Abstract
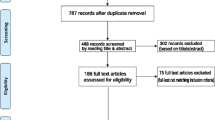
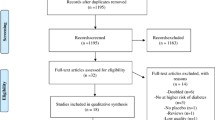
Past research has shown the importance of zinc in several metabolic processes, such as the glucidic metabolism. The present systematic review aims to discuss zinc’s participation in the glycemic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) patients. In order to accomplish that, a systematic search was performed in the Pubmed database using the following indexed and theme-related descriptors: “zinc” AND “type 2 diabetes mellitus”, AND MeSH terms related to glycemic control combined with the boolean operator OR. In total, 1078 articles were retrieved from the research, of which 15 articles of original studies conducted with DM2 patients were included, with three being about the effect of mineral supplementation and 12 reporting observational studies. The main findings of these studies consisted of low body contents of zinc and high excretion of zinc in urine. Hyperglycemia was one of the mechanisms that caused these alterations owing to its interference in zinc reabsorption via renal cells. Another evidence was the negative correlation between the glycated hemoglobin percentage (%HbA1c) and the plasma zinc levels. Additionally, it has been observed that zinc supplementation in DM2 patients has improved glycemic control, since the %HbA1c significantly reduced in these individuals. This present review shows the positive effect of adequate zinc levels on glycemic control, whether it is through dietetic ingestion or supplementation, since its role in insulin homeostasis is clear.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Maroof RA, Al-Sharbatti SS (2006) Serum zinc levels in diabetic patients and effect of zinc supplementation on glycemic control of type 2 diabetics. Saudi Med J 27:344–350
Badran M, Morsy R, Soliman H, Elnimr T (2016) Assessment of trace elements levels in patients with type 2 diabetes using multivariate statistical analysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 33:114–119. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2015.10.006
Basaki M, Saeb M, Nazifi S, Shamsaei HA (2012) Zinc, copper, iron, and chromium concentrations in young patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res 148:161–164. doi:10.1007/s12011-012-9360-6
Basuki W, Hiromura M, Sakurai H (2007) Insulinomimetic Zn complex (Zn(opt)2) enhances insulin signaling pathway in 3 T3-L1 adipocytes. J Inorg Biochem 101:692–699. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2006.12.015
Capdor J, Foster M, Petocz P, Samman S (2013) Zinc and glycemic control: a meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled supplementation trials in humans. J Trace Elem Med Biol 27:137–142. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.08.001
Chasapis CT, Loutsidou AC, Spiliopoulou CA, Stefanidou ME (2012) Zinc and human health: an update. Arch Toxicol 86:521–534. doi:10.1007/s00204-011-0775-1
Chausmer AB (1998) Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 17:109–115. doi:10.1080/07315724.1998.1071873
Chimienti F (2013) Zinc, pancreatic islet cell function and diabetes: new insights into an old story. Nutr Res Rev 26:1–11. doi:10.1017/S0954422412000212
Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Favier A (2004) Identification and cloning of a B-cell-specific zinc transporter, ZnT-8, localized into insulin secretory granules. Diabetes 53:2330–2337. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.9.2330
Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Pattou F, Schuit F, Garcia-Cuenca R, Vandewalle B, Kerr-Conte J, Van Lommel L, Grunwald D, Favier A, Seve M (2006) In vivo expression and functional characterization of the zinc transporter ZnT8 in glucose-induced insulin secretion. J Cell Sci 119:4199–4206. doi:10.1242/jcs.03164
Doddigarla Z, Parwez I, Ahmad J (2015) Correlation of serum chromium, zinc, magnesium and SOD levels with HbA1c in type 2 diabetes: a cross sectional analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr 10:126–129. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2015.10.008
Dufner-Beattie J, Wang F, Kuo YM, Gitschier J, Eide D, Andrews GK (2003) The acrodermatitis enteropathica gene ZIP4 encodes a tissue-specific, zinc-regulated zinc transporter in mice. J Biol Chem 278:33474–33481. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305000200
Ekmecioglu C (2001) The role of trace elements for the health of elderly individuals. Nahrung 45:309–316. doi:10.1002/1521-3803(20011001)45:5<309:AID-FOOD309>3.0.CO;2-0
Fukada T, Yamasaki S, Nishida K, Murakami M, Hirano T (2011) Zinc homeostasis and signaling in health and diseases. J Biol Inorg Chem 16:1123–1134. doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0797-4
Gross JL, Silveiro SP, Camargo JL, Reichelt AJ, Azevedo MJ (2002) Diabetes Melito: diagnóstico, Classificação e Avaliação do Controle Glicêmico. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 46:16–26. doi:10.1590/S0004-27302002000100004
