Abstract
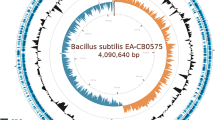
Whole genome sequencing of a copper resistant (CuR) black rot strain of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) isolated from a broccoli plant in Trinidad revealed a unique operon for copper resistance. The cop genes of strain Xcc-BrA1 were determined to be present on a 160 to 180 kb plasmid shown to be non-conjugative with other xanthomonads. While nucleotide comparison of a putative 8.0 Kbp copLABMGF gene cluster identified in Xcc-BrA1 genome did not reveal any homologous region with other known CuR Xanthomonas strains from diverse origins, the comparison of the translated amino acid sequence indicated similarity with X. citri, X. c. pv. citrumelonis and X. vesicatoria Cop proteins. Cloning of the copLAB gene cluster from Xcc-BrA1 conferred copper resistance to other copper-sensitive xanthomonads. Although Xcc-BrA1 harbors copLAB genes with similar sizes and organization and is able to grow on Cu-amended medium as other CuR xanthomonads, the phylogenetic analysis of nucleotide sequences indicates that the cop cluster in Xcc-BrA1 is unique and distantly related to other copLAB genes from Xanthomonas and Stenotrophomonas. The origin of copper resistance genes in Xcc-BrA1 is likely a result of horizontal gene acquisition from a still unknown phylloplane cohabitant. The findings of this study have implications for the management of crop diseases caused by CuR xanthomonads. Future studies could focus on and determining the distribution, overall importance and appropriate control measures for strains harbouring these unique genes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schäffer, A. A., Zheng Zhang, J. Z., Miller, W., & Lipman, D. J. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25(17), 3389–3402.
Alvarez, A. M. (2000). Black rot of crucifers. In Mechanisms of resistance to plant diseases (pp. 21–52). Dordrecht: Springer.
Amuthan, G., & Mahadevan, A. (1994). Replicon typing of plasmids of phytopathogenic xanthomonads. Plasmid, 32(3), 328–332.
Andersen, G. L., Menkissoglou, O., & Lindow, S. E. (1991). Occurence and properties of copper-tolerant strains of Pseudomonas syringae isolated from fruit tress in California. Phytopathology, 81(6), 648–656.
Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., Kingston, R. E., Moore, D. D., Seidman, J. G., Smith, J. A., & Struhl, K. (1999). Short protocols in molecular biology (4th ed.). New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Bender, C. L., & Cooksey, D. A. (1987). Molecular cloning of copper resistance genes from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Journal of Bacteriology, 169, 470–474.
Basim, H., Stall, R. E., Minsavage, G. V., & Jones, J. B. (1999). Chromosomal gene transfer by conjugation in the plant pathogen Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria. Phytopathology, 89(11), 1044–1049.
Basim, H., Minsavage, G. V., Stall, R. E., Wang, J., Shanker, S., & Jones, J. B. (2005). Characterization of a unique chromosomal copper resistance gene cluster from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(12), 8284–8291.
Behlau, F., Canteros, B. I., Minsavage, G. V., Jones, J. B., & Graham, J. H. (2011). Molecular characterization of copper resistance genes from Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and Xanthomonas alfalfae subsp. citrumelonis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(12), 4089–4096. doi:10.1128/aem.03043-10.
Behlau, F., Canteros, B. I., Jones, J. B., & Graham, J. H. (2012a). Copper resistance genes from different xanthomonads and citrus epiphytic bacteria confer resistance to Xanthomonas citri subsp citri. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 133(4), 949–963. doi:10.1007/s10658-012-9966-8.
Behlau, F., Jones, J. B., Myers, M. E., & Graham, J. H. (2012b). Monitoring for resistant populations of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and epiphytic bacteria on citrus trees treated with copper or streptomycin using a new semi-selective medium. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 132(2), 259–270.
Behlau, F., Hong, J. C., Jones, J. B., & Graham, J. H. (2013). Evidence for acquisition of copper resistance genes from different sources in citrus-associated xanthomonads. Phytopathology, 103(5), 409–418. doi:10.1094/phyto-06-12-0134-r.
Bender, C. L., & Cooksey, D. A. (1986). Indigenous plasmids in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato: conjugative transfer and role in copper resistance. Journal of Bacteriology, 165(2), 534–541.
Bender, C. L., Malvick, D. K., Conway, K. E., George, S., & Pratt, P. (1990). Characterization of pXV10A, a copper resistance plasmid in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56(1), 170–175.
