Abstract
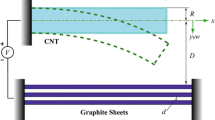
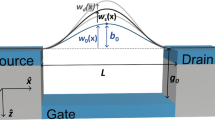
In this study, we developed a general method to analytically tackle a kind of movable boundary problem from the viewpoint of energy variation. Having grouped the adhesion of a micro-beam, droplet and carbon nanotube (CNT) ring on a substrate into one framework, we used the developed line of reasoning to investigate the adhesion behaviors of these systems. Based upon the derived governing equations and transversality conditions, explicit solutions involving the critical parameters and morphologies for the three systems are successfully obtained, and then the parameter analogies and common characteristics of them are thoroughly investigated. The presented method has been verified via the concept of energy release rate in fracture mechanics. Our analyses provide a new approach for exploring the mechanism of different systems with similarities as well as for understanding the unity of nature. The analysis results may be beneficial for the design of nano-structured materials, and hold potential for enhancing their mechanical, chemical, optical and electronic properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bico, J., Roman, B., Moulin, L., et al.: Adhesion: Elastocapillary coalescence in wet hair. Nature 432, 690 (2004)
Gao, H. J., Wang, X., Yao, H. M., et al.: Mechanics of hierarchical adhesion structure of gecko. Mechanics of Materials 37, 275–285 (2005)
Maxwell, J. C.: Capillary Action. Encyclopaedia Britannica, Vol. II. Cambridge University Press, London (1980)
Clanet, C., Quere, D.: Onset of menisci. Journal of Fluid Mechnics 460, 131–149 (2002)
Liu, J. L.: Analogies between a meniscus and a cantilever. Chinese Physics Letters 26, 116803 (2009)
Neinhuis, C., Barthlott, W.: Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Annals of Botany 79, 667–677 (1997)
Hu, D. L., Chan, B., Bush, J. W.: The hydrodynamics of water strider locomotion. Nature 424, 663–666 (2004)
Wu, C. W., Kong, X. Q., Wu, D.: Micronanostructures of the scales on a mosquito’s legs and their role in support. Physical Review E 76, 017301 (2007)
Mlot, N. J., Tovey, C. A., Hu, D. L.: Fire ants self-assemble into waterproof rafts to survive floods. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108, 7669–7673 (2011)
Parker, A. R., Lawrence, C. R.: Water capture by a desert beetle. Nature 414, 33–34 (2001)
Wenzel, R. N.: Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry 28, 988–994 (1936)
Cassie, A. B. D., Baxter, S.: Wettability of porous surfaces. Transactions of Faraday Society 40, 546–551 (1944)
Liu, J. L., Mei, Y., Xia, R.: A new wetting mechanism based upon triple contact line pinning. Langmuir 27, 196–200 (2011)
Bormasshenko, E., Whyman, G.: Variational approach to wetting problems: calculation of a shape of sessile liquid drop deposited on a solid substrate in external field. Chemical Physics Letters 463, 103–105 (2008)
Marmur, A.: Contact angles in constrained wetting. Langmuir 12, 5704–5708 (1996)
Swain, P. S., Lipowsky, R.: Contact angles on heterogeneous surfaces: a new look at Cassie’s and Wenzels laws. Langmuir 14, 6772–6780 (1998)
Hui, C. Y., Jagota, A., Lin, Y. Y., et al.: Constaints on microcontact printing imposed by stamp formation. Langmuir 18, 1394–1407 (2002)
De Boer, M. P., Michalske, T. A.: Accurate method for determining adhesion of cantilever beams. Journal of Applied Physics 86, 817–827 (1999)
Mastrangelo, C. H., Hsu, C. H.: Mechanical stability and adhesion of microstructures under capillary forces, part II: Experiments. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 2, 44–55 (1993)
Liu, J. L.: Theoretical analysis on capillary adhesion of microsized plates with a substrate. Acta Mechanica Sinica 26, 217–223 (2010)
Zhao, Y. P., Wang, L. S., Yu, T. X.: Mechanics of adhesion in MEMS: A review. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 17, 519–546 (2003)
Wang, Z. L., Song, J. H.: Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on Zinc Oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312, 242–246 (2006)
Baughman, R. H., Zakhidov, A. A., de Heer, W. A.: Carbon nanotubes: The route toward applications. Science 297, 787–792 (2002)
Zheng, M., Ke, C. H.: Mechanical deformation of carbon nanotube nano-rings on flat substrate. Journal of Applied Physics 109, 074304 (2011)
Hertel, T., Walkup, R. E., Avouris, P.: Deformation of carbon nanotubes by surface van der Waals forces. Physical Review B 58, 13870–13873 (1998)
Pantano, A., Parks, D. M., Boyce, M. C.: Mechanics of deformation of single- and multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 52, 789–821 (2004)
Pugno, N. M.: An analogy between the adhesion of liquid drops and single walled nanotubes. Scripta Materialia 58, 73–75 (2008)
Roman, B., Gay, C., Clanet, C.: Pendulum, drops and rods: A physical analogy. http://www.pmmh.espci.fr/benoit/publi.html
Majidi, C.: Remarks on formulating an adhesion problem using Euler’s elastica (draft). Mechanics Research Communications 34, 85–90 (2006)
Roman, B., Bico, J.: Elasto-capillarity: deforming an elastic structure with a liquid drop. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 22, 493101 (2010)
Rice, J. R.: A path independent integral and the approximate analysis of strain concentration. Journal of Applied Mechanics 35, 379–386 (1968)
Tang, T., Jagota, A., Hui, C. Y.: Adhesion between singlewalled carbon nanotubes. Journal of Applied Physics 97, 074304 (2005)
Zhou, W., Huang, Y., Liu, B., et al.: Self-folding of singleand multiwall carbon nanotubes. Applied Physics Letters 90, 073107 (2007)
Seifert, U.: Adhesion of vesicles in two dimensions. Physical Review A 43, 6803–6814 (1991)
Oyharcabal, X., Frisch, T.: Peeling off an elastica from a smooth attractive substrate. Physical Review E 71, 036611 (2005)
Makowski, J. D., Gawarikar, A. S., Talghader, J. J.: Adhesion energy in nanogap InP/InGaAs microcantilevers. Applied Physics Letters 89, 243508 (2006)
Tang, T., Glassmaker, N. J.: On the Inextensible ElasticaModel for the Collapse of Nanotubes. Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids 15, 591–606 (2010)
Liu, B., Yu, M. F., Huang, Y.: Role of lattice registry in the full collapse and twist formation of carbon nanotubes. Physical Review B 70, 161402 (2004)
Tang, T., Jagota, A., Hui, C. Y., et al.: Collapse of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Journal of Applied Physics 97, 074310 (2005)
Buehler, M. J., Kong, Y., Gao, H., et al.: Self-folding and unfolding of carbon nanotubes. Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology 128, 3–10 (2006)
Mikata, Y.: Approximate solutions for a self-folding problem of carbon nanotubes. Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology 132, 011013 (2010)
Glassmaker, N. J., Hui, C. Y.: Elastica solution for a nanotube formed by self-adhesion of a folded thin film. Journal of Applied Physics 96, 3429–3444 (2004)
Bishopp, K. E., Drucker, D. C.: Large deflection of cantilever beams. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics 3, 272–275 (1945)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11272357 and 11102140), Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (200804251520 and 20110141120024) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2009AQ006).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JL., Xia, R. A unified analysis of a micro-beam, droplet and CNT ring adhered on a substrate: Calculation of variation with movable boundaries. Acta Mech Sin 29, 62–72 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0202-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0202-8