Abstract
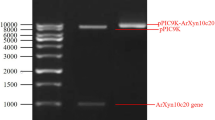
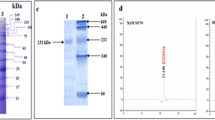
Xylanases (EC 3.2.1.8) are hydrolytic enzymes that have found widespread application in the food, feed, and paper-pulp industries. Streptomyces sp. FA1 xynA was expressed as a secreted protein in Pichia pastoris, and the xylanase was applied to the production of Chinese steamed bread for the first time. The optimal pH and the optimal temperature of XynA were 5.5 and 60 °C, respectively. Using beechwood as substrate, the K m and V max were 2.408 mg mL−1 and 299.3 µmol min−1 mg−1, respectively. Under optimal conditions, a 3.6-L bioreactor produced 1374 U mL−1 of XynA activity at a protein concentration of 6.3 g L−1 after 132 h of fermentation. Use of recombinant XynA led to a greater increase in the specific volume of the CSB than could be achieved using commercial xylanase under optimal conditions. This study provides the basis for the application of the enzyme in the baking industry.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biely P (1985) Microbial xylanolytic systems. Trends Biotechnol 3:286–290
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Celik E, Calik P (2012) Production of recombinant proteins by yeast cells. Biotechnol Adv 30:1108–1118. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.09.011
Cereghino JL, Cregg JM (2000) Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:45–66
Choi JH, Lee OS, Shin JH, Kwak YY, Kim YM, Rhee IK (2006) Thermostable xylanase encoded by xynA of Streptomyces thermocyaneoviolaceus: cloning, purification, characterization and production of xylooligosaccharides. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:57–63
Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2002) Arabinoxylans and endoxylanases in wheat flour bread-making. J Cereal Sci 35:225–243. doi:10.1006/jcrs.2001.0433
Courtin CM, Gelders GG, Delcour JA (2001) Use of two endoxylanases with different substrate selectivity for understanding arabinoxylan functionality in wheat flour breadmaking. Cereal Chem 78:564–571. doi:10.1094/Cchem.2001.78.5.564
Daly R, Hearn MT (2005) Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: a useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production. J Mol Recognit 18:119–138. doi:10.1002/jmr.687
Dornez E, Gebruers K, Cuyvers S, Delcour JA, Courtin CM (2007) Impact of wheat flour-associated endoxylanases on arabinoxylan in dough after mixing and resting. J Agric Food Chem 55:7149–7155. doi:10.1021/jf071363m
He J, Su L, Sun X, Fu J, Chen J, Wu J (2014) A novel xylanase from Streptomyces sp. FA1: purification, characterization, identification, and heterologous expression. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 19:8–17. doi:10.1007/s12257-013-0490-2
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino-acid-sequence similarities. Biochem J 280:309–316
Hu H, Guo M, Ghu J (2004) Analysis of key enzymes in metabolic pathways of recombinant Pichia pastoris (MutS) at transition phase. J East China Univ Sci Technol 30:392–397
Li J, Zhang H, Wu M, Wang C, Dong Y, Zhu L, Zhang P (2014) Expression and characterization of hyperthermotolerant xylanases, SyXyn11P and SyXyn11E, in Pichia pastoris and Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:3476–3487. doi:10.1007/s12010-014-0786-5
Li N, Meng K, Wang Y, Shi P, Luo H, Bai Y, Yang P, Yao B (2008) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a new xylanase with broad temperature adaptability from Streptomyces sp S9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:231–240. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1533-z
Li Z, Xiong F, Lin Q, d’Anjou M, Daugulis AJ, Yang DS, Hew CL (2001) Low-temperature increases the yield of biologically active herring antifreeze protein in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 21:438–445. doi:10.1006/prep.2001.1395
Liu W, Shi P, Chen Q, Yang P, Wang G, Wang Y, Luo H, Yao B (2010) Gene cloning, overexpression, and characterization of a xylanase from Penicillium sp CGMCC 1669. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1–12. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8719-4
Liu X, Wu D, Wu J, Chen J (2013) Optimization of the production of Aspergillus niger alpha-glucosidase expressed in Pichia pastoris. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:533–540. doi:10.1007/s11274-012-1207-y
Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22:249–270. doi:10.1002/yea.1208
McHunu NP, Singh S, Permaul K (2009) Expression of an alkalo-tolerant fungal xylanase enhanced by directed evolution in Pichia pastoris and Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 141:26–30. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.02.021
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Qiu Z, Shi P, Luo H, Bai Y, Yuan T, Yang P, Liu S, Yao B (2010) A xylanase with broad pH and temperature adaptability from Streptomyces megasporus DSM 41476, and its potential application in brewing industry. Enzyme Microbial Technol 46:506–512. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2010.02.003
Shi P, Qiu Z, Bai Y, Yuan T, Huang H, Pan X, Yang P, Zhang W, Yao B (2012) A new xylanase from Streptomyces megasporus DSM 41476 with high yield of xylobiose. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:687–692. doi:10.1007/s11274-011-0863-7
Standards N (2009) Determination of xylanase activity in feed additives-Spectrophotometric method. Chinese National Standards GB/T 23874
Su D, Ding C, Li L, Su D, Zheng X (2005) Effect of endoxylanases on dough properties and making performance of Chinese steamed bread. Eur Food Res Technol 220:540–545. doi:10.1007/s00217-005-1170-z
Vardakou M, Katapodis P, Samiotaki M, Kekos D, Panayotou G, Christakopoulos P (2003) Mode of action of family 10 and 11 endoxylanases on water-unextractable arabinoxylan. Int J Biol Macromol 33:129–134. doi:10.1016/s0141-8130(03)00077-1
Verjans P, Dornez E, Delcour JA, Courtin CM (2010) Selectivity for water-unextractable arabinoxylan and inhibition sensitivity govern the strong bread improving potential of an acidophilic GH11 Aureobasidium pullulans xylanase. Food Chem 123:331–337. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.04.039
Wan L, Zhu S, Li Y, Liu S, Yang H, Li S, Li Y, Cheng J, Lu X (2011) Production and characterization of LEA29Y, a variant of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4-immunoglobulin, in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:543–551. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3277-4
Wang Y, Wang Z, Du G, Hua Z, Liu L, Li J, Chen J (2009) Enhancement of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase production in recombinant Pichia pastoris according to the ratio of methanol to cell concentration. Bioresour Technol 100:1343–1349. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.049
Zhang J-h WuD, Chen J, Wu J (2011) Enhancing functional expression of β-glucosidase in Pichia pastoris by co-expressing protein disulfide isomerase. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 16:1196–1200. doi:10.1007/s12257-011-0136-1
Zhang PP, He ZH, Chen DS, Zhang Y, Larroque OR, Xia XC (2007) Contribution of common wheat protein fractions to dough properties and quality of northern-style Chinese steamed bread. J Cereal Sci 46:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.10.007
Acknowledgments
This work received financial support from the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (31425020), the project of outstanding scientific and technological innovation group of Jiangsu Province, the 111 Project (No. 111-2-06), Student Innovation Training Program (2014027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wu, J., Zheng, K. et al. A xylanase from Streptomyces sp. FA1: heterologous expression, characterization, and its application in Chinese steamed bread. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43, 663–670 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1736-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1736-8