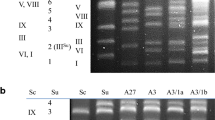
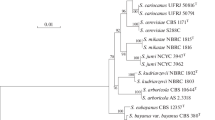
Abstract
Direct genetic testing for hybrid sterility unambiguously showed that the newly described yeast Saccharomyces arboricolus Wang et Bai is reproductively isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Saccharomyces bayanus, Saccharomyces cariocanus, Saccharomyces kudriavzevii, Saccharomyces mikatae and Saccharomyces paradoxus and, therefore, represents a new biological species of the genus Saccharomyces. Combined phylogenetic analysis of the rDNA repeat sequences (18S, 26S, ITS), nuclear ACT1 and mitochondrial ATP9 genes revealed that S. arboricolus, along with S. kudriavzevii and S. bayanus, is distantly related to the other four biological species.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belloch C, Pérez-Torrado R, Gonzáles SS, Pérez-Ortin JE, Garcia-Martinez J, Querol A, Barrio E (2009) Chimeric genomes of natural hybrids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces kudriavzevii. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2534–2544
Boekhout T, Theelen B, Diaz M, Fell JW, Hop WCJ, Abeln ECA, Dromer F, Meyer W (2001) Hybrid genotypes in the pathogenic yeast Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiology 147:891–907
Bradbury J, Richards K, Niederer H, Lee S, Rod Dunbar P, Gardner R (2006) A homozygous diploid subset of commercial wine yeast strains. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 89:27–37
Cliften P, Sudarsanam P, Desikan A, Fulton L, Fulton B, Majors J, Waterston R, Cohen BA, Johnston M (2003) Finding functional features in Saccharomyces genomes by phylogenetic footprinting. Science 301:71–76
Daniel HM, Sorrel TC, Meyer W (2001) Partial sequence analysis of the actin gene and its potential for studying the phylogeny of Candida species and their teleomorphs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1593–1606
Dujon B, Sherman D, Fischer G et al (2004) Genome evolution in yeasts. Nature 430:35–44
Dunn B, Sherlock G (2008) Reconstruction of the genome origins and evolution of the hybrid lager yeast Saccharomyces pastorianus. Genome Res 18:1610–1623
Gonzáles SS, Barrio E, Gafner J, Querol A (2006) Natural hybrids from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Saccharomyces bayanus and Saccharomyces kudriavzevii in wine fermentations. FEMS Yeast Res 6:1221–1234
Gonzáles SS, Barrio E, Querol A (2008) Molecular characterization of new natural hybrids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and S. kudriavzevii in brewing. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2314–2320
Gordon JL, Wolfe KH (2008) Recent allopolyploid origin of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii strain ATCC 42981. Yeast 25:449–456
Groth G, Hansen J, Piŝkur J (1999) A natural chimeric yeast containing genetic material from three species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1933–1938
James SA, Collins MD, Roberts IN (2001) Phylogenetic analysis of the psychrophobic yeast Arxiozyma telluris and the reinstatement of Candida pintolopesii (van Uden) Meyer et Yarrow and Candida slooffii van Uden et do Carmo Sousa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1917–1925
James SA, Bond CJ, Stratford M, Roberts IN (2005) Molecular evidence for the existence of natural hybrids in the genus Zygosaccharomyces. FEMS Yeast Res 5:747–755
Kellis M, Patterson N, Endrizzi M, Birren B, Lander ES (2003) Sequencing and comparison of yeast species to identify genes and regulatory elements. Nature 423:241–254
Kellis M, Birren BW, Lander ES (2004) Proof and evolutionary analysis of ancient genome duplication in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 428:617–624
Kielland-Brandt CM, Nillson-Tillgren T, Gjermansen C, Hollenberg S, Pedersen MB (1995) Genetics of brewing yeasts. In: Rose AH, Wheals A, Harrison JS (eds) The yeasts, vol 6. Academic Press, London, pp 223–254
Koch MA, Dobeš C, Mitchell-Olds T (2003) Multiple hybrid formation in natural populations: concerted evolution of internal transcribed spacer of nuclear ribosomal DNA (ITS) in North American Arabis divaricarpa (Brassicaceae). Mol Biol Evol 20:338–350
Kodama Y, Kielland-Brandt MC, Hansen J (2005) Lager brewing yeast. In: Sunnerhagen P, Piškur J (eds) Comparative genomics: using fungi as models. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 145–164
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Kurtzman CP (2003) Phylogenetic circumscription of Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces and other members of the Saccharomycetaceae, and the proposal of the new genera Lachancea, Nakaseomyces, Naumovia, Vanderwaltozyma and Zygotorulaspora. FEMS Yeast Res 4:233–245
Lachance MA, Daniel HM, Meyer W, Prasad GS, Gautam SP, Boundy-Mills K (2003) The D1/D2 domain of the large-subunit rDNA of the yeast species Clavispora lusitaniae is unusually polymorphic. FEMS Yeast Res 4:253–258
Le Jeune C, Lollier M, Demuyter C, Erny C, Legras JL, Aigle M, Masneuf-Pomarède I (2007) Characterization of natural hybrids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum. FEMS Yeast Res 7:540–549
Liti G, David B, Barton H, Louis EJ (2006) Sequence diversity, reproductive isolation and species concepts in Saccharomyces. Genetics 174:839–850
Liti G, Carter DM, Moses AM et al (2009) Population genomics of domestic and wild yeasts. Nature 458(7236):337–341
