Abstract
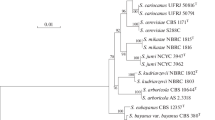
Genetic hybridization, sequence and karyotypic analyses of natural Saccharomyces yeasts isolated in different regions of Taiwan revealed three biological species: Saccharomyces arboricola, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces kudriavzevii. Intraspecies variability of the D1/D2 and ITS1 rDNA sequences was detected among S. cerevisiae and S. kudriavzevii isolates. According to molecular and genetic analyses, the cosmopolitan species S. cerevisiae and S. kudriavzevii contain local divergent populations in Taiwan, Malaysia and Japan. Six of the seven known Saccharomyces species are documented in East Asia: S. arboricola, S. bayanus, S. cerevisiae, S. kudriavzevii, S. mikatae, and S. paradoxus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aa E, Townsend JP, Adams RI, Nielsen KM, Taylor JW (2006) Population structure and gene evolution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 6:702–715
Bon E, Neuvéglise C, Casaregola S, Artiguenave F, Wincker P, Aigle M, Durrens P (2000) Genomic exploration of the hemiascomycetous yeasts: 5. Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum. FEBS Lett 48:37–41
Chang CF, Huang LY, Chen SF, Lee CF (2012a) Kloeckera taiwanica sp. nov., a new ascomycetous apiculate yeast species isolated in Taiwan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1434–1437
Chang CF, Liu YR, Chen SF, Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Lee CF (2012b) Five novel species of the anamorphic genus Candida in the Cyberlindnera clade isolated from natural substrates in Taiwan. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 102:9–21
Fay JC, Benavides JA (2005) Evidence for domesticated and wild populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet 1:66–71
Fischer G, James SA, Roberts IN, Oliver SG, Louis EJ (2000) Chromosomal evolution in Saccharomyces. Nature 405:451–454
Goffeau A, Barrell BG, Bussey H, Davis RW, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel JD, Jacq C, Johnston M, Louis EJ, Mewes HW, Murakami Y, Philippsen P, Tettelin H, Oliver SG (1996) Life with 6000 genes. Science 274:546–567
Greig D (2009) Reproductive isolation in Saccharomyces. Heredity 102:39–44
Hittinger CT, Rokas A, Carroll SB (2004) Parallel inactivation of multiple GAL pathway genes and ecological diversification in yeasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:14144–14149
Hittinger CT, Gonçalves P, Sampaio JP, Dover J, Johnston M, Rokas A (2010) Remarkably ancient balanced polymorphisms in a multi-locus gene network. Nature 464(7285):54–58
Johnson LJ, Koufopanou V, Goddard MR, Hetherington R, Schafer SM, Burt A (2004) Population genetics of the wild yeast Saccharomyces paradoxus. Genetics 166:43–52
Johnston JR, Mortimer RK (1959) Use of snail digestive juice in isolation of yeast spore tetrads. J Bacteriol 78:292
Kellis M, Patterson N, Endrizzi M, Birren B, Lander ES (2003) Sequencing and comparison of yeast species to identify genes and regulatory elements. Nature 423:241–254
Kudrjawzev VI (1960) Die Systematik der Hefen. Akademie-Verlag GmbH, Berlin
Kurtzman CP (2003) Phylogenetic circumscription of Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces and other members of the Saccharomycetaceae, and the proposal of the new genera Lachancea, Nakaseomyces, Naumovia, Vanderwaltozyma and Zygotorulaspora. FEMS Yeast Res 4:233–245
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (2003) Phylogenetic relationships among yeasts of the “Saccharomyces complex” determined from multigene sequence analyses. FEMS Yeast Res 3:417–432
Lee CF, Yao CH, Liu YR, Hsieh CW, Young SS (2009) Lachancea dasiensis sp. nov., an ascosporogenous yeast isolated from soil and leaves in Taiwan. Int J Syst Envol Microbiol 59:1818–1822
Legras JL, Merdinoglu D, Cornuet JM, Karst F (2007) Bread, beer and wine: Saccharomyces cerevisiae diversity reflects human history. Mol Ecol 16:2091–2102
Libkind D, Hittinger CT, Valériod E, Carla Gonçalves C, Jim Doverb J, Johnstonb M, Gonçalves P, Sampaio JP (2011) Microbe domestication and the identification of the wild genetic stock of lager-brewing yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:14539–14544
Liti G, Peruffo A, James SA, Roberts IN, Louis EJ (2005) Inferences of evolutionary relationships from a population survey of LTR-retrotransposons and telomeric-associated sequences in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex. Yeast 22:177–192
Liti G, David B, Barton H, Louis EJ (2006) Sequence diversity, reproductive isolation and species concepts in Saccharomyces. Genetics 174:839–850
Liti G, Carter DM, Moses AM, Warringer J, Parts L, James SA, Davey RP, Roberts IN, Burt A, Koufopanou V, Tsai IJ, Bergman CN, Bensasson D, O’Kelly MJT, van Oudenaarden A, Barton DBT, Bailes E, Nguyen Ba AN, Jones M, Quail MA, Goodhead I, Sims S, Smith F, Blomberg A, Durbin R, Louis EJ (2009) Population genomics of domestic and wild yeasts. Nature 458:337–341
