Abstract
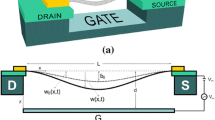
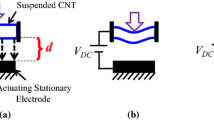
The tip charge concentration and rippling phenomenon can substantially affect the electromechanical performance of actuators fabricated from cantilever carbon nanotube (CNT). However, these important phenomena are often ignored in the theoretical beam models. In this article, the influence of rippling deformation, Casimir attraction and tip concentration charge on the dynamic pull-in characteristics of nanotube actuators is investigated using a modified Euler–Bernoulli beam theory. To express the Casimir attraction of cylinder-plate geometry, two approaches e.g. proximity force approximation (PFA) for small separations and Drichlet asymptotic approximation for large separations are considered. The charge concentration at the CNT tip is included in the governing equation using Dirac delta function. It is demonstrated that the rippling deformation and tip charge concentration can substantially decrease the dynamic pull-in voltage of the nano-actuator. The rippling deformation of CNT increases the pull-in time while the concentrated charge at the CNT end reduces the pull-in time of the nano-system. Results of the present study are beneficial to precise design and fabrication of electromechanical CNT actuators. Comparison between the obtained results and those reported in the literature by experiments and molecular dynamics, verifies the integrity of the present analysis.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasnejad B, Rezazadeh G, Shabani R (2013) Stability analysis of a capacitive fgm micro-beam using modified couple stress theory. Acta Mech Solida Sin 26(4):427–440
Arroyo M, Belytschko T (2003) Nonlinear mechanical response and rippling of thick multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 91:215505
Bordag M, Mohideen U, Mostepanenko VM (2001a) New developments in the Casimir effect. Phys Rep 353:1–205
Bordag M, Mohideen U, Mostepanenko VM (2001b) New developments in the Casimir effect. Phys Rep 353:1
Bulgac A, Magierski P, Wirzba A (2006) Scalar Casimir effect between Dirichlet spheres or a plate and a sphere. Phys Rev D 73:025007
Buscher R, Emig T (2005) Geometry and spectrum of Casimir forces. Phys Rev Lett 94:133901
Casimir HBG (1948) On the attraction between two perfectly conducting plates. Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen 51:793
Casimir HBG, Polder D (1948) The influence of retardation of the London-van der Waals forces. Phys Rev Lett 73:360
Chan HB, Bao Y, Zou J, Cirelli RA, Klemens F, Mansfield WM, Pai CS (2008) measurements of the Casimir force between a gold sphere and a silicon surface with nanoscale v trench arrays. Phys Rev Lett 101:030401
Dequesnes M, Rotkin SV, Aluru NR (2002) Parameterization of continuum theories for single wall carbon nanotube switches by molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Electron 1(3):313–316
Dequesnes M, Tang Z, Aluru NR (2004) Static and dynamic analysis of carbon nanotube-based switches. J Eng Mater Technol 126(3):230–237
Desquenes M, Rotkin SV, Alaru NR (2002) Calculation of pull-in voltages for carbonnanotube based nanoelectromechanical switches. Nanotechnology 13:120–131
Emig T, Jaffe RL, Kardar M, Scardicchio A (2006) Casimir interaction between a plate and a cylinder. Phys Rev Lett 96:080403
Farrokhabadi A, Koochi A, Abadyan M (2014a) Modeling the instability of CNT tweezers using a continuum model. Microsyst Technol 20(2):291–302
Farrokhabadi A, Abadian N, Rach R, Abadyan M (2014b) Theoretical modelling of the Casimir force-induced instability in freestanding nanowires with circular cross-section. Physica E 63:67–80
Guo JG, Zhao YP (2004) Influence of van der Waals and Casimir forces on electrostatic torsional actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 13(6):1027
Gupta SS, Batra RC (2008) Continuum structures equivalent in normal mode vibrations to single-walled carbon nanotubes. Comput Mater Sci 43(4):715–723
Hayt WH, Buck JA (2001) Engineering electromagnetic, 6th edn. McGrawHill, New York
Hwang HJ, Kang JW (2005) Carbon-nanotube-based nanoelectromechanical switch. Physica E 27:163–175
Jackson JD (1975) Classical Electrodynamics. Wiley, New York
