Abstract
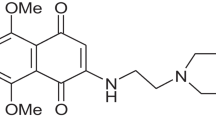
We investigated the effects of the algicide thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 on microbial community in mesocosm experiments. The TD49 concentration exponentially decreased over time, with half-life of 3.5 h, following addition in the seawater (R 2 = 0.98, P < 0.001). Among microbial communities, heterotrophic bacteria and heterotrophic nanoflagellates (HNFs) grew well in all treatments following the addition of TD49. The abundance of HNFs lagged behind the increase in heterotrophic bacteria by 24 h in the 0.2 and 0.4 μM TD49 concentrations (R 2 = 0.28, P < 0.05), and by 48 h in the 0.6 and 1.0 μM TD49 concentrations (R 2 = 0.30, P < 0.05). This implies a strong concentration-dependent top-down effect of TD49 on microbial communities, with indications that the degradation of planktonic organisms, including the target alga, led to high heterotrophic bacteria concentrations, which in turn stimulated the population growth of predatory HNF. However, total ciliate numbers remained relatively low in the TD49 treatments relative to the control and blank groups, suggesting limited carbon flow from bacteria to these grazers even though the abundance of aloricate ciliates gradually increased toward the end of the experimental period, particularly at the high TD49 concentrations. TD49 appears to provide an environmentally safe approach to the control of harmful algal blooms (HABs) in aquatic ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek, S. H., Jang, M. C., Son, M., Kim, S. W., Cho, H., & Kim, Y. O. (2013a). Algicidal effects on Heterosigma akashiwo and Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae), and toxic effects on natural plankton assemblages by a thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 in a microcosm. Journal of Applied Phycology, 25, 1055–1064.
Baek, S. H., Son, M., Bae, S. W., Shin, K., Na, D. H., Cho, H., Yamaguchi, M., Kim, Y. O., & Kim, S. W. (2013b). Algicidal activity of the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 against the harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama in a mesocosm encloser. Journal of Applied Phycology, 25, 1555–1565.
Baek, S. H., Son, M., Jung, S. W., Na, D. H., Cho, H., Yamaguchi, M., Kim, S. W., & Kim, Y. O. (2014a). Enhanced species-specific chemical control of harmful and non-harmful algal bloom species by the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49. Journal of Applied Phycology, 26, 311–321.
Baek, S. H., Shin, K., Son, M., Bae, S. W., Cho, H., Na, D. H., Kim, Y. O., & Kim, S. W. (2014b). Algicidal effect of yellow clay and the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 on the fish-killing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides in microcosm experiments. Journal of Applied Phycology, 26, 2367-2378.
Bieglmayer, C., Prager, G., & Niederle, B. (2002). Kinetic analyses of parathyroid hormone clearance as measured by three rapid immunoassays during parathyroidectomy. Clinical Chemistry, 48, 1731–1737.
Iwataki, M., Wong, M. W., & Fukuyo, Y. (2002). New record of Heterocapsa circularisequama (Dinophyceae) from Hong Kong. Fisheries Science, 68, 1161–1163.
Jeong, J. H., Jin, H. J., Sohn, C. H., Suh, K. H., & Hong, Y. K. (2000). Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. Journal of Applied Phycology, 12, 37–43.
Jeong, H. J., Kim, J. S., Yoo, Y. D., Kim, S. T., Song, J. Y., Kim, T. H., Seong, K. A., Kang, N. S., Kim, M. S., Kim, J. H., Kim, S., Ryu, J., Lee, H. M., & Yih, W. H. (2008). Control of the harmful alga Cochlodinium polykrikoides by the naked ciliate Strombidinopsis jeokjo in mesocosm enclosures. Harmful Algae, 7, 368–377.
Kamiyama, T., Itakura, S., & Nagasaki, K. (2000). Changes in microbial loop components: effects of a harmful algal bloom formation and its decay. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 21, 21–30.
Kim, H. G. (2006). Mitigation and controls of HABs. In E. Granéli & J. T. Turner (Eds.), Ecology of harmful algae. Ecological studies (pp. 327–338). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Kim, J. S., Kim, J. C., Lee, S., Lee, B. H., & Cho, K. Y. (2006). Biological activity of L-2-azetidinecarboxylic acid, isolated from Polygonatum odoratum var. pluriflorum, against several algae. Aquatic Botany, 85, 1–6.
