Abstract
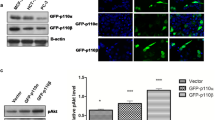
In order to explain the contribution of the protein kinase Cα (PKCα) in apoptosis induced by photo-activation of hypericin (Hyp), a small interfering RNA was used for post-transcriptional silencing of pkcα gene expression. We have evaluated the influence of Hyp photo-activation on cell death in non-transfected and transfected (PKCα−) human glioma cells (U-87 MG). No significant differences were detected in cell survival between non-transfected and transfected PKCα− cells. However, the type of cell death was notably affected by silencing the pkcα gene. Photo-activation of Hyp strongly induced apoptosis in non-transfected cells, but the level of necrotic cells in transfected PKCα− cells increased significantly. The differences in cell death after Hyp photo-activation are demonstrated by changes in: (i) reactive oxygen species production, (ii) Bcl-2 phosphorylation on Ser70 (pBcl-2(Ser70)), (iii) cellular distributions of pBcl-2(Ser70) and (iv) cellular distribution of endogenous anti-oxidant glutathione and its co-localization with mitochondria. In summary, we suggest that post-transcriptional silencing of the pkcα gene and the related decrease of PKCα level considerably affects the anti-apoptotic function and the anti-oxidant function of Bcl-2. This implies that PKCα, as Bcl-2 kinase, indirectly protects U-87 MG cells against oxidative stress and subsequent cell death.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mellor H, Parker PJ (1998) The extended protein kinase C superfamily. Biochem J 332:281–292
Nishizuka Y (1995) Protein kinases.5. Protein-kinase-C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular-responses. Faseb Journal 9:484–496
Jiffar T, Kurinna S, Suck G et al (2004) PKC alpha mediates chemoresistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia through effects on Bcl2 phosphorylation. Leukemia 18:505–512
Nikoletopoulou V, Markaki M, Palikaras K, Tavernarakis N (2013) Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Cell Research 1833:3448–3459
Merino D, Bouillet P (2009) The Bcl-2 family in autoimmune and degenerative disorders. Apoptosis 14:570–583
Koc M, Nad’ova Z, Truksa J, Ehrlichova M, Kovar J (2005) Iron deprivation induces apoptosis via mitochondrial changes related to Bax translocation. Apoptosis 10:381–393
Ackermann EJ, Taylor JK, Narayana R, Bennett CF (1999) The role of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in endothelial apoptosis elucidated with antisense oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem 274:11245–11252
Ruvolo PP, Deng XM, Carr BH, May WS (1998) A functional role for mitochondrial protein kinase C alpha in Bcl2 phosphorylation and suppression of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273:25436–25442
Blagosklonny MV, Giannakakou P, el-Deiry WS et al (1997) Raf-1/bcl-2 phosphorylation: a step from microtubule damage to cell death. Cancer Res 57:130–135
Voehringer DW (1999) BCL-2 and glutathione: alterations in cellular redox state that regulate apoptosis sensitivity. Free Radic Biol Med 27:945–950
Franco R, Cidlowski JA (2009) Apoptosis and glutathione: beyond an antioxidant. Cell Death Differ 16:1303–1314
Circu ML, Aw TY (2008) Glutathione and apoptosis. Free Radical Res 42:689–706
Wilkins HM, Marquardt K, Lash LH, Linseman DA (2012) Bcl-2 is a novel interacting partner for the 2-oxoglutarate carrier and a key regulator of mitochondrial glutathione. Free Radic Biol Med 52:410–419
Malik F, Kumar A, Bhushan S et al (2007) Reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial dysfunction in the apoptotic cell death of human myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells by a dietary compound with a ferin A with concomitant protection by N-acetyl cysteine. Apoptosis 12:2115–2133
Papa L, Gomes E, Rockwell P (2007) Reactive oxygen species induced by proteasome inhibition in neuronal cells mediate mitochondrial dysfunction and a caspase-independent cell death. Apoptosis 12:1389–1405
Shen S, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Gong X (2013) Sarsasapogenin induces apoptosis via the reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway and ER stress pathway in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441:519–524
Miskovsky P (2002) Hypericin - A new antiviral and antitumor photosensitizer: mechanism of action and interaction with biological macromolecules. Curr Drug Targets 3:55–84
Kocanova S, Buytaert E, Matroule JY et al (2007) Induction of heme-oxygenase 1 requires the p38(MAPK) and PI3K pathways and suppresses apoptotic cell death following hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Apoptosis 12:731–741
Huntosova V, Alvarez L, Bryndzova L et al (2010) Interaction dynamics of hypericin with low-density lipoproteins and U87-MG cells. Int J Pharm 389:32–40