Kang JW, Kong SC, Hwang HJ (2006) Electromechanical analysis of suspended carbon nanotubes for memory applications. Nanotechnology 17:2127–2134
Ke C, Espinosa HD (2005) Numerical analysis of nanotube-based NEMS devices-part I: electrostatic charge distribution on multiwalled nanotubes. J Appl Mech 72(5):726–731
Ke C-H, Pugno N, Peng B, Espinosa HD (2005) Experiments and modeling of carbon nanotube-based NEMS devices. J Mech Phys Solids 53:1314–1333
Keblinski P, Nayak SK, Zapol P, Ajayan PM (2002) Charge distribution and stability of charged carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 89(25):255503
Koochi A, Fazli N, Rach R, Abadynan M (2014) Modeling the pull-in instability of the CNT-based probe/actuator under the Coulomb force and the van der Waals attraction. Latin Am J Solids Struct 11(8):1315–1328
Lamoreaux SK (2005) The Casimir force: background, experiments, and applications. Rep Prog Phys 68:201–236
Li C, Chou TW (2004) Mass detection using carbon nanotube-based nanomechanical resonators. Appl Phys Lett 84:5246
Li H, Kardar M (1998) Fluctuation-induced forces between rough surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 67:3275
Li C, Thostenson ET, Chou TW (2008) Sensors and actuators based on carbotn nanotubes and their composites: a review. Comp Sci Technol 68:1227–1249
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2005) Nonlinear behavior for nanoscales electrostatic actuators with Casimir force. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 23:1777
Loh OY, Espinosa HD (2012) Nanoelectromechanical contact switches. Nat Nanotechnol 7:283–295
Lombardo FC, Mazzitelli FD, Villar PI (2008) Numerical evaluation of the Casimir interaction between cylinders. Phys Rev D 78:085009
Mahar B, Laslau C, Yip R, Sun Y (2007) Development of carbon nanotube-based sensors-a review. IEEE Sens J 7(2):266–284
Mehdipour I, Barari A, Ganji DD (2012) Effects of rippling deformation and mid-plane stretching on non-linear vibration for embedded carbon nanotube. Int J Multiscale Comput Eng 10(3):295–305
Nakayama Y (2002) Scanning probe microscopy installed with nanotube probes and nanotube tweezers. Ultramicroscopy 91(1–4):49–56
Ouakad HM, Younis MI (2008) Nonlinear dynamics of electrically actuated carbon nanotube resonators. J Comput Nonlinear Dyn 5(1):011009
Rahi SJ, Emig T, Jaffe RL, Kardar M (2008) Casimir forces between cylinders and plates. Phys Rev A 78:012104
Sears A, Batra RC (2006) Buckling of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under axial compression. Phys Rev B 73:085410
Sedighi HM, Daneshmand F (2014) Static and dynamic pull-in instability of multi-walled carbon nanotube probes by He’s iteration perturbation method. J Mech Sci Technol 28(9):3459–3469
Soltani P, Ganji DD, Mehdipour I, Farshidianfar A (2012) Nonlinear vibration and rippling instability for embedded carbon nanotubes. J Mech Sci Technol 26(4):985–992
Teo LP (2011a) First analytic correction to the proximity force approximation in the Casimir effect between two parallel cylinders. Phys Rev D 84:065027
Teo LP (2011b) Casimir, interaction between a cylinder and a plate at finite temperature: exact results and comparison to proximity force approximation. Phys Rev D 84:025022
Wang Z (2009) Effects of substrate and electric fields on charges in carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev B 79:155407
Wang XY, Wang X (2004) Numerical simulation for bending modulus of carbon nanotubes and some explanations for experiment. Comp Part B 35:79–86
Wang X, Wang XY, Xiao J (2005) A non-linear analysis of the bending modulus of carbon nanotubes with rippling deformations. Compos Struct 69:315–321
Zou J, Marcet Z, Rodriguez AW, Reid MTH, McCauley AP, Kravchenko II, Lu T, Bao Y, Johnson SG, Chan HB (2013) Casimir forces on a silicon micromechanical chip. Nature Commun 4:1845
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sedighi, H.M., Farjam, N. A modified model for dynamic instability of CNT based actuators by considering rippling deformation, tip-charge concentration and Casimir attraction. Microsyst Technol 23, 2175–2191 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2956-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2956-6