Abstract
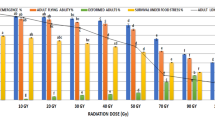
Tuta absoluta is a key pest of tomato crops originating from South America. The consequences of X-radiation on this species were studied under laboratory controlled conditions. The effect of radiation on adult emergence was evaluated exposing male and female pupae to increasing X-rays. Adult emergence decreased as doses of X-radiation increased, with the appearance of deformities such as malformed wings and bent legs at doses ≥350 Gy. Besides, males and females obtained from irradiated pupae were out crossed with untreated counterparts to explore the effects of X-radiation on inherited sterility. (a) Irradiated male × untreated female crosses. Both fecundity and fertility of the untreated females were reduced by radiation, and the effect was stronger as the doses increased. Neither the longevity of parental males and F1 adults nor the sex ratios of the F1 and F2 generations were affected by X-radiation (F1 and F2: first and second generation of descendants of irradiated adults). Inherited sterility effects were manifested by a significant reduction in the F1 fecundity, F1 fertility, and the amount of larvae and pupae produced. Doses of 200–250 Gy could be used to induce inherited sterility in T. absoluta males. (b) Untreated male × irradiated female crosses. The minimum dose at which irradiated females were completely sterile was 200 Gy. The present study is the first study in T. absoluta that provides the starting point for implementing the inherited sterility in this species.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
Agresti A (1996) An introduction to categorical data analysis. Wiley & Sons, Inc, University of Florida, USA
Arthur V (2004) Use of gamma radiation to control three Lepidopteran pests in Brazil. Irradiation as a phytosanitary treatment of food and agricultural commodities. In: Proceedings of the final research coordination meeting organized by the joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture, 2002, Vienna, Austria, pp 45–50
Ayvaz A, Albayrak S, Tunçbilek AS (2007) Inherited sterility in Mediterranean flour moth Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): effect of gamma radiation on insect fecundity, fertility and developmental period. J Stored Prod Res 43:234–239
Bakri A, Mehta K, Lance DR (2005) Sterilizing insects with ionizing radiation. In: Dyck VA, Hendrichs J, Robinson AS (eds) Sterile insect technique. Principles and practice in area-wide integrated pest management. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 233–268
Bloem S, Carpenter JE (2001) Evaluation of population suppression by irradiated Lepidoptera and their progeny. Fla Entomol 84:165–170
Bloem S, Bloem KA, Carpenter JE, Calkins CO (1999) Inherited sterility in codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): effect of substerilizing doses of radiation on insect fecundity, fertility and control. Ann Entomol Soc Am 92:222–229
Bloem S, Bloem KA, Carpenter JE, Calkins CO (2001) Season-long releases of partially sterile males for control of codling moth, Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), in Washington apples. Environ Entomol 30:763–769
Bloem S, Carpenter JE, Hofmeyr JH (2003) Radiation biology and inherited Sterility in false codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J Econ Entomol 96:1724–1731
Boshra SA (2007) Effect of high-temperature pre irradiation on reproduction and mating competitiveness of male Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) and their F1 progeny. J Stored Prod Res 43:73–78
Botto EN, Ceriani SA, López SN, Saini ED, Cedola CV, Segade G, Viscarret M (2000) Control biológico de plagas hortícolas en ambientes protegidos. La experiencia Argentina hasta el presente. RIA 29:83–98
Carpenter JE, Gross HR (1993) Suppression of feral Heliothis zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations following the infusion of inherited sterility from released substerile males. Environ Entomol 22:1084–1091
Carpenter JE, Young JR, Sparks AN (1986) Fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): comparison of inherited deleterious effects in progeny from irradiated males and females. J Econ Entomol 79:47–49
Carpenter JE, Young JR, Sparks AN, Cromroy HL, Chowdhury MA (1987) Corn earworn (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): effects off substerilizing doses of radiation and inherited sterility on reproduction. J Econ Entomol 80:483–489
