Abstract
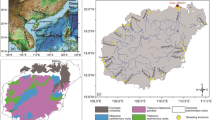
To study the status and source of aluminum (Al) contamination, a total of 21 sampling sites along six rivers near Xi’an City (Shaanxi province, China) were investigated during 2008–2010. The results indicated that the average concentration of total Al (Alt) in the six rivers increased by 1.6 times from 2008 to 2010. The spatial distribution of Alt concentrations in the rivers near Xi’an City was significantly different, ranged from 367 μg/L (Bahe River) to 1,978 μg/L (Taiping River). The Alt concentration was highest near an industrial area for pulp and paper-making (2,773 μg/L), where the Al level greatly exceeded the water quality criteria of both the USA (Criterion Continuous Concentration, 87 μg/L) and Canada (100 μg/L). The average concentration of inorganic monometric aluminum (Alim) was 72 μg/L which would pose threats to fishes and other aquatic lives in the rivers. The concentrations of exchangeable Al (Alex) in the sediment of the Taiping River sampled were relatively high, making it to be an alternative explanation of increasing Al concentrations in the rivers near Xi’an City. Furthermore, an increasing Al level has been detected in the upstream watershed near Xi’an City in recent years, which might indicate another notable pollution source of Al.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adomako, D., Nyarko, B. J. B., Dampare, S. B., Serfor-Armah, Y., Osae, S., Fianko, J. R., & Akaho, E. H. K. (2008). Determination of toxic elements in waters and sediments from River Subin in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 141, 165–175.
Alexopoulos, E., McCrohan, C. R., Powell, J. J., Jugdaohsingh, R., & White, K. N. (2003). Bioavailability and toxicity of freshly neutralized aluminium to the freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 45, 509–514.
APHA (American Public Health Association), AWWA (American Water Works Association), & WEF (Water Environment Federation) (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, DC.
ASTDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (1999). Toxicological profile for aluminum. Atlanta, Georgia.
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) (2000). Standard test methods for moisture, ash and organic matter of peat and other organic soils. ASTM D2974-00, Pennsylvania.
Australian Government (2000). Aquatic ecosystem. In Australian Government, Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts (Ed.), Australian and New Zealand guidelines for fresh and marine water quality. Canberra.
Baker, J. P., & Schofield, C. L. (1982). Aluminum toxicity to fish in acidic waters. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 18(1–3), 289–309.
Baldigo, B. P., Lawrence, G. B., & Simonin, H. A. (2007). Persistent mortality of brook trout in episodically acidified streams of the southwestern Adirondack Mountains, New York. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 136(2), 121–134.
Bi, S. P., Gan, N., Lu, X. C., Ni, H. Y., Lin, H., Wang, X. L., et al. (2003). Evaluation of aluminum speciation in surface waters in China and its environmental risk assessment. Environmental Geology, 45, 65–71.
Bloom, P. R., Weaver, R. M., & McBride, M. B. (1978). The spectrophotometric and fluorometric determination of aluminum with 8-hydroxyquinoline and butyl acetate extraction. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 713–716.
British Geological Survey. (2007). World mineral production 2001–05. Keyworth, Nottingham: British Geological Survey.
Cannata-Andía, J. B. (2000). Adynamic bone and chronic renal failure: an overview. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 320(2), 81–84.
Carver, B. F., & Ownby, J. D. (1995). Acid soil tolerance in wheat. Advances in Agronomy, 54, 117–173.
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment) (2003). Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: aluminium. In Canadian environmental quality guidelines. Winnipeg.
Čiamporová, M. (2002). Morphological and structural responses of plant roots to aluminium at organ, tissue, and cellular levels. Biologica Plantarum, 45(2), 161–171.
Instituto Nacional de Ecología (1989). Criterios Ecológicos de Calidad del Agua. CE-CCA-001/89. Secretaría del Medio Ambientey Recursos Naturales, México. (in Spanish)
Delhaize, E., & Ryan, P. R. (1995). Aluminum toxicity and tolerance in plants. Plant Physiology, 107, 315–321.