Kim, J. M., Shin, K., Lee, K., & Park, B. K. (2008). In situ ecosystem-based carbon dioxide perturbation experiments: design and performance evaluation of a mesocosm facility. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 6, 208–217.
Kim, Y. M., Wu, Y., Duong, T. U., Ghodake, G. S., Kim, S. W., Jin, E. S., & Cho, H. (2010). Thiazolidinediones as a novel class of algicides against red tide harmful algal species. Applied Biochemistry Biotechnology, 162, 2273–2283.
Kim, S. J., Yim, E. C., Park, I. T., Kim, S. W., & Cho, H. (2011). Comparison of the acute toxicities of novel algicides, thiazolidinediones derivatives TD49 and TD53, to various marine organisms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 30, 2810–2816.
Kim, Y. M., Wu, Y., Duong, T. U., Jung, S. G., Kim, S. W., Cho, H., & Jin, E. S. (2012). Algicidal activity of thiazolidinediones derivatives against harmful algal blooming species. Marine Biotechnology, 14, 312–322.
Lee, H. K., Cho, H., & Han, H. K. (2010). Improved dissolution of poorly water soluble TD49, a novel algicidal agent, via the preparation of solid dispersion. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 40, 181–185.
Matsuyama, Y. (2012). Impacts of the harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama bloom on shellfish aquaculture in Japan and some experimental studies on invertebrates. Harmful Algae, 14, 144–155.
Munawar, M., & Weisse, T. (1989). Is the ‘microbial loop’ an early warning indicator of anthropogenic stress? Hydrobiologia, 188(189), 163–174.
Nagasaki, K., Tomaru, Y., Tarutani, K., Katanozaka, N., Yamanaka, S., Tanabe, H., & Yamaguchi, M. (2003). Growth characteristics and intraspecies host specificity of a large virus infecting the dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 2580–2586.
Park, T. G., Lim, W. A., Park, Y. T., Lee, C. K., & Jeong, H. J. (2014). Economic impact, management and mitigation of red tides in Korea. Harmful Algae, 30S, S131–S143.
Preston, B. L. (2002). Indirect effects in aquatic exotoxicology: implications for ecological risk assessment. Environmental Management, 29, 311–323.
Scholz, N. L., Fleishman, E., Brown, L., Werner, I., Johnson, M. L., Brooks, M. L., Mitchelmore, C. L., & Schlenk, D. (2012). A perspective on modern pesticides, pelagic fish declines, and unknown ecological resilience in highly managed ecosystems. BioScience, 62, 428–434.
Shin, J. J., Kim, S. W., Cho, H., & Kim, S. J. (2012). Examination of bioconcentration of a new algicide, thiazolidinedione derivative (TD49) to marine organisms. Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering Journal, 27, 91–96.
Wang, J. Q., Yutao, Y. T. L. I. U., Sun, C. C., Cheng, Y. W., & Xu, X. S. R. (2007). A background investigation of toxic algae and bio-toxin in the Yangtze Estuary. Transaction of Oceanology and Limnology, 1, 52–61.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (grant no. M1071118001-08 M1118-00110), KIMST (PM58160) and KIOST (PE99316) projects. We express our gratitude to the National Research Institute of Fisheries and Environment of Inland Sea, Japan, for providing Heterocapsa circularisquama strains.
Compliance with ethical standards
ᅟ
Conflict of interest
Authors Seung Ho Baek, Moonho Son, Si Wouk Kim, Jaewon Ryu, Hoon Cho, and Young Ok Kim has received research grants from No M1071118001-08 M1118-00110., KIMST (PM58160) and KIOST (PE99316) projects. Authors Kyoungsoon Shin, Keun-Hyung Choi, Seung Won Jung, Ik Kyo Chung, and Myung-Soo Han have a position on advisory board or board of directors or other type of management relationships.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from all individual participants for whom identifying information is included in this article.

Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, M., Baek, S.H., Shin, K. et al. Effects of the algicide, thiazolidinedione derivative TD49, on microbial communities in a mesocosm experiment. Environ Monit Assess 187, 163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4367-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4367-z