Carpenter JE, Bloem S, Bloem KA (2001) Inherited sterility in Cactoblastis cactorum (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Fla Entomol 84:537–542
Carpenter JE, Bloem S, Marec F (2005) Inherited sterility in insects. In: Dyck VA, Hendrichs J, Robinson AS (eds) Sterile insect technique principles and practice in area-wide integrated pest management, Chap 2.4. Springer, Netherlands, pp 115–146
de Coelho MCF, Franca FH (1987) Biologia, quetotaxia da larva e descricao da pupa e adulto da traca-do-tomateiro. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 22:129–135
de Siqueira HA, Guedes RN, Picanço MC (2000) Insecticide resistance in populations of Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera:Gelechiidae). Agric Forest Entomol 2:147–153
Desneux N, Wajnberg E, Wyckhuys KAG, Burgio G, Arpaia S, Narváez-Vasquez CA, González-Cabrera J, Catalán Ruescas D, Tabone E, Frandon J, Pizzol J, Poncet C, Cabello T, Urbaneja A (2010) Biological invasion of European tomato crops by Tuta absoluta: ecology, geographic expansion and prospects for biological control. J Pest Sci 83:197–215
Desneux N, Luna MG, Guillemaud T, Urbaneja A (2011) The invasive South American tomato pinworm, Tuta absoluta, continues to spread in Afro-Eurasia and beyond: the new threat to tomato world production. J Pest Sci 84:403–408
Dhouibi MH, Abderahmane CT (2001) The effect of substerilizing doses of gamma radiation on the pupae of the carob moth Ectomyelois ceratoniae (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). In: Proceedings of the symposium evaluation of population, suppression by irradiated Lepidoptera and their progeny. FAO/IAEA Final Research Coordination Meeting, 28–30 May 1998. Penang, Malaysia, IAEA-D4- RC-561, pp 43–48
Haddi K, Berger M, Bielza P, Cifuentes D, Field LM, Gorman K, Rapisarda C, Williamson MS, Bass C (2012) Identification of mutations associated with pyrethroid resistance in the voltage-gated sodium channel of the tomato leaf miner (Tuta absoluta). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:1–8
Henneberry TJ, Clayton TE (1988) Effects of gamma radiation on pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) pupae: adult emergence, reproduction, mating, and longevity of emerged adults and their F1 progeny. J Econ Entomol 81:322–326
Knipling EF (1955) Possibilities in insect control or eradication through the use of sexually sterile males. J Econ Entomol 48:459–462
LaChance LE (1967) The induction of dominant lethal mutations in insects by ionizing radiation and chemicals—as related to the sterile-male technique of insect control In: Wright JW, Pal R (eds) Genetics of insect vectors of disease. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 617–650
LaChance LE (1985) Genetic methods for the control of the lepidopteran species: status and potential. U. S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC
Lietti MM, Botto E, Alsogaray RA (2005) Insecticide resistance in Argentine populations of Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae). Neotrop Entomol 34:113–119
Makee H, Saour G (1997) Inherited effects in F1 progeny of partially sterile male Pthorimaea operculella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J Econ Entomol 90:1097–1101
Makee H, Saour G (2003) Noninherited sterility in irradiated Pthorimaea operculella females. J Appl Entomol 127:489–493
Makee H, Tafesh N, Marec F (2008) Analysis of radiation-induced W chromosome aberrations in the codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.), by Xuorescence in situ hybridization techniques. J Pest Sci 81:143–151
Mansour M (2010) Effects of gamma radiation on the Mediterranean flour moth, Ephestia kuehniella, eggs and acceptability of irradiated eggs by Trichogramma cacoeciae females. J Pest Sci 83:243–249
Marec F, Kollárová I, Pavelka J (1999) Radiation- induced inherited sterility combined with a genetic sexing system in Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 92:250–259
Marec F, Tothová A, Sahara K, Traut W (2001) Meiotic pairing of sex chromosome fragments and its relation to atypical transmission of a sex-linked marker in Ephestia kuehniella (Insecta: Lepidoptera). Heredity 87:659–671
Mastrangelo T, Parker AG, Jessup A, Pereira R, Orozco-Dávila D, Islam A, Dammalage T, Walder JMM (2010) A new generation of X ray irradiators for insect sterilization. J Econ Entomol 103:85–94
