Manage 14:239–245
Kim JS, Kim JC, Lee S, Lee BH, Cho KY (2006) Biological activity of L-2-azetidinecarboxylic acid, isolated from Polygonatum odoratum var. pluriflorum, against several algae. Aquat Bot 85:1–6
Lam AKY, Prepas EE, Spink D, Hrudey SE (1995) Chemical control of hepatotoxic phytoplankton: implications for human health. Water Res 29:1845–1854
Lee HK, Cho H, Han HK (2010) Improved dissolution of poorly water soluble TD49, a novel algicidal agent, via the preparation of solid dispersion. J Pharma Invest 40:181–185
Lee YJ, Choi J-K, Kim EK, Youn S-H, Yang EJ (2008) Field experiments on mitigation of harmful algal blooms using a Sophorolipid–Yellow clay mixture and effects on marine plankton. Harmful Algae 7:154–162
Lehman JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkinson WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA (1995) An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR). J Biol Chem 270:12953–12956
Li FM, Hu HY (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel antialgal allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Appl Environ Microb 71:6545–6553
Liu J, Zhang H, Yang W, Gao J, Ke Q (2004) Studies on biquaternary ammonium salt algaecide for removing red tide. Mar Sci Bull 6:60–65
Matsuyama Y (1999) Harmful effect of dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama on shellfish aquaculture in Japan. Jpn Agric Res Q 33:283–293
Matsuyama Y, Kimura A, Fujii H, Takayama H, Uchida T (1997) Occurrence of a Heterocapsa circularisquama red tide and subsequent damages to shellfish in western Hiroshima Bay, Seto Inland Sea, Japan in 1995. Bull Nansei Natl Fish Res Inst 30:189–207
Na G, Choi W, Chun Y (1996) A study on red tide control with Loess suspension. J Aquacult 9:239–245
Nagai K, Matsuyama Y, Uchida Y, Yamaguchi M, Ishimura M, Nishimura A, Akamatsu S, Honjo T (1996) Toxicity and LD50 levels of the red tide dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama on juvenile pearl oysters. Aquaculture 144:149–154
Nagasaki K, Tomaru Y, Tarutani K, Katanozaka N, Yamanaka S, Tanabe H, Yamaguchi M (2003) Growth characteristics and intraspecies host specificity of a large virus infecting the dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2580–2586
Nagasaki K, Tarutani K, Yamaguchi M (1999) Growth characteristics of Heterosigma akashiwo virus and its possible use as a microbiological agent for red tide control. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:898–902
Nakamura Y (1998) Biomass, feeding and production of Noctiluca scintillans in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. J Plankton Res 20:2213–2222
Russell JB, Dombrowski DB (1980) Effect of pH on the efficiency of growth by pure culture of rumen bacteria in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:604–610
Schrader KK, Nanayakkara NPD, Tucker CS, Rimando AM, Ganzera M, Schaneberg BT (2003) Novel derivatives of 9,10-anthraquinone are selective algicides against the musty-odor cyanobacterium Oscillatoria perornata. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5319–5327
Sigee DC, Glenn R, Andrews MJ, Bellinger EG, Butler RD, Epton HAS, Hendry RD (1999) Biological control of cyanobacteria: principle and possibilities. Hydrobiologia 395/396:161–172
Shirota A (1989) Red tide problem and countermeasures. Int J Aquat Fish Technol 1:195–293
Shumway SE, Frank DM, Ewart LM, Ward JE (2003) Effect of yellow loess on clearance rate in seven species of benthic, filter-feeding invertebrates. Aquacult Res 34:1391–1402
Sengco MR, Anderson DM (2004) Controlling harmful algal blooms through clay flocculation. J Eukaryot Microbiol 51:169–172
Tamai K (1999) Current status of outbreaks and fisheries damages due to Heterocapsa circularisquama. Bull Plankton Soc Jpn 46:153–154 (In Japanese)
Tarutani K, Nagasaki K, Itakura S, Yamaguchi M (2001) Isolation of a virus infecting the novel shellfish killing dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. Aquat Microb Ecol 23:103–111
Terlizzi DE, Ferrier MD, Armbrester EA, Anlauf KA (2002) Inhibition of dinoflagellate growth by extracts of barley straw (Hordeum vulgare). J Appl Phycol 14:275–280
Yu ZM, Zou JZ, Ma X (1994) Application of clays to removal of red tide organisms 1. Coagulation of red tide organisms with clays. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 12:193–200
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Pioneer Research Center Program through the National Research Program of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (grant no. M1071118001-08M1118-00110) and KIOST projects (PE98745). We would like to express to National Research Institute of Fisheries and Environment of Inland Sea, Japan for providing some of the H. circularisquama strain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, S.H., Son, M., Bae, S.W. et al. Algicidal activity of the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 against the harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama in a mesocosm enclosure. J Appl Phycol 25, 1555–1565 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9953-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9953-7