Doll, R. (1993). Review: Alzheimer's disease and environmental aluminium. Age and Ageing, 22, 138–153.
Driscoll, C. T., Lawrence, G. B., Bulger, A. J., Butler, T. J., Cronan, C. S., Eager, C., et al. (2001). Acidic deposition in the northeastern United States: sources and inputs, ecosystem effects, and management strategies. BioScience, 51(3), 180–198.
European Food Safety Authority. (2008). Safety of aluminium from dietary intake. The EFSA Journal, 754, 1–34.
Exley, C., Wicks, A. J., Hubert, R. B., & Birchall, D. J. (1996). Kinetic constraints in acute aluminium toxicity in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Journal of Theoretical Biology, 179(1), 25–31.
Ferrier, R. C., McMahon, R. G., Walker, T. A. B., Harriman, R., Edwards, A. C., & King, D. (1992). Experimental stream acidification—the influence of sediment and streambed vegetation. Journal of Hydrology, 140(1–4), 361–370.
Flaten, T. P. (2001). Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer's disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Research Bulletin, 55(2), 187–196.
Garrels, R. M., Mackenzie, F. T., & Hunt, C. (1975). Chemical cycles and the global environment: assessing human influences. Los Altos, California: William Kaufmann, Inc.
Guzmán, F. T., González, F. J. A., & Martínez, R. R. (2010). Implementing Lecane quadridentata acute toxicity tests to assess the toxic effects of selected metals (Al, Fe and Zn). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 287–295.
Kockum, P. C. F., Herbert, R. B., & Gislason, S. R. (2006). A diverse ecosystem response to volcanic aerosols. Chemical Geology, 231, 57–66.
Lawrence, G. B., Sutherland, J. W., Boylen, S. W., Nierzwicki-Bauer, B. M., Momen, B. P. B., & Simonin, H. A. (2007). Acid rain effects on aluminum mobilization clarified by inclusion of strong organic acids. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 93–98.
Liu, W., Luan, Z., Li, L., & Tang, H. (1997). Concentrations and fractionation of aluminum in natural and drinking water samples. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 17(2), 167–172 (in Chinese).
Locke, A. (1991). Zooplankton responses to acidification: a review of laboratory bioassays. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 60(1–2), 135–148.
Lu, X., Li, L. Y., Lei, K., Wang, L., Zhai, Y., & Zhai, M. (2010). Water quality assessment of Wei River, China using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(8), 1693–1699.
Ma, J. F., Ryan, P. R., & Delhaize, E. (2001). Aluminium tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids. Trends in Plant Science, 6(6), 273–278.
Ma, S., Yin, J., Cao, H., Yu, D., Zhou, J., & Zhang, J. (2002). Study on speciation distribution of aluminumin Dianchi Lake. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 21(2), 120–123 (in Chinese).
MacAvoy, S. E., & Bulger, A. J. (1995). Survival of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) embryos and fry in streams of different acid sensitivity in Shenandoah National Park, USA. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 85(2), 445–450.
Matsumoto, H. (2000). Cell biology of aluminum toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. International Review of Cytology, 200, 1–46.
Matúš, P., Kubová, J., Bujdoš, M., Streško, V., & Medveď, J. (2004). Chemical partitioning of aluminium in rocks, soils, and sediments acidified by mining activity. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 379, 96–103.
May, H. M., & Nordstrom, D. K. (1991). Assessing the solubilities and reaction kinetics of aluminous minerals in soils. In B. Ulrich & M. E. Sumner (Eds.), Soil Acidity (pp. 125–148). Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Mortula, M., Bard, S. M., Walsh, M. E., & Gagnon, G. A. (2009). Aluminum toxicity and ecological risk assessment of dried alum residual into surface water disposal. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 36, 127–136.
Poléo, A. B. S., Lydersen, E., Rosseland, B. O., Kroglund, F., Salbu, B., Vogt, R. D., & Kvellestad, A. (1994). Increased mortality of fish due to changing Al-chemistry of mixing zones between limed streams and acid tributaries. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 75(3–4), 339–351.