Bolot, S., Roux, B., Carrere, S., Jiang, B., Tang, J., Arlat, M., & Noël, L. D. (2013). Genome sequences of three atypical Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris strains, CN14, CN15, and CN16. Genome Announcements, 1(4), e00465–e00413.
Bouzar, H., Jones, J. B., Stall, R. E., Louws, F. J., Schneider, M., Rademaker, J. L. W., de Bruijn, F. J., & Jackson, L. E. (1999). Multiphasic analysis of xanthomonads causing bacterial spot disease on tomato and pepper in the Caribbean and Central America: evidence for common lineages within and between countries. Phytopathology, 89, 328–335.
Canteros, B. I.. (1996). Copper resistance in Xanthomonas campestris pv. citri. International Conference on Plant pathogenic Bacteria. 26–29 August, Madras, Chennai, India.
Canteros, B. I., Minsavage, G. V., Pring, D. R., & Stall, R. E. (1989). Plasmid-encoded copper resistance in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. In: Klement, Z. (Ed.), Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Plant Pathogenic Bacteria (pp. 351-356). Hungary: Akademiai Kiado, Budapest
Canteros, B. I., Minsavage, G. V., Jones, J. B., & Stall, R. E. (1995). Diversity of plasmids in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Phytopathology, 85(12), 1482–1486.
Canteros, B. I., Gochez, A. M., Rybak, M. A., Minsavage, G. V., Jones, J. B., & Stall, R. E. (2010). Management and characterization of plasmid-encoded copper resistance in Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri. International Conference on Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. 12. ICPPB. 2010 06 07–11, June 7–11, 2010. Saint-Denis, France. FR.
Cervantes, C., & Gutierrez-Corona, F. (1994). Copper resistance mechanisms in bacteria and fungi. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 14(2), 121–137.
Cha, J. S., & Cooksey, D. A. (1991). Copper resistance in Pseudomonas syringae mediated by periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 88(20), 8915–8919.
Cooksey, D. A. (1990). Genetics of bactericide resistance in plant pathogenic bacteria. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 28, 201–219.
Crossman, V. C., Gould, J. M., Dow, G. S., Vernikos, A., Okazaki, M., Sebaihia, D., Saunders, C., Arrowsmith, T., Carver, N., Peters, E., Adlem, A., Kerhornou, A., Lord, L., Murphy, K., Seeger, R., Squares, S., Rutter, M. A., Quail, M. A., Rajandream, D., Harris, C., Churcher, S. D., Bentley, J., Parkhill, N. R., & Avison, M. B. (2008). The complete genome, comparative and functional analysis of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia reveals an organism heavily shielded by drug resistance determinants. Genome Biology, 9, R74.
da Silva, A. R., Ferro, J. A., Reinach, F. C., Farah, C. S., Furlan, L. R., Quaggio, R. B., Monteiro-Vitorello, C. B., Van Sluys, M. A., Almeida, N. A., Alves, L. M. C., & Do Amaral, A. M. (2002). Comparison of the genomes of two Xanthomonas pathogens with differing host specificities. Nature, 417(6887), 459–463.
Efron, B., Halloran, E., & Holmes, S. (1996). Bootstrap confidence levels for phylogenetic trees. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 93(23), 13429–13429.
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783–791.
Horvath, D. M., Stall, R. E., Jones, J. B., Pauly, M. H., Vallad, G. E., Dahlbeck, D., Staskawicz, B. J., & Scott, J. W. (2012). Transgenic resistance confers effective field level control of bacterial spot disease in tomato. PloS One, 7(8), e42036. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042036.
Hötte, B., Rath-Arnold, I., Pühler, A., & Simon, R. (1990). Cloning and analysis of a 35.3-kilobase DNA region involved in exopolysaccharide production by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Journal of Bacteriology, 172(5), 2804–2807.
Hsiao, Y., Liu, Y., Lee, P., Hsu, P., Tseng, S., & Pan, Y. (2011). Functional characterization of copA gene encoding multicopper oxidase in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(17), 9290–9302.
Jones, J. B., Lacy, G. H., Bouzar, H., Stall, R. E., & Schaad, N. W. (2004). Reclassification of the xanthomonads associated with bacterial spot disease of tomato and pepper. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 27, 755–762.
Lee, Y. A., Hendson, M., Panopoulos, N. J., & Schroth, M. N. (1994). Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and sequence analysis of copper resistance genes from Xanthomonas campestris pv. juglandis: homology with small blue copper proteins and multicopper oxidase. Journal of Bacteriology, 176(1), 173–188.