Liu CH, Young SS, Chang TC, Lee CF (2008) Candida dajiaensis sp. nov., Candida yuanshanicus sp. nov., Candida jianshihensis sp. nov., and Candida sanyiensis sp. nov., four anamorphic, ascomycetous yeast species isolated from soil in Taiwan. FEMS Yeast Res 8:815–822
Lopes CA, Barrio E, Querol A (2010) Natural hybrids of S. cerevisiae × S. kudriavzevii share alleles with European wild populations of Saccharomyces kudriavzevii. FEMS Yeast Res 10:412–421
Louis EJ (2011) Population genomics and speciation in yeasts. Fungal Biol Rev 25:136–142
Mayr E (1942) Systematics and the origin of species. Columbia University Press, New York
Michailova YuV, Castello S, Naumova ES, Naumov GI (2009) Allo- and sympatric sibling species of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DNA–DNA reassociation. Ecol Genet 7(4):3–7 (in Russian)
Naumov GI (1980) The biological species Saccharomyces terrestris. Dokl Biol Sci (Engl Transl) 249(1–6):1248–1250
Naumov GI (1986) Genetic differentiation and ecology of the yeast Saccharomyces paradoxus Batschinskaia. Dokl Biol Sci (Engl Transl) 289–291:213–216
Naumov GI (1987) Genetic basis for classification and identification of the ascomycetous yeasts. Stud Mycol 30:469–475
Naumov GI (1996) Genetic identification of biological species in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex. J Ind Microbiol 17:295–302
Naumov GI (1999) Divergent population of Saccharomyces paradoxus in the Hawaii Islands: an in statu nascendi yeast species. Dokl Biol Sci (Engl Transl) 364:51–53
Naumov GI (2000) New variety Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum comb. nov. revealed by genetic analysis. Microbiology (Engl Transl) 69:338–342
Naumov GI, Kondratieva VI, Naumova TI, Gudkova NK (1983) Genetic bases for classification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A study of survival of hybrid ascospores. Zh Obs Biol 44:648–660 (in Russian)
Naumov GI, Kondratieva VI, Naumova ES (1986) Methods for hybridization of homothallic yeast diplonts and haplonts. Sov Biotechnol (Engl Transl) 6:29–32
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Lantto RA, Louis EJ, Korhola M (1992) Genetic homology between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its sibling species S. paradoxus and S. bayanus: electrophoretic karyotypes. Yeast 8:599–612
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Azbukina ZM, Korhola M, Gaillardin C (1993) Genetic and karyotypic identification of Saccharomyces yeasts from Far East Asia. Cryptogam Mycol 14:85–93
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Hagler AN, Mendonзa-Hagler LC, Louis EJ (1995a) A new genetically isolated population of the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex from Brazil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 67:351–355
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Louis EJ (1995b) Two new genetically isolated populations of the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex from Japan. J Gen Appl Microbiol 41:499–505
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Sancho ED (1996) Genetic reidentification of Saccharomyces strains associated with black knot disease of trees in Ontario and Drosophila species in California. Can J Microbiol 42:335–339
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Sniegowski PD (1997) Differentiation of European and Far East Asian populations of Saccharomyces paradoxus by allozyme analysis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:341–344
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Sniegowski PD (1998) Saccharomyces paradoxus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae are associated with exudates of North American oaks. Can J Microbiol 44:1045–1050
Naumov GI, James SA, Naumova ES, Louis EJ, Roberts IN (2000) Three new species in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex: Saccharomyces cariocanus, Saccharomyces kudriavzevii and Saccharomyces mikatae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1931–1942
Naumov GI, Gazdiev DO, Naumova ES (2003) The finding of the yeast species Saccharomyces bayanus in Far East Asia. Microbiology (Engl Transl) 72:738–743
Naumov GI, Serpova EV, Naumova ES (2006) A genetically isolated population of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Malaysia. Microbiology (Engl Transl) 75:201–205
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Masneuf-Pomarède I (2010) Genetic identification of new biological species Saccharomyces arboricolus Wang et Bai. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 98:1–7
Naumova ES, Naumov GI, Molina FI (2000) Genetic variation among European strains of Saccharomyces paradoxus: results from DNA fingerprinting. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:86–92
Naumova ES, Naumov GI, Masneuf-Pomarède I, Aigle M, Dubourdieu D (2005) Molecular genetic study of introgression between Saccharomyces bayanus and S. cerevisiae. Yeast 22:1099–1115