Mastro VC (1993) Gypsy-moth F1 sterility program: current status. In: Proceedings of the symposium: radiation induced F1 sterility in Lepidoptera for area wide control. FAO/IAEA, 9-13 September 1991, Arizona, pp 125–129
Mehta K, Parker A (2011) Characterization and dosimetry of a practical X-ray alternative to self-shielded gamma irradiators. Radiat Phys Chem 80:107–113
Nguyen Thi QH, Nguyen Thanh TT (2001) Radiation-induced F1 sterility in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae): potential for population suppression in the field. Fla Entomol 84:199–208
North DT (1975) Inherited sterility in Lepidoptera. Annu Rev Entomol 20:167–182
North DT, Holt GG (1969) Population suppression by transmission of inherited sterility to progeny of irradiated cabbage loopers, Trichoplusia ni. Can Entomol 101:513–520
North DT, Holt GG (1971) Inherited sterility and its use in population suppression of Lepidoptera, pp 87–97. In: Proceedings of the symposium application of induced sterility for control of lepidoptera populations. FAO/IAEA, Viena, 1970
Ostergen G, Morris R, Wakoning T (1958) A study in Hyacinthus on chromosome size and breakability by X-rays. Hereditas 44:1–17
Pereyra PC, Sánchez NE (2006) Effect of two Solanaceous plants on developmental and population parameters of the tomato leaf miner, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Neotrop Entomol 35:671–676
Proverbs MD (1962) Progress on the use of induced sexual sterility for the control of the codling moth Carpocapsa pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae). P Entomol Soc Ont 92:5–11
Proverbs MD, Newton JR, Logan DM (1978) Suppression of codling moth, Laspeyresia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae), by release of sterile and partially sterile moths. Can Entomol 110:1095–1102
Salazar ER, Araya JE (1997) Detección de resistencia a insecticidas en la polilla del tomate. Simiente 67:8–22
Seth RK, Sharma VP (2001) Inherited sterility by substerilizing radiation in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): bio-efficacy and potential for pest suppression. Fla Entomol 84:183–193
Sparrow AH, Sparrow RC, Thompson KH, Schairer LA (1965) The use of nuclear and chromosomal variables in determining and predicting radiosensitivities. Radiat Bot 5:101–132
StatPoint (2011) Statistical software. StatPoint Technologies, Inc., Warrenton
StatSoft (2000) Statistica for Windows. Computer program manual. StatSoft Inc., Tulsa
Suomalainen E (1969) On the sex chromosome trivalent in some Lepidoptera females. Chromosoma 28:298–308
Sutrisno S, Hoedaya MS, Sutardi D, Rahayu A (1993) Radiation induced F1 sterility in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.), and tropical armyworm, Spodoptera lituria F. In: Proceedings of the symposium Radiation induced F1 sterility in Lepidoptera for area wide control. FAO/IAEA, 9–13 September 1991, Arizona, pp 23–36
Tobías CA (1952) The dependence of some biological effects of radiation on the rate of energy loss. In: Proceedings of the symposium on radiobiology. Wiley, New York, pp 357–392
Tothová A, Marec F (2001) Chromosomal principle of radiation-induced F1 sterility in Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Genome 44:172–184
Traut W, Marec F (1997) Sex chromosome differentiation in some species of Lepidoptera (Insecta). Chromosome Res 5:283–291
Wolf KW (1996) The structure of condensed chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis of insects. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 25:37–62
Wolf KW, Novák K, Marec F (1997) Kinetic organization of metaphase I bivalents in spermatogenesis of Lepidoptera and Trichoptera species with small chromosome numbers. Heredity 79:135–143
Acknowledgments
We thank Ana María López for helpful comments on earlier version of our manuscript. We also thank Andrea Andorno and Carmen Hernández for technical support. Thanks to reviewers for their comments that helped us to improve our manuscript. This investigation received financial support from Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (Argentina) and IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by N. Desneux.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cagnotti, C.L., Viscarret, M.M., Riquelme, M.B. et al. Effects of X-rays on Tuta absoluta for use in inherited sterility programmes. J Pest Sci 85, 413–421 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-012-0455-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-012-0455-9