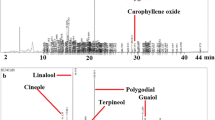
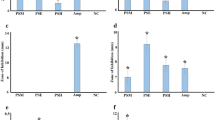
Abstract
A wide variety of herbal remedies are used in traditional African medicine to treat inflammatory disorders, including some autoimmune diseases. Thirty-four extracts from 13 South African plant species traditionally used for the treatment of inflam mation were investigated for their ability to control a microbial trigger for ankylosing spondylitis (Klebsiella pneumoniae). Twenty-six of the extracts (76.5 %) inhibited the growth of K. pneumoniae. Methanol and water extracts of Ballota africana, Carpobrotus edulis leaves, Kigellia africana, Lippia javanica, Pelargonium fasiculata, Syzygium cordatum (including bark), Terminalia pruinoides and Terminalia sericea were effective K. pneumoniae inhibitors, with MIC values <1000 µg/ml. The roots of Tulbaghia violaceae and bark from Warburgia salutaris also demonstrated efficacy. The most potent extracts were examined by RP-HPLC and UV–Vis spectroscopy for the presence of resveratrol. Methanolic extracts of B. africana, C. edulis leaves, L. javanica, T. pruinoides and T. sericea, as well as aqueous B. africana, T. pruinoides and T. sericea extracts, displayed peaks with retention times and UV–Vis spectra consistent with the presence of resveratrol. Resveratrol was generally a minor component, indicating that resveratrol was not solely responsible for the anti-Klebsiella growth inhibitory properties. Plant extracts with K. pneumoniae inhibitory activity were either non-toxic, or of low toxicity in the Artemia (brine shrimp) nauplii bioassay. Their low toxicity and antibiotic bioactivity against K. pneumoniae indicate their potential for both preventing the onset of ankylosing spondylitis and minimising its symptoms once the disease is established.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alataha D, Kapral T, Smolen JS (2003) Toxicity profiles of traditional disease modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:482–486
Ashayeri-Panah M, Feizabadi MM, Eftekhar F (2014) Correlation of multi-drug resistance, integron and blaESBL gene carriage with genetic fingerprints of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Jundishapur J Microbiol 7(2):e8747
Aslam SN, Stevenson PC, Kokubun T et al (2009) Antibacterial and antifungal activity of cicerfuran and related 2-arylbenzofurans and stilbenes. Microbiol Res 165(2):191–195
Baines M, Ebringer A, Avakian H et al (1990) The use of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) and radiobinding assay to investigate the cross-reactivity of Klebsiella antigens and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis patients and healthy controls. Scand J Rheumatol 19:341–349
Blankenberg-Sprenkels SD, Fielder M, Feltkamp TW et al (1998) Antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Dutch patients with ankylosing spondylitis and acute anterior uveitis and to Proteus mirabilis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 25:743–747
Braun J, Sieper J (2007) Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet 369:1379–1390
Braun J, Bollow M, Remlinger G et al (1998) Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA B27-positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis Rheum 41:58–67
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Listing J et al (2005) Decreased incidence of anterior uveitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with the anti-tumor necrosis factor agents infliximab and entanercept. Arthritis Rheum 52(8):2447–2451
Braun J, van den Berg R, Baraliakos X et al (2011) 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:896–904
Chou CT, Uksila J, Toivanen P (1998) Enterobacterial antibodies in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 16:161–164
Cock IE (2008) Assessment of the toxicity of selected Australian native plant extracts using the Artemia franciscana nauplii bioassay. Internet J Toxicol 5(2)
Cock IE (2009) Antibacterial activity of Eucalyptus major and Eucalyptus baileyana methanolic extracts. Internet J Microbiol 6(1)
Cock IE, Kukkonen L (2011) An examination of the medicinal potential of Scaevola spinescens: toxicity, antibacterial and antiviral activities. Pharmacog Res 3(2):85–94
Cock IE, Mohanty S (2011) Evaluation of the antibacterial activity and toxicity of Terminalia ferdinandiana fruit extracts. Pharmacog J 3(20):72–79
Cock IE, van Vuuren SF (2014) Anti-Proteus activity of some South African medicinal plants: their potential for the prevention of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 22:23–36. doi:10.1007/s10787-013-0179-3
Ebringer A, Rashid T, Wilson C et al (2006) Ankylosing spondylitis as an auto-immune disease linked to intestinal Klebsiella infection: prospects for a new therapeutic approach. Curr Rheumatol Rev 2:55–68
Elmali N, Baysal O, Harma A et al (2007) Effects of resveratrol in inflammatory arthritis. Inflammation 30:1–6