Haase H, Maret W (2005) Fluctuations of cellular, available zinc modulate insulin signaling via inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Trace Elem Med Biol 19:37–42. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.02.004
Huang L (2014) Zinc and its transporters, pancreatic β-cells, and insulin metabolism. Vitam Horm. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800174-5.00014-4
Huang L, Yan M, Kirschke CP (2010) Over-expression of ZnT7 increases insulin synthesis and secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by promoting insulin gene transcription. Exp Cell Res. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.06.017
Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Micronutrients (2001) Dietary reference intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. National Academy Press, Washington
Jansen J, Karges W, Rink L (2009) Zinc and diabetes-clinical links and molecular mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 20:399–417. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.01.009
Jasen J, Rosenkranz E, Overbeck S, Warmuth S, Mocchegiani E, Giacconi R, Weiskirchen R, Karges W, Rink L (2012) Disturbed zinc homeostasis in diabetic patients by in vitro and in vivo analysis of insulinomimetic activity of zinc. J Nutr Biochem 23:1458–1466. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.09.008
Jayawardena R, Ranasinghe P, Galappatthy P, Malkanthi RLDK, Constantine GR, Katulanda P (2012) Effects of zinc supplementation on diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr 4:1–11. doi:10.1186/1758-5996-4-13
Jeong J, Eide DJ (2013) The SLC39 family of zinc transporters. Mol Aspects Med 34:612–619. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2012.05.011
Kambe T, Hashimoto A, Fujimoto S (2014) Current understanding of ZIP and ZnT zinc transporters in human health and diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:3281–3295. doi:10.1007/s00018-014-1617-0
Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Kazi N, Jamali NK, Arain MB, Jalbani N, Kandhro GA (2008) Copper, chromium, manganese, iron, nickel, and zinc levels in biological samples of diabetes mellitus patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 122:1–18. doi:10.1007/s12011-007-8062-y
Khan FA, Jameil NAI, Arjumand S, Khan MF, Tabassum H, Alenzi N, Hijazy S, Alenzi S, Subaie S, Fatima S (2015) Comparative study of serum copper, iron, magnesium and zinc in type 2 diabetes-associated proteinuria. Biol Trace Elem Res 168:321–329. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0379-3
Koga M, Kasayama S (2010) Clinical impact of glycated albumin as another glycemic control marker. Endocr J 57:751–762. doi:10.1507/endocrj.K10E-138
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174. doi:10.2307/2529310
Lemaire K, Ravier MA, Schraenen A, Creemers JW, Van de Plas R, Granvik M, Van Lommel L, Waelkens E, Chimienti F, Rutter GA, Gilon P, in’t Veld PA, Schuit FC (2009) Insulin crystallization depends on zinc transporter ZnT8 expression, but is not required for normal glucose homeostasis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14872–14877. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906587106
Lima VBS, Sampaio FA, Bezerra DLC, Moita Neto JM, Marreiro DN (2011) Parameters of glycemic control and their relationship with zinc concentrations in blood and with superoxide dismutase enzyme activity in type 2 diabetes patients. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 55:701–707. doi:10.1590/S0004-27302011000900006
Lönnerdal BO (2000) Dietary factors influencing zinc absorption. J Nutr 130:1378–1383
Luo YY, Zhao J, Han XY, Zhou XH, Wu J, Ji LN (2015) Relationship between serum zinc level and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin Med J 128:3276–3282. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.171357
Mafra D, Cozzolino SMF (2004) Importância do zinco na nutrição humana. Rev. Nutr 17:79–87. doi:10.1590/S1415-52732004000100009
Marreiro DN, Martins MPSC, Sousa SSR, Torres VIS, Pires LV, Nogueira NN, Lima JMC, Monte SJH (2007) Urinary excretion of zinc and metabolic control of patients with diabetes type 2. Biol Trace Elem Res 120:42–50. doi:10.1007/s12011-007-8000-z
Maruthur NM, Clark JM, Fu M, Linda KWH, Shuldiner AR (2015) Effect of zinc supplementation on insulin secretion: interaction between zinc and SLC30A8 genotype in old order amish. Diabetologia 58:295–303. doi:10.1007/s00125-014-3419-1
Masood N, Baloch GHm Ghori RA, Memon IA, Memon MA, Memon MS (2009) Serum zinc and magnesium in type-2 diabetic patients. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 19:483–486
Myers SA, Nield A, Myers M (2012) Zinc transporters, mechanisms of action and therapeutic utility: implications for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Nutr Metabol. doi:10.1155/2012/173712