Lugo, A. J., Elibox, W., Jones, J. B., & Ramsubhag, A. (2013). Copper resistance in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris affecting crucifers in Trinidad. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 136, 1–10.
Mellano, M. A., & Cooksey, D. A. (1988). Nucleotide sequence and organization of copper resistance genes from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Journal of Bacteriology, 170(6), 2879–2883.
Minsavage, G. V., Canteros, B. I., & Stall, R. E. (1990). Plasmid-mediated resistance to streptomycin in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Phytopathology, 80(8), 719–723.
Potnis, N., Krasileva, K., Chow, V., Almeida, N. F., Patil, P. B., Ryan, R. P., Sharlach, M., Behlau, F., Dow, J. M., Momol, M., White, F. F., Preston, J. F., Vinatzer, B. A., Koebnik, R., Setubal, J. C., Norman, D. J., Staskawicz, B. J., & Jones, J. B. (2011). Comparative genomics reveals diversity among xanthomonads infecting tomato and pepper. BMC Genomics, 12, 146. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-146.
Potnis, N., Timilsina, S., Strayer, A., Shantharaj, D., Barak, J. D., Paret, M. L., Vallad, G. E., & Jones, J. B. (2015). Bacterial spot of tomato and pepper: diverse Xanthomonas species with a wide variety of virulence factors posing a worldwide challenge. Molecular Plant Pathology, 16(9), 907–920.
Qian, W., Jia, Y., Ren, S., He, Y., Feng, J., Lu, L., Sun, Q., Ying, G., Tang, D., & Tang, H. (2005). Comparative and functional genomic analyses of the pathogenicity of phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Genome Research, 15(6), 757–767.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning (Vol. 2). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sigee, D. C. (2005). Bacterial plant pathology: Cell and molecular aspects. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Stall, R. E., Loschke, D. C., & Jones, J. B. (1986). Linkage of copper resistance and avirulence loci on a self-transmissible plasmid in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Phytopathology, 76(2), 240–243.
Staskawicz, B., Dahlbeck, D., Keen, N., & Napoli, C. (1987). Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race 0 and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. Journal of Bacteriology, 169(12), 5789–5794.
Swings, J., & Civerolo, E. L. (1993). Xanthomonas. London: Chapman & Hall.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Peterson Filipski, A., et al. (2013). MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197.
Teixeira, E. C., Franco de Oliveira, J. C., Marques Novo, M. T., & Bertolini, M. C. (2008). The copper resistance operon copAB from Xanthomonas axonopodis pathovar citri: gene inactivation results in copper sensitivity. Microbiology, 154(2), 402–412.
Timilsina, S., Jibrin, M. O., Potnis, N., Minsavage, G. V., Kebede, M., Schwartz, A., Bart, R., Staskawicz, B., Boyer, C., & Vallad, G. E. (2015). Multilocus sequence analysis of Xanthomonads causing bacterial spot of tomato and pepper plants reveals strains generated by recombination among species and recent global spread of Xanthomonas gardneri. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81(4), 1520–1529.
Trevors, J. T. (1986). Plasmid curing in bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 1(3–4), 149–157.
Vivian, A., Murillo, J., & Jackson, R. W. (2001). The roles of plasmids in phytopathogenic bacteria: mobile arsenals? Microbiology, 147(4), 763–780.
Voloudakis, A., Carol, E., Bender, L., & Cooksey, D. A. (1993). Similarity between copper resistance genes from Xanthomonas campestris and Pseudomonas syringae. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59(5), 1627–1634.
Voloudakis, A., Therese, E., Reignier, M., & Cooksey, D. A. (2005). Regulation of resistance to copper in Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(2), 782–789.
Ward, H. P., & O’Garro, L. W. (1992). Bacterial spot of pepper and tomato in Barbados. Plant Disease, 76(10), 1046–1048.
Williams, P. H., Staub, T., & Sutton, J. C. (1972). Inheritance of resistance in Cabbage to black rot. Phytopathology, 62(2), 247–252.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the staff of the Department of Life Sciences of the University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago, for their assistance in executing this study and Jose Huguet Tapia from the Department of Plant Pathology, University of Florida, Gainesville, for his help and expert comments and suggestions about the bioinformatics approach used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Franklin Behlau, Alberto M. Gochez and Alshia Janel Lugo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behlau, F., Gochez, A.M., Lugo, A.J. et al. Characterization of a unique copper resistance gene cluster in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris isolated in Trinidad, West Indies. Eur J Plant Pathol 147, 671–681 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-1035-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-1035-2