Fielder M, Pirt SJ, Tarpey I et al (1995) Molecular mimicry and ankylosing spondylitis: possible role of a novel sequence in pullulanase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. FEBS Lett 369:243–248
Huang C, Wang Y, Wang J et al (2013) TSG (2,3,4′,5-tetrahydroxystilbene 2-o-β-d-glucoside) suppresses induction of pro-inflammatory factors by attenuating the binding activity of nuclear factor-κB in microglia. J Neuroinflammation 10:129
Jayatilake G, Jayasuriya H, Lee E et al (1993) Kinase inhibitors from Polygonum cuspidatum. J Nat Prod 56(10):1805–1810
Joseph CC, Moshi MJ, Innocent E et al (2008) Isolation of a stilbene glycoside and other constituents of Terminalia sericea. African J Trad Comp Med 4(4):383–386
Lanzilli G, Cottarelli A, Nicotera et al (2012) Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol and polydatin by in vitro IL-17 modulation. Inflammation 35(1):240–248
Lawrence RC, Helmick CH, Arnett FC et al (1998) Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disorders in the United States. Arthritis Rheum 41:778–799
Maki-Ikola O, Penttinen M, von Essen R et al (1997) IgM, IgG and IgA class enterobacterial antibodies in serum and synovial fluid in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 36:1051–1053
Nathisuwan S, Burgess DS, Lewis JS (2001) Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: epidemiology, detection, and treatment. Pharmacotherapy 21(8):920–928
Paulo L, Ferreira S, Gallardo E et al (2010) Antimicrobial activity and effects of resveratrol on human pathogenic bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1533–1538
Rashid T, Ebringer A (2007) Ankylosing spondylitis is linked to Klebsiella—the evidence. Clin Rheumatol 26:858–864. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0488-7
Ruebhart DR, Wickramasinghe W, Cock IE (2009) Protective efficacy of the antioxidants vitamin E and Trolox against Microcystis aeruginosa and Microcystin-LR in Artemia franciscana nauplii. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 72:1567–1575
Sautron C, Cock IE (2014) Antimicrobial activity and toxicity of Syzygium australae and Syzygium leuhmannii fruit extracts. Pharmacog Commn 4(1):53–60
Schwimmbeck PL, Yu DTY, Oldstone MBA (1987) Autoanti-bodies to HLA-B27 in the sera of HLA-B27 patients with ankylosing spondylitis and Reiter’s syndrome: molecular mimicry with Klebsiella pneumoniae as a potential mechanism of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 166:173–181
Sirdaarta J, Cock IE (2008) Vitamin E and TroloxTM reduce toxicity of Aloe barbadensis Miller juice in Artemia franciscana nauplii but individually are toxic at high concentrations. Internet J Toxicol 5(1)
Sirdaarta J, Cock IE (2010) Effect of Aloe barbadensis Miller juice on oxidative stress biomarkers in aerobic cells using Artemia franciscana as a model. Phytother Res 24:360–364
Tani Y, Tiwana H, Hukuda S et al (1997) Antibodies to Klebsiella, Proteus and HLA-B27 peptides in Japanese patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 24:109–114
Tiwana H, Wilson C, Walmsley RS et al (1997) Antibody response to gut bacteria in ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Rheumatol Int 17:11–16
Van Wyk BE, van Oudtshoorn B, Gericke N (2009) Medicinal plants of South Africa, 2nd edn. Briza Publications, Pretoria South Africa
Vesoul J, Cock IE (2011) An examination of the medicinal potential of Pittosporum phylliraedes: toxicity, antibacterial and antifungal activities. Pharmacog Commn 1(2):8–17
Wang WB, Lai HC, Hsueh PR et al (2006) Inhibition of swarming and virulence factor expression in Proteus mirabilis by resveratrol. J Med Microbiol 55:1313–1321
Welsh J, Avakian H, Cowling P et al (1980) Ankylosing spondylitis, HLA-B27 and Klebsiella. I: cross-reactivity studies with rabbit antisera. Br J Exp Pathol 61:85–91
Winnett V, Boyer H, Sirdaarta J, Cock IE (2014) The potential of Tasmannia lanceolata as a natural preservative and medicinal agent: antimicrobial activity and toxicity. Pharmacog Commn 4(1):42–52
Acknowledgments
The authors are most grateful to Andrew Hankey, chief botanist at the Walter Sisulu Botanical Gardens in Johannesburg, South Africa, for providing and identifying the plant materials used in these studies. They also thank Professor Charles de Koning and Myron Johnson of the Dept Chemistry, Witwatersrand University for access to their HPLC and assistance with its operation. Financial support was provided by the Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cock, I.E., van Vuuren, S.F. The potential of selected South African plants with anti-Klebsiella activity for the treatment and prevention of Ankylosing spondylitis. Inflammopharmacol 23, 21–35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-014-0222-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-014-0222-z