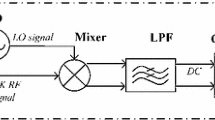
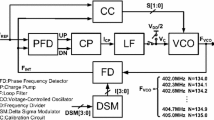
Abstract
This paper reports a low-voltage low-power injection-locked oscillator suitable for short range wireless transmitter applications in a wireless body area network (WBAN). Low-power transmitter with high efficiency is a major design challenge for short range wireless communication. Unlike conventional transmitters used for cellular communication, injection-locked transmitter shows reduced power consumption and high transmitter efficiency. The core block of an injection-locked transmitter is an injection-locked oscillator. In this work a low-voltage low-power injection-locked LC oscillator has been designed and fabricated employing self-cascode structure and body-terminal coupling. The proposed oscillator has been realized using 0.18-μm RF CMOS process. Experimental results indicate that the prototype oscillator can operate with a supply voltage as low as 0.9 V and consumes only 1.4 mW of power. The relatively low-voltage and low-power operation of the design makes it highly suitable for low-power transmitter applications.
















Similar content being viewed by others

References
Dupire, T., Tanguay, L. F., & Sawan, M. (2006). Low power CMOS transmitter for biomedical sensing devices. 13th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (pp. 339–342).
Chee, Y. H., Niknejad, A. M., & Rabaey, J. M. (2006). An ultra-low-power injection-locked transmitter for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 41(8), 1740–1748.
Porret, A.-S., Melly, T., Vittoz, E. A., & Enz, C. C. (2000). Tradeoffs and design of an ultra low power UHF transceiver in a standard digital CMOS process. Proceedings of the 2000 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (pp. 273–278), Rapallo, Italy.
Choi, P., Park, H., Nam, L., Kang, K., Ku, Y., Shin, S., Park, S., Kim, T., Choi, H., Kim, S., Min, S., Kim, M., Park, S., & Lee, K. (2003). An experimental coin-sized radio for extremely low power WPAN (IEEE 802.15.4) application at 2.4 GHz. Digest of Technical Papers, 2003 International Solid State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) (pp. 92–93).
Molnar, A. et al. (2004). An ultra-low power 900 MHz RF transceiver for wireless sensor networks. IEEE CICC (pp. 401–404).
Tanguay, L.-F., & Sawan, M. (2009). An ultra-low power ISM-band integer-N frequency synthesizer dedicated to implantable medical Microsystems. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 58, 205–214.
Hajimiri, A., & Lee, T. H. (1999). The design of low noise oscillators. Norwell, MA: Kluwer.
Rofougaran, A., Chang, G., Rael, J. J., Chang, Y.-C., Rofougaran, M., Chang, P. J., et al. (1998). A single-chip 900 MHz spread-spectrum wireless transceiver in 1 μm CMOS—part I: architecture and transmitter design. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 33, 515–534.
Tiebout, M. (2001). Low power low phase noise differentially tuned quadrature VCO design in standard CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 36, 1018–1024.
Andreani, P., Bonfanti, A., Romano, L., & Samori, C. (2002). Analysis and design of a 1.8 GHz CMOS LC quadrature VCO. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 37, 1737–1747.
Kim, H.-R., Cha, C.-Y., Oh, S.-M., Yang, M.-S., & Lee, S.-G. (2004). A very low-power quadrature VCO with back-gate coupling. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 39(6), 952–955.
Thierry, T., Jean-Baptiste, B., Hervé, L., & Yann, D. (2006). RF CMOS body-effect circuits. Microelectronics Journal, 37(11), 1251–1260.
Ahmed, H., De Vries, C., & Mason, R. (2003). A Digitally Tuned 1.1 GHz Subharmonic Injection-Locked VCO in 0.18 μm CMOS. Proceedings of the 29th European Solid-State Circuit Conference (pp. 81–84).
Hsieh, H.-H., & Lu, L.-H. (2006). A low-phase-noise K-band CMOS VCO. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 10(10), 552–554.
Li, X., Shekhar, S., & Allstot, D. (2005). Gm-boosted common gate LNA and differential Colpitts VCO/QVCO in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 40(12), 2609–2619.
Wang, T.-P., Chang, C.-C., Liu, R.-C., Tsai, M.-D., Sun, K.-J., Chang, Y.-T., et al. (2006). A low-power oscillator mixer in 0.18-μm CMOS Technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(1), 88–95.
Deen, M. J., Murji, R., Fakhr, A., Jafferali, N., & Ngan, W. L. (2005). Low-power CMOS integrated circuits for radio frequency applications. IEEE Proceedings of Circuits Devices Systems, 152(5), 509–521.
Lee, C.-C., Chuang, H.-R., & Lu, C.-L. (2007). A 16-GHz CMOS differential Colpitts VCO for DS-UWB and 60-GHz direct conversion receiver applications. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 49(10), 2489–2491.
Hsieh, H.-H., & Lu, L.-H. (2007). A high-performance CMOS voltage controlled oscillator for ultra-low-voltage operations. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 55(3), 467–473.
Hsieh, H.-H., Chung, K.-S., & Lu, L.-H. (2005). Ultra-low-voltage mixer and VCO in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE RFIC Symposium (pp. 167–170).
Tsai, M.-D., Cho, Y.-H., & Wang, H. (2005). A 5-GHz low phase noise differential Colpitts CMOS VCO. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 15(5), 327–329.
Choi, T.-Y., Lee, H., Katehi, L. P. B., & Mohammadi, S. (2005). A low phase noise 10 GHz VCO in 0.18-μm CMOS process. 2005 European Microwave Conference (Vol. 3, pp. 4).
Mostafa, A. H., & El-Gamal, M. N. (2001). A CMOS VCO architecture for sub-1 volt high frequency (8.7–10 GHz) RF applications. 2004 International Symposium of Low Power Electronics and Design (pp. 247–250).
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge MOSIS for providing the opportunities for fabricating the integrated circuit chip under MOSIS Educational Program (MEP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haider, M.R., Islam, S.K. & Mahfouz, M.R. A low-voltage low-power injection-locked oscillator for wearable health monitoring systems. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 66, 145–154 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-010-9513-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-010-9513-5