Abstract
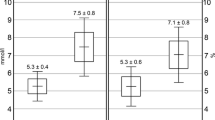
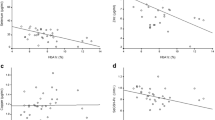
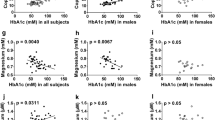
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with alterations in the metabolism of zinc (Zn) and magnesium (Mg). The aim of the present study was to estimate the serum levels of these trace elements in patients with type 2 diabetes in relation to their glycemic status. Eighty seven type 2 diabetics & 30 apparently healthy sex and age matched control subjects were selected for the study. S-Zn and S-Mg levels were significantly low in type 2 diabetes patients. The serum levels of glucose were negatively correlated with serum levels of Zn and Mg of diabetic subjects. The low serum levels of Zn and Mg in diabetics compared to control subjects may be due to the poor glycemic control. Our study shows S-Zn & S-Mg levels are inversely related to glycemic status (HbA1C) of type 2 diabetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Power AC. Diabetes mellitus. In: Harrison’s principles of internal medicine.17th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2005. p. 2275.
Sicree R, Shaw J, Zimmet P. The global burden- diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/the-global-burden. Accessed 1 Dec 2012.
Hussain F, Arif MM, Sheikh MA, Nawaz H, Jamil A. Trace elements status in type 2 diabetes. Bangladesh J Med Sci. 2009;8:52–6.
Nourmuhammadi IK, Kochecki-Shaabani M, Gohari L. Zinc, copper, chromium, manganese and magnesium levels in serum and hair of insulin dependent diabetics. J Trace Elem Metab. 2001;2:88–100.
Winterberg B, Bocchichchio M, Horsdorf TH, Lahi H, Lison AE, Zimkley H. Zinc in treatment of diabetic patients. Trace Elem Med. 1989;6:173–7.
Roth HP, Kirchgessner M. Zinc and insulin metabolism. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1981;3:13–32.
Shenkin A, Baines M, Fell GS, et al. Vitamins and trace elements. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE, editors. Teitz textbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics. 4th ed. New Delhi: Elsevier; 2006. p. 1137–9.
Endres DB, Rude RK. Mineral and bone metabolism. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE, editors. Teitz textbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics. 4th ed. New Delhi: Elservier; 2006. p. 1909–12.
Resnick LM, Gupta RK, Bhargava KK, Hgruenspan H, Alderman MH, Laragh J. Magnesium deficiency in diabetes. Hypertension. 1991;17:951–7.
Trinder P. Determination of Glucose in Blood Using Glucose Oxidase with an Alternative Oxygen Acceptor. Ann Clin Biochem. 1969;6:24–7.
Nathan DM, et al. The clinical information value of the glycosylated hemoglobin assay. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:341–6.
Zinc-Akita A, Yiamashita S. Colorimetric method for the estimation of zinc. Clin Chem. 1989;35:552–4.
Mag-Gindler E, et al. Colorimetric determination with bound calmagite of magnesium in human blood serum. Clin Chem. 1971;17:662.
Kaur HP. HbA1c (Glycosylated hemoglobin) in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Ind J Cl Bioch. 2007;22(supl):272.
Lopes B. Mechanisms and management of diabetes mellitus. J Ind J Cl Bioch. 2007;22(supl):270.
Anetor JI, Seniobi A, Aiose OA, Aqbedana EQ. Decreased serum magnesium and zinc levels: atherogenic implications in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Nigerians. Int J Nutr Health. 2002;16:291–300.
Soinio M, Marniemi J, Laakso M, Pyorala K, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T. Serum zinc level and coronary heart disease events in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Diabetes Care. 2007;30:523–8.
Kareem I, Jaweed SA, Bardapurkar JS, Patil VP. Study of magnesium, glycosylated hemoglobin and lipid profile in diabetic retinopathy. Ind J Clin Bioch. 2004;19:124–7.
Rusu ML, Marutoiu C, Rusu LD, Marutoiu OF, Hotoleanu C, Poanta L. Testing of magnesium, zinc and copper blood levels in diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis Seria F Chemia. 2005;8:61–3.
Walter RM, Uriu-Hare JY, Olin KL, Oster MH, Anawalt BD, Critchfield JW, et al. Copper, zinc, manganese, and magnesium status and complications of diabetes mellitus. Int J Diab Care. 1991;14:1050–6.
Hussain F, Maan MA, Sheikh MA, Nawaz H, Jamil A. Trace element status in type 2 diabetes. Int J Bangladesh J Med Sci. 2009;8:52–6.
Nsonwu AC, Usoro CA, Etukudo MH, Usoro IN. Glycemic control and serum and urine levels of zinc and magnesium in diabetics in Calabar, Nigeria. Int J Pakistan J Nutr. 2006;5:75–8.
Hussain SA, Khadim HM, Khalaf BH, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Sahib AS. Effects of melatonin and zinc on glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with metformin. Int J Saudi Med. 2006;27:1483–8.
Duzguner V, Kaya S. Effect of zinc on the lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant defense systems of the alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. Int J Free Radical Biol Med. 2007;42:1481–6.
Roussel AM, Kerkeni A, Zouari N, Mahjoub S, Matheau JM, Anderson RA. Antioxidant effects of zinc supplementation in Tunisians with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Am Coll Nutr. 2003;22:316–21.
Singh RB, Niaz MA, Rastogi SS, Bajaj S, Gaoli Z, Shoumin Z. Current zinc intake and risk of diabetes and coronary artery disease and factors associated with insulin resistance in rural and urban populations of north India. Int J Am Coll Nutr. 1998;17:564–70.
Tosiello L. Hypomagnesaemia and diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:1143–8.
Conflicts of interest
None
Contributor’s details
Satwika Sinha- She designed the study, performed the experiments, did acquisition of data or analysis and interpretation of data and prepared the manuscript.
Sukanta Sen- He performed the literature search, assisted in supervised the data analysis, edited and reviewed the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S., Sen, S. Status of zinc and magnesium levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its relationship with glycemic status. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 34, 220–223 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-014-0196-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-014-0196-9