Masneuf I, Hansen J, Groth C, Piŝkur J, Dubourdieu D (1998) New hybrids between Saccharomyces sensu stricto yeast species found among wine and cider production strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3887–3892
Mayr E (1942) Systematics and the origin of species. Columbia University Press, NY
Montrocher R, Verner M-C, Briolay J, Gautier C, Marmeisse R (1998) Phylogenetic analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae group based on polumorphisms of rDNA spacer sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:295–303
Mortimer R, Contopoulou R (1991) Yeast genetic stock center catalogue, 7th edn. Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Division of Genetics, University of California at Berkeley, Berkeley, 107 pp
Muller LAH, McCusker JH (2009) A multispecies-based taxonomic microarray reveals interspecies hybridization and introgression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 9:143–152
Naumov GI (1987) Genetic basis for classification and identification of the ascomycetous yeasts. Stud Mycol 30:469–475
Naumov GI (1996) Genetic identification of biological species in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex. J Ind Microbiol 17:295–302
Naumov GI (2000) New variety Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum comb. nov. revealed by genetic analysis. Microbiology (Engl Transl) 69:338–342
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Lantto RA, Louis EJ, Korhola M (1992) Genetic homology between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its sibling species S. paradoxus and S. bayanus: electrophoretic karyotypes. Yeast 8:599–612
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Hagler AN, Mendonça-Hagler LC, Louis EJ (1995a) A new genetically isolated population of the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex from Brazil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 67:351–355
Naumov GI, Naumova ES, Louis EJ (1995b) Two new genetically isolated populations of the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex from Japan. J Gen Appl Microbiol 41:499–505
Naumov GI, James SA, Naumova ES, Louis EJ, Roberts IN (2000) Three new species in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex: Saccharomyces cariocanus, Saccharomyces kudriavzevii and Saccharomyces mikatae. Int J Syst Evol Microb 50:1931–1942
Naumova ES, Naumov GI, Masneuf-Pomarede I, Aigle M, Dubourdieu D (2005) Molecular genetic study of introgression between Saccharomyces bayanus and S. cerevisiae. Yeast 22:1099–1115
Nguyen H-V, Gaillardin C (2005) Evolutionary relationships between the former species Saccharomyces uvarum and the hybrids Saccharomyces bayanus and Saccharomyces pastorianus; reinstatement of Saccharomyces uvarum (Beijerinck) as a distinct species. FEMS Yeast Res 5:471–483
Nguyen H-V, Lepingle A, Gaillardin C (2000) Molecular typing demonstrates homogeneity of Saccharomyces uvarum strains and reveals the existence of hybrids between S. uvarum and S. cerevisiae, including the S. bayanus type strain CBS 380. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:71–85
Pulvirenti A, Nguyen H, Caggia C, Giudici P, Rainieri S, Zambonelli C (2000) Saccharomyces uvarum, a proper species within Saccharomyces sensu stricto. FEMS Microbiol Lett 192:191–196
Rokas A, Williams BL, King N, Carroll SB (2003) Genome-scale approaches to resolving incongruence in molecular phylogenies. Nature 425:798–804
Scannelll DR, Butler G, Wolfe KH (2007) Yeast genome evolution—the origin of the species. Yeast 24:929–942
Sherman F (1991) Getting started with yeast. In: Guthrie Ch, And Fink GR (eds) Guide to yeast genetics and molecular biology. Academic press, New York, pp 3–21
Sikorski RS, Boeke JD (1991) In vitro mutagenesis and plasmid shuffling: from cloned gene to mutant yeast. In: Guthrie Ch, And Fink GR (eds) Guide to yeast genetics and molecular biology. Academic press, New York, pp 302–318
Smart K (2007) Brewing yeast genomes and genome-wide expression and proteome profiling during fermentation. Yeast 24:993–1013
Spirek M, Yang Jun, Groth C, Petersen RF, Langkjaer RB, Naumova ES, Sulo P, Naumov GI, Piškur J (2003) High-rate evolution of Saccharomyces sensu lato chromosomes. FEMS Yeast Res 3:363–373
Vaughan-Martini A, Kurtzman CP (1985) Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among species of the genus Saccharomyces sensu stricto. Int J Syst Bacteriol 35:508–511
Vaughan-Martini A, Martini A (1987) Three newly delimited species of Saccharomyces sensu stricto. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 53:77–84
Wang SA, Bai FY (2008) Saccharomyces arboricolus sp. nov., a yeast species from tree bark. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:510–514
Watanabe T, Murata Y, Oka S, Iwahashi H (2004) A new approach to species determination for yeast strains: DNA microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization using a yeast DNA microarray with 6000 genes. Yeast 21:351–365
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Fen-Yang Bai for kindly supplying yeast strains. G.I.N. and E.S.N. were supported by ISVV-ENITA Grants (France) and in part by a grant from the Russian Fund for Basic Research (No. 09-04-00664).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naumov, G.I., Naumova, E.S. & Masneuf-Pomarède, I. Genetic identification of new biological species Saccharomyces arboricolus Wang et Bai. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 98, 1–7 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9441-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9441-5