Naito Y, Yoshikawa Y, Yasui H (2011) Cellular mechanism of zinchinokitiol complexes in diabetes mellitus. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 84:298–305. doi:10.1246/bcsj.20100262
Nakayama A, Hiromura M, Adachi Y, Sakurai H (2008) Molecular mechanism of antidiabetic zinc-allixin complexes: regulations of glucose utilization and lipid metabolism. J Biol Inorg Chem 13:675–684. doi:10.1007/s00775-008-0352-0
Nsonwu AC, Usoro CAO, Etukudo MH, Usoro IN (2006) Influence of Age, gender and duration of diabetes on serum and urine levels of zinc, magnesium, and chromium in type 2 diabetics in Calabar, Nigeria. Turk J Biochem 1:107–114
Oh HM, Yoon JS (2008) Glycemic control of type 2 diabetic patients after short-term zinc supplementation. Nutr Res Pract 2:283–288
Parham M, Amini M, Aminorroaya A, Heidarian E (2008) Effect of zinc supplementation on microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes: a double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Rev Diabetic Stud 5:102–109. doi:10.1900/RDS.2008.5.102
Ranasinghe P, Pigera S, Galappatthy P, Katulanda P, Constantine GR (2015) Zinc and diabetes mellitus: understanding molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. DARU J Pharm Sci 17:23–44. doi:10.1186/s40199-015-0127-4
Saharia GK, Goswami RK (2013) Evaluation of serum zinc status and glycated hemoglobin of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Assam. J Lab Physicians 5:30–33. doi:10.4103/0974-2727.115923
Salgueiro MJ, Krebs N, Zubillaga MB, Weil R, Postaire E, Lysionek A, Caro RA, De Paoli T, Hager A, Boccio J (2001) Zinc and diabetes mellitus: is there a need of zinc supplementation in diabetes mellitus patients? Biol Trace Elem Res 81:215–228. doi:10.1385/BTER:81:3:21
Savarino L, Granchi D, Ciapetti G, Cenni E, Ravaglia G, Forti P, Maroli F, Mathiolio R (2001) Serum concentrations of zinc and selenium in elderly people; result in healthy nonagenarians/centenarians. Exp Gerontol 36:327–339. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(00)00218-7
Seve M, Chimienti F, Favier A (2002) Role of intracellular zinc in programmed cells death. Pathol Biol 50:212–221
Shan Z, Bao W, Zhang Y, Rong Y, Wang X, Jin Y, Song Y, Yao P, Sun C, Hu FB, Liu L (2014) Interactions between zinc transporter-8 gene (SLC30A8) and plasma zinc concentrations for impaired glucose regulation and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 63:1796–1803. doi:10.2337/db13-0606
Silvestri S, Orlando P, Brugè F, Falcioni G, Tiano L (2016) Effect of different metals on oxidative state and mitochondrial membrane potential in trout erythrocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 134:280–285. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.07.040
Sinha S, Sen S (2014) Status of zinc and magnesium levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its relationship with glycemic status. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 34:220–223. doi:10.1007/s13410-014-0196-9
Sun Q, van Dam RM, Willet WC, Hu FB (2009) Prospective study of zinc intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care 31:629–634. doi:10.2337/dc08-1913
Vanquero MP (2002) Magnesium and trace elements in the elderly; intake, status and recommendations. J Nutr Health Ageing 6:147–153
Viktorínová A, Tošerová E, Križko M, Ďuračková Z (2009) Altered metabolism of copper, zinc, and magnesium is associated with increased levels of glycated hemoglobin in patients with diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 58:1477–1482. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2009.04.035
Wijesekara N, Chimienti F, Wheeler MB (2009) Zinc, a regulator of islet function and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Obes Metabol 11:202–214. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01110.x
Xu J, Zhou Q, Liu G, Tan Y, Cai L (2013) Analysis of serum and urinal copper and zinc in Chinese Northeast population with the prediabetes or diabetes with and without complications. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:1–11. doi:10.1155/2013/635214
Yerlikaya FH, Toker A, Aribaş A (2013) Serum trace elements in obese women with or without diabetes. Indian J Med Res 137:339–345
Yoshiwaka Y, Ueda E, Kojima Y, Sakurai H (2004) The action mechanism of zinc(II) complexes with insulinomimetic activity in rat adipocytes. Life Sci 76:741–751. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.02.006
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the research funding from CNPq (Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Proc. n° 455117/2014-4) related to the theme of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Carvalho, G.B., Brandão-Lima, P.N., Maia, C.S.C. et al. Zinc’s role in the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Biometals 30, 151–162 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-9996-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-9996-y