Qin, R., Chen, F., & Gao, J. (2011). Long-Term Application of chemical fertilizers and rice straw on soil aluminum toxicity. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 42(1), 66–74.
Quiroz-Vázquez, P., Sigee, D. C., & White, K. N. (2010). Bioavailability and toxicity of aluminium in a model planktonic food chain (Chlamydomonas – Daphnia) at neutral pH. Limnologica, 40, 269–277.
Samac, D. A., & Tesfaye, M. (2003). Plant improvement for tolerance to aluminum in acid soils—a review. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 75, 189–207.
Schofield, C. L., & Trojnar, J. R. (1980). Aluminum toxicity to brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) in acidified waters. In T. Y. Toribara, M. W. Miler, & P. E. Morrow (Eds.), Polluted Rain: proceedings of the twelfth Rochester international conference on environmental toxicity (pp. 341–366). New York: Plenum Press.
Swartz, R., Dombrouski, R. J., Burnatowska-Hledin, M. A., & Mayor, G. H. (1987). Microcytic anemia in dialysis patients: reversible marker of aluminum toxicity. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 9, 217–223.
Tipping, E., Ohnstad, M., & Woof, C. (1989). Adsorption of aluminum by stream particulates. Environmental Pollution, 57(2), 85–96.
U.S. EPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2008). National recommended water quality criteria. Washington, DC.
Ure, A., Quevauviller, P., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Improvements in the determination of extractable contents of trace elements in soil and sediment prior to certification. BCR Report EUR 14763 EN, Commission of the European Communities, Brussels.
Van Benschoten, J. E., & Ezwald, J. K. (1990). Measuring Al during water treatment: methodology and application. Journal of American Water Works Association, 82, 71–78.
Walna, B., Siepak, J., Drzymała, S., & Sobczyński, T. (2005). Research on aluminium speciation in poor forest soils using the sequential extraction method. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 14(2), 243–250.
Warby, R. A. F., Johnson, C. E., & Driscoll, C. T. (2008). Changes in aluminum concentrations and speciat ion in lakes across the Northeastern U.S. following reductions in acidic deposition. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(23), 8668–8674.
WHO (World Health Organization) (1997). Environmental health criteria 194: aluminium. Geneva.
Wisniewski, H. M., & Wen, G. Y. (2007). Aluminium and Alzheimer's disease. In D. J. Chadwick & J. Whelan (Eds.), Ciba Foundation Symposium 169—Aluminium in Biology and Medicine. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Wren, C. D., & Stephenson, G. L. (1991). The effect of acidification on the accumulation and toxicity of metals to freshwater invertebrates. Environmental Pollution, 71(2–4), 205–241.
Xi'an Municipal Bureau of Statistics, & NBS Survey Office in Xi'an. (2010). Xi'an Statistical Yearbook-2010. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
Xi'an Research Institute of Environmental Protection. (2010). Environmental Quality and Monitoring Report-Xi'an 2010. Xi'an, Shaanxi. (in Chinese)
Yang, Z., Gao, B., & Yue, Q. (2010). Coagulation performance and residual aluminum speciation of Al2(SO4)3 and polyaluminum chloride (PAC) in Yellow River water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 165(1), 122–132.
Zhang, K., & Zhou, Q. (2005). Toxic effects of Al-based coagulants on Brassica chinensis and Raphanus sativus growing in acid and neutral conditions. Environmental Toxicology, 20(2), 179–187.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Major projects of National Science and Technology on control and rectification of water body pollution (grant no. 2009ZX07012-002-002) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 20907036 and 20936004). Dr. Rong Gao and Guichun Wang (Xi'an Research Institute of Environmental Protection) are thanked for their assistance with field work. The efforts of Shuang Guo, Jiang Liu, and Chaonan Ji are highly appreciated, especially for the sampling and laboratory analysis. Professor Jih-Gaw Lin, Dr. Shucheng Yang, and Yishan Lin are also gratefully acknowledged for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., He, Y., Liang, J. et al. Distribution and source analysis of aluminum in rivers near Xi’an City, China. Environ Monit Assess 185, 1041–1053 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2612-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2612-2