Kocanova S, Hornakova T, Hritz J et al (2006) Characterization of the interaction of hypericin with protein kinase c in U-87 MG human glioma cells. Photochem Photobiol 82:720–728
Dzurova L, Petrovajova D, Nadova Z, Huntosova V, Miskovsky P, Stroffekova K (2014) The role of anti-apoptotic protein kinase Calpha in response to hypericin photodynamic therapy in U-87 MG cells. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 11:213–226
Petrovajova D, Jancura D, Miskovsky P et al (2013) Monitoring of singlet oxygen luminescence and mitochondrial autofluorescence after illumination of hypericin/mitochondria complex: a time-resolved study. Laser Phys Lett 10:7
Buriankova L, Nadova Z, Jancura D et al (2010) Synchrotron based Fourier-transform infrared microspectroscopy as sensitive technique for the detection of early apoptosis in U-87 MG cells. Laser Phys Lett 7:613–620
Kascakova S, Nadova Z, Mateasik A et al (2008) High level of low-density lipoprotein receptors enhance hypericin uptake by U-87 MG cells in the presence of LDL. Photochem Photobiol 84:120–127
Ehrlichova M, Koc M, Truksa J, Naldova Z, Vaclavikova R, Kovarr J (2005) Cell death induced by taxanes in breast cancer cells: cytochrome c is released in resistant but not in sensitive cells. Anticancer Res 25:4215–4224
Mandavilli BS, Janes MS. (2010) Detection of intracellular glutathione using ThiolTracker violet stain and fluorescence microscopy. Curr Protoc cytom Chapter 9:Unit 9.35–Unit 39.35
Huntosova V, Nadova Z, Dzurova L, Jakusova V, Sureau F, Miskovsky P (2012) Cell death response of U87 glioma cells on hypericin photoactivation is mediated by dynamics of hypericin subcellular distribution and its aggregation in cellular organelles. Photochem Photobiol Sci 11:1428–1436
Adhikary G, Chew YC, Reece EA, Eckert RL (2010) PKC-delta and -eta, MEKK-1, MEK-6, MEK-3, and p38-delta Are Essential Mediators of the Response of Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes to Differentiating Agents. J Invest Dermatol 130:2017–2030
Lahn M, Kohler G, Sundell K et al (2004) Protein kinase C alpha expression in breast and ovarian cancer. Oncology 67:1–10
Finkel T (2011) Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol 194:7–15
Lindsay J, Esposti MD, Gilmore AP (2011) Bcl-2 proteins and mitochondria-Specificity in membrane targeting for death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:532–539
Ruvolo PP, Deng X, May WS (2001) Phosphorylation of Bcl2 and regulation of apoptosis. Leukemia 15:515–522
Esteve JM, Mompo J, De La Asuncion JG et al (1999) Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA and glutathione oxidation in apoptosis: studies in vivo and in vitro. Faseb J 13:1055–1064
Zimmermann AK, Loucks FA, Schroeder EK, Bouchard RJ, Tyler KL, Linseman DA (2007) Glutathione binding to the Bcl-2 homology-3 domain groove - A molecular basis for Bcl-2 antioxidant function at mitochondria. J Biol Chem 282:29296–29304
Vairetti M, Ferrigno A, Bertone R, Richelmi P, Berte F, Freitas I (2005) Apoptosis vs. necrosis: glutathione-mediated cell death during rewarming of rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1740:367–374
Benderdour M, Charron G, Comte B et al (2004) Decreased cardiac mitochondrial NADP(+)-isocitrate dehydrogenase activity and expression: a marker of oxidative stress in hypertrophy development. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H2122–H2131
Hockenbery DM, Oltvai ZN, Yin XM, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell 75:241–251
Kane DJ, Sarafian TA, Anton R et al (1993) Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death - decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science 262:1274–1277
Voehringer DW, Meyn RE (2000) Redox Aspects of Bcl-2 Function. Antioxid Redox Signal 2:537–550
Hochman A, Sternin H, Gorodin S et al (1998) Enhanced oxidative stress and altered antioxidants in brains of Bcl-2-deficient mice. J Neurochem 71:741–748
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by: the FP7 EU project CELIM 316310, the project of the Slovak Res. and Dev. Agency APVV-0242-11, the project of the Agency of the Ministry of Education of Slovak (Republic for the Structural funds of the European Union: Doktorand (ITMS code: 26110230013) and KVARK (ITMS code: 26110230084) and by the International Program for Scientific Cooperation (PICS N°5398) from the CNRS. This work forms a part of the co-tutoring doctoral study of J. J. (P. J. Safarik University and UPMC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joniova, J., Misuth, M., Sureau, F. et al. Effect of PKCα expression on Bcl-2 phosphorylation and cell death by hypericin. Apoptosis 19, 1779–1792 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1043-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1043-7