Abstract
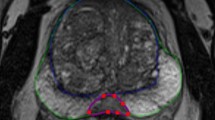
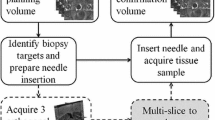
Accurate and fast segmentation and volume estimation of the prostate gland in magnetic resonance (MR) images are necessary steps in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of prostate cancer. This paper presents an algorithm for the prostate gland volume estimation based on the semi-automated segmentation of individual slices in T2-weighted MR image sequences. The proposed sequential registration-based segmentation (SRS) algorithm, which was inspired by the clinical workflow during medical image contouring, relies on inter-slice image registration and user interaction/correction to segment the prostate gland without the use of an anatomical atlas. It automatically generates contours for each slice using a registration algorithm, provided that the user edits and approves the marking in some previous slices. We conducted comprehensive experiments to measure the performance of the proposed algorithm using three registration methods (i.e., rigid, affine, and nonrigid). Five radiation oncologists participated in the study where they contoured the prostate MR (T2-weighted) images of 15 patients both manually and using the SRS algorithm. Compared to the manual segmentation, on average, the SRS algorithm reduced the contouring time by 62 % (a speedup factor of 2.64×) while maintaining the segmentation accuracy at the same level as the intra-user agreement level (i.e., Dice similarity coefficient of 91 versus 90 %). The proposed algorithm exploits the inter-slice similarity of volumetric MR image series to achieve highly accurate results while significantly reducing the contouring time.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
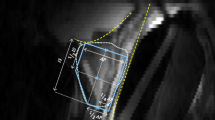
The entire image is not used as the ROI because registration usually gives a poor result in this case. Therefore, the ROI is usually limited by the user before the registration starts [5, 6]. SRS was designed specifically for the prostate gland where the cross section of the prostate is small at the base and the apex and it usually becomes larger as we approach the mid-gland region. We used a slightly enlarged ROI because the second slice was more likely to contain a larger portion of the prostate than the first slice when we navigated from the base to the apex. Thus, the second slice might not cover the whole prostate if we use the same ROI. The 30 % ROI enlargement was selected based on the empirical data.
References
Prostate Cancer Canada, “What’s your number? Prostate cancer Canada annual report.,” www.prostatecancer.ca, 2010
Smith WL, et al: “Prostate volume contouring: a 3D analysis of segmentation using 3DTRUS, CT, and MR”. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67(4):1238–1247, 2007
Steenbakkers RJ, Deurloo KE, Nowak PJ, Lebesque JV, van Herk MM, Rasch CR: “Reduction of dose delivered to the rectum and bulb of the penis using MRI delineation for radiotherapy of the prostate.”. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 57:1269–1279, 2003
Jonsson JH, Karlsson MG, Karlsson M, Nyholm T: “Treatment planning using MRI data: an analysis of the dose calculation accuracy for different treatment regions”. Radiat Oncol 5:62, 2010. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-5-62
Klein S, van der Heide UA, Raaymakers BW, Kotte ANTJ, Staring M, Pluim JPW, “Segmentation of the prostate in MR images by atlas matching,” IEEE Conf. Biomed. Imaging, 2007, pp.1300 - 1303
Klein S, van der Heide UA, Lips IM, van Vulpen M, Staring M, Pluim JPW: Automatic segmentation of the prostate in 3D MR images by atlas matching using localized mutual information. Med Phys 35:1407–1417, 2008
Dowling J, Fripp J, Greer P, Patterson J, Our selin S, Salvador O:“Automatic atlas-based segmentation of the prostate: A MICA 2009 Prostate segmentation challenge entry”, In: Workshop in Med. Image Compute. Assist. Intern, 2009, pp. 1724
Langerak TR, van der Heide UA, Kotte ANTJ, Viergever MA, van Vulpen M, Pluim JPW: Label Fusion in Atlas-Based Segmentation Using a Selective and Iterative Method for Performance Level Estimation (SIMPLE). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:2000–2008, 2010
Martin S, Troccaz J, Daanen V: Automated segmentation of the prostate in 3D MR images using a probabilistic atlas and a spatially constrained deformable model. Med Phys 37:1579–1590, 2010
Warfield SK, Zou KH, Wells WM: Simultaneous Truth and Performance Level Estimation (STAPLE): An Algorithm for the Validation of Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:903–921, 2004
Cheng R, Turkbey B, Senseney J, Bernardo M, Bokinsky A, Gandler W, McCreedy E, Pohida T, Choyke P, McAuliffe MJ:“2D registration guided models for semi-automatic MRI prostate segmentation”. Proc. SPIE 8669, Medical Imaging 2013: Image Processing, 86692V, 2013, doi:10.1117/12.2006225.
Radiation therapy oncology group, “contouring atlases.,” www.rtog.org/CoreLab/ContouringAtlases.aspx.
Langer DL, van der Kwast TH, Evans AJ, Trachtenberg J, Wilson BC, Haider MA: Prostate cancer detection with multi-parametric MRI: Logistic regression analysis of quantitative T2, diffusion-weighted imaging, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 30:327–334, 2009
Hentschel B, Oehler W, Strau D, Ulrich A, Malich A: Definition of the CTV Prostate in CT and MRI by Using CT-MRI Image Fusion in IMRT Planning for Prostate Cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 187(3):183–190, 2011. doi:10.1007/s00066-010-2179-1
Maintz JBA, Viergever MA: A survey of medical image registration. Med Image Anal 2:1–36, 1998
Brown LG: A survey of image registration techniques. ACM Comput Surv 24:325–376, 1992
Thirion JP: Image matching as a diffusion process: an analogy with Maxwell’s demons. Med Image Anal 196:243–260, 1998
Guimond A, Roche A, Ayache N, Meunier J: Three-dimensional multimodal brain warping using the demons algorithm and adaptive intensity corrections. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(1):58–69, 2001
Wang H, Dong L, O’Daniel J, Mohan R, Garden AS, Ang KK, Kuban DA, Bonnen M, Chang JY, Cheung R: Validation of an accelerated ‘demons’ algorithm for deformable image registration in radiation therapy. Phys Med Biol 50(12):2887–2905, 2005
Kroon DJ, “Multimodality nonrigid demon algorithm image registration”, MatlabCentral, www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/21451- multimodality-non-rigid-demon-algorithm-imageregistration.
Martin S, Rodrigues G, Patil N, Bauman G, D’Souza D, Sexton T, Palma D, Louie AV, Khalvati F, Tizhoosh HR, Gaede S: “Multiphase validation of atlas-based automatic and semiautomatic segmentation strategies for prostate MRI”. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1(85(1)):95–100, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.07.046
Al-Qunaieer FS, Tizhoosh HR, Rahnamayan S: Multi-resolution level sets with shape priors: a validation report for 2D segmentation of prostate gland in T2W MR images. J Digit Imaging 27(6):833–847, 2014
Khalvati F, Salmanpour A, Rahnamayan S, Rodrigues G, Tizhoosh HR: “Inter-slice bidirectional registration-based segmentation of the prostate gland in MR and CT image sequences”. Med Phys 40(12):123503-1–123503-11, 2013
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank FedDev Ontario, Canada, for supporting this research. The authors would also like to thank Segasist Technologies for providing DICOM datasets and experts’ markings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalvati, F., Salmanpour, A., Rahnamayan, S. et al. Sequential Registration-Based Segmentation of the Prostate Gland in MR Image Volumes. J Digit Imaging 29, 254–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9844-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9844-y