Abstract
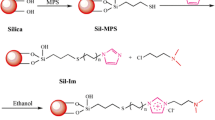
Hydrophobic selectivity is a key factor that has made C18-bonded phases the main separation materials for HPLC since its development. However, hydrophobic compounds tend to be strongly retained in these phases meaning that large amounts of organic mobile phases are required. In this work, a new stationary phase was prepared from the immobilization of poly(dimethyl-co-alkylmethylsiloxane) (PDAS) over silica particles using microwave radiation. The optimized conditions for preparation of the stationary phase used 720 W of radiation for 10 min. The chromatographic performance and methylene selectivity in the separation of hydrophobic compounds by this new Si(PDAS) phase were similar to those obtained by typical C18-bonded phases. However, the lower hydrophobicity of the organic layer in the Si(PDAS) phase resulted in separation about 40 % faster than typical C18 phases, requiring more aqueous mobile phases. The Si(PDAS) phase showed lower silanophilic activity than that of typical C18 phases due to a more effective polymeric coating of the silica surface.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirkland J (2004) J Chromatogr A 1060:9–21
Tanaka N, Nagayama H, Kobayashi H, Ikegami T, Hosoya K, Ishizuka N, Minakuchi H, Nakanishi K, Cabrera K, Lubda D (2000) J High Resolut Chromatogr 23:111–116
Qiu HD, Liang XJ, Sun M, Jiang SX (2011) Anal Bioanal Chem 399:3307–3322
Fekete S, Oláh E, Fekete J (2012) J Chromatogr A 1228:57–71
Liang XJ, Wang S, Liu SJ, Liu X, Jiang SX (2012) J Sep Sci 35:2003–2009
Schure MR, Rafferty JL, Zhang L, Siepmann JI (2013) LC-GC N Am 31:630–637
Löchmuller CH, Wilder DR (1979) J Chromatogr Sci 17:574–579
Sándi Á, Bede Á, Szepesy L, Rippel G (1997) Chromatographia 45:206–214
Strohschein S, Pursch M, Lubda D, Albert K (1988) Anal Chem 70:13–18
Buszewski B, Kowalska S, Stepnowski P (2006) J Sep Sci 29:1116–1125
Tonhi E, Collins KE, Collins CH (2006) J Chromatogr A 1119:135–139
Leo AJ (1987) J Pharmacol Sci 76:166–168
Hayward SJ, Lei YD, Wania F (2006) Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2018–2027
Faria AM, Collins CH, Jardim ICSF (2009) J Braz Chem Soc 20:1385–1398
Begnini FR, Jardim ICSF (2013) J Chromatogr A 1297:113–122
da Silva CGA, Collins CH, Lesellier E, West C (2013) J Chromatogr A 1315:176–187
Dib SR, Faria AM (2014) Chromatographia 77:533–541
Silva RB, Gushikem Y, Collins CH (2001) J Sep Sci 24:49–54
Faria AM, Collins KE, Collins CH (2007) J Chromatogr A 1156:51–59
Borges EM, Collins CH (2012) J Chromatogr A 1227:174–180
Lopes NP, Collins KE, Jardim ICSF (2004) J Chromatogr A 1030:225–229
Morais LSR, Jardim ICSF (2005) J Chromatogr A 1073:127–135
Collins CH, Silva CR, Faria AM, Collins KE, Jardim ICSF (2009) J Braz Chem Soc 20:604–612
Novais AS, Ribeiro Filho JF, Amaral EMF, Faria AM (2015) Quim Nova 38:274–279. doi:10.5935/0100-4042.20140312
Kimata K, Iwaguchi K, Onishi S, Jinno K, Eksteen R, Hosoya K, Arki M, Tanaka N (1989) J Chromatogr Sci 27:721–728
Bachmann S, Melo LFC, Silva RB, Anazawa TA, Jardim ICSF, Collins KE, Collins CH, Albert K (2001) Chem Mater 13:1874–1879
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Instituto de Química at the Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP, São Paulo, Brazil) for some spectroscopic characterizations and for the column packing. The authors thank FAPEMIG (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais) and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) for fellowships and financial support. This work is a collaboration research project of members of the Rede Mineira de Química (RQ-MG) supported by FAPEMIG (Project: CEX-RED-00010-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, G.O., da Silva, C.G.A. & Faria, A.M. A New Stationary Phase for Analysis of Hydrophobic Compounds by RP-LC. Chromatographia 79, 19–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2993-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2993-9