Abstract
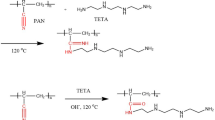
Viscose fiber was oxidized with sodium periodate to prepare a reactive dialdehyde viscose fiber (DAVF) containing abundant aldehyde groups. A solid amine adsorbent (DAVF-PEI) with high amino density for CO2 capture was then prepared by modifying DAVF with polyethylenimine (PEI). Response surface methodology (RSM) based on a three-level, three-factorial design was used to optimize the synthesis conditions of DAVF, in which multiple linear regression equations of aldehyde content and fiber mass loss degree were constructed. The well-designed DAVF was then employed as a support to graft with PEI via Schiff base reaction to prepare a solid amine fiber (DAVF-PEI) for CO2 adsorption. The experimental results verified that DAVF-PEI possessed good thermo-stability and high CO2 adsorption capacity (4.11 mmol/g). DAVF-PEI also showed promising regeneration performance, which could maintain almost the same adsorption capacity for CO2 after ten adsorption and desorption recycles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini M, Younesi H, Bahramifar N, Lorestani AAZ, Ghorbani F, Daneshi A, Sharifzadeh M (2008) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of lead biosorption in an aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. J Hazard Mater 154:694–702
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76:965–977
Calvini P, Conio G, Princi E, Vicini S, Pedemonte E (2006) Viscometric determination of dialdehyde content in periodate oxycellulose part II. Topochemistry of oxidation. Cellulose 13:571–579
Deanna M, D’Alessandro Berend S, Jeffrey RL (2010) Carbon dioxide capture: prospects for new materials. Angew Chem Int Edit 49:6058–6082
Drese JH, Choi S, Lively RP, Koros WJ, Fauth DJ, Gray ML, Jones CW (2009) Synthesis–structure–property relationships for hyperbranched aminosilica CO2 adsorbents. Adv Funct Mater 19:3821–3832
Gray ML, Soong Y, Champagne KJ, Pennline H, Baltrus JP, Stevens JRW, Khatri R, Chuang SSC, Filburn T (2005) Improved immobilized carbon dioxide capture sorbents. Fuel Process Technol 86:1449–1455
Harun N, Nittaya T, Douglas PL (2012) Dynamic simulation of MEA absorption process for CO2 capture from power plants. Int J Greenh Gas Control 10:295–309
Hicks JC, Se JH, Fauth DJ (2008) Designing adsorbents for CO2 capture from flue gas-hyperbranched aminosilicas capable of capturing CO2 reversibly. J Am Chem Soc 130:274–278
Kalavathy MH, Regupathi I, Pillai MG, Miranda LR (2009) Modelling, analysis and optimization of adsorption parameters for H3PO4 activated rubber wood sawdust using response surface methodology (RSM). Colloids Surf B 70:35–45
Kim HK, Kim JG, Cho JD, Hong JW (2003) Optimization and characterization of UV-curable adhesives for optical communications by response surface methodology. Polym Test 22:899–906
Kim UJ, Wada M, Kuga S (2004) Solubilization of dialdehyde cellulose by hot water. Carbohyd Polym 56:7–10
Kumari S, Chauhan GS (2014) New Cellulose-lysine schiff-base-based sensor-adsorbent for mercury ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:5908–5917
Li W, Choi S, Drese J (2010) Steam-stripping for regeneration of supported amine-based CO2 adsorbents. Chemsuschem 3:899–903
Li H, Wu B, Mu C, Lin W (2011) Concomitant degradation in periodate oxidation of carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohyd Polym 84:881–886
Liu XL, Wang LJ, Song XP, Song HN, Zhao JR, Wang SF (2012a) A kinetic model for oxidative degradation of bagasse pulp fiber by sodium periodate. Carbohyd Polym 90:218–223
Liu Y, Wang JT, Zheng Y, Wang AQ (2012b) Adsorption of methylene blue by kapok fiber treated by sodium chlorite optimized with response surface methodology. Chem Eng J 184:248–255
Pevida C, Plaza MG, Arias B (2008) Surface modification of activated carbons for CO2 capture. Appl Surf Sci 254:7165–7172
Potthast A, Kostic M, Schiehser S, Kosma P, Rosenau T (2007) Studies on oxidative modifications of cellulose in the periodate system: molecular weight distribution and carbonyl group profiles. Holzforschung 61:662–667
Sayari A, Belmabkhout Y, Serna-Guerrero R (2011) Flue gas treatment via CO2 adsorption. Chem Eng J 171:760–774
Schrier J (2012) Carbon dioxide separation with a two-dimensional polymer membrane. Acs Appl Mater Inter 4:3745–3752
Serna-Guerrero R, Sayari A (2010) Modeling adsorption of CO2 on amine-functionalized mesoporous Silica. 2: kinetics and breakthrough curves. Chem Eng J 161:182–190
Siriwardane RV, Shen MS, Fisher EP, Poston JA (2001) Adsorption of CO2 on molecular sieves and activated carbon. Energy Fuels 15:279–284
Sirvio J, Hyvakko U, Liimatainen U, Niinimaki J, Hormia O (2011) Periodate oxidation of cellulose at elevated temperatures using metal salts as cellulose activators. Carbohyd Polym 83:1293–1297
Wang X, Ma X, Song C (2012) Molecular basket sorbents polyethylenimine–SBA-15 for CO2 capture from flue gas: characterization and sorption properties. Micropor Mesopor Mater 169:103–111
Wu M, Kuga S (2006) Cationization of cellulose fabrics by polyallylamine binding. J Appl Polym Sci 100:1668–1672
Wu QH, Chen SX, Liu H (2014) Effect of surface chemistry of polyethyleneimine-grafted polypropylene fiber on its CO2 adsorption. RSC Adv 4:27176–27183
Xu T, Wu QH, Chen SX, Deng MW (2015) Preparation of polypropylene based hyperbranched absorbent fibers and the study of their adsorption of CO2. RSC Adv 5:32902–32908
Yang Y, Li HC, Chen SX, Zhao YN, Li QH (2010) Preparation and characterization of a solid amine adsorbent for capturing CO2 by grafting allylamine onto PAN fiber. Langmuir 26:13897–13902
Zhang QK, Zhang SJ, Chen SX, Li PY, Qin TY, Yuan SG (2008) Preparation and characterization of a strong basic anion exchanger by radiation-induced grafting of styrene onto poly(tetrafluoroethylene) fiber. J Colloid Interface Sci 322:421–428
Zhao Y, Seredych M, Zhong Q, Bandosz TJ (2013) Superior performance of copper based mof and aminated graphite oxide composites as CO2 adsorbents at room temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4951–4959
Zhuang LZ, Chen SX, Lin RJ, Xu XZ (2013) Preparation of a solid amine adsorbent based on polypropylene fiber and its performance for CO2 capture. J Mater Res 28:2881–2889
Zukal A, Dominguez I, Mayerova J, Ejka J (2009) Functionalization of delaminated zeolite ITQ-6 for the adsorption of carbon dioxide. Langmuir 25:10314–10321
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51473187), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2014A030313192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Hou, X., Ma, B. et al. The oxidation of viscose fiber optimized by response surface methodology and its further amination with PEI for CO2 adsorption. Cellulose 23, 2539–2548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0955-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0955-5