Naumova ES, Naumov GI, Michailova YuV, Martynenko NN, Masneuf-Pomarède I (2011) Genetic diversity study of the yeast Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum reveals introgressed subtelomeric Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes. Res Microbiol 162(2):204–213
Nguyen H-V, Gaillardin C (2005) Evolutionary relationships between the former species Saccharomyces uvarum and the hybrids Saccharomyces bayanus and Saccharomyces pastorianus; reinstatement of Saccharomyces uvarum (Beijerinck) as a distinct species. FEMS Yeast Res 5:471–483
Nguyen H-V, Lepingle A, Gaillardin C (2000) Molecular typing demonstrates homogeneity of Saccharomyces uvarum strains and reveals the existence of hybrids between S. uvarum and S. cerevisiae, including the S. bayanus type strain CBS 380. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:71–85
Nguyen H-V, Legras JL, Neuvéglise C, Gaillardin C (2011) Deciphering the hybridisation history leading to the lager lineage based on the mosaic genomes of Saccharomyces bayanus strains NBRC 1948 and CBS 380T. PLoS One 6(10):e25821
Pulvirenti A, Nguyen H, Caggia C, Giudici P, Rainieri S, Zambonelli C (2000) Saccharomyces uvarum, a proper species within Saccharomyces sensu stricto. FEMS Microbiol Lett 192:191–196
Replansky T, Koufopanou V, Greig D, Bell G (2008) Saccharomyces sensu stricto as a model system for evolution and ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 23:494–501
Reuter M, Bell G, Greig D (2007) Increased outbreeding in yeast in response to dispersal by an insect vector. Curr Biol 17:R81–R83
Sampaio JP, Gonçalves P (2008) Natural populations of Saccharomyces kudriavzevii in Portugal are associated with oak bark and are sympatric with S. cerevisiae and S. paradoxus. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2144–2152
Schacherer J, Shapiro JA, Ruderfer DM, Kruglyak L (2009) Comprehensive polymorphism survey elucidates population structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 458:342–346
Scheda R, Yarrow D (1968) Variation in the fermentative pattern of some Saccharomyces species. Arch Mikrobiol 61:310–316
Sherman F (1991) Getting started with yeast. In: Guthrie Ch, Fink GR (eds) Guide to yeast genetics and molecular biology. Academic press, New York, pp 3–21
Sikorski RS, Boeke JD (1991) In vitro mutagenesis and plasmid shuffling: from cloned gene to mutant yeast. In: Guthrie Ch, Fink GR (eds) Guide to yeast genetics and molecular biology. Academic press, New York, pp 302–318
Sniegowski PD, Dombrovski PD, Fingerman E (2002) Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces paradoxus coexist in a natural woodland site in North America and display different levels of reproductive isolation from European conspecifics. FEMS Yeast Res 1:299–306
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Vaughan-Martini A (1989) Saccharomyces paradoxus comb. nov., a newly separated species of the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex based upon nDNA/nDNA homologies. Syst Appl Microbiol 12:179–182
Vaughan-Martini A, Kurtzman CP (1985) Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among species of the genus Saccharomyces sensu stricto. Int J Syst Bacteriol 35:508–511
Vaughan-Martini A, Martini A (1987) Three newly delimited species of Saccharomyces sensu stricto. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 53:77–84
Vaughan-Martini A, Martini A (2011) Saccharomyces Meyen ex Reess (1870). In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts a taxonomic study. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 733–746
Vavilov NI (1992) Origin and geography of cultivated plants. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wang SA, Bai FY (2008) Saccharomyces arboricolus sp. nov., a yeast species from tree bark. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:510–514
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank J.P. Sampaio for kindly supplying Portuguese strains of S. kudriavzevii. This work was supported by a Russian-Taiwanese joint grant from Russian Foundation for Basic Research, Russia (No. 10-04-92008) and the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC 99-2923-B-134-001-MY3). Synthesis of oligonucleotide primers and sequencing of the D1/D2 and ITS1 rDNA fragments were performed using the equipment of the Centre for Collective Use of GosNIIgenetika, having partial financial support from the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (State Contract no. 16.552.11.7029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naumov, G.I., Lee, CF. & Naumova, E.S. Molecular genetic diversity of the Saccharomyces yeasts in Taiwan: Saccharomyces arboricola, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces kudriavzevii . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103, 217–228 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9803-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9803-2