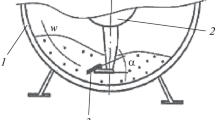
Abstract
A systematic estimation of the amount of tool wear is nearly impossible because there is no universally accepted test for determining soil abrasiveness. Laboratory devices that have been developed in recent years have fewer limitations than older methods, but they are unique and are under development. A new device has been developed and used at the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran, to evaluate how geological factors affect soil abrasion behavior. Samples with known geological characteristics including hardness (mineralogy), grain size, and grain roundness were prepared and tested using the new abrasion test unit. The results indicate a direct linear relationship between the relative mineral hardness (Mohs scale) and abrasion. Moreover, the results of the abrasion testing showed increasing abrasion with grain size and angularity. Furthermore, the impact of moisture content was also examined, and the amount of measured wear followed an approximately bell shaped curve relative to the water content, as has been reported in similar studies by other research groups. Additional testing of the samples for shear strength showed a good correlation between the shear strengths of the specimens and the abrasivity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi Gharahbagh E, Rostami J, Palomino AM (2011) New soil abrasion testing method for soft ground tunneling applications. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 26(5):604–613
Alavi Gharahbagh E, Qiu T, Rostami J (2013) Evaluation of granular soil abrasivity for wear on cutting tools in excavation and tunneling equipment. J Geotech Geoenviron 139(10):1718–1726
Alavi Gharahbagh E, Rostami J, Talebi K (2014) Experimental study of the effect of conditioning on abrasive wear and torque requirement of full face tunneling machines. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 41:127–136
Alber M, Yaralı O, Dahl F, Bruland A, Käsling H, Michalakopoulos TN, Cardu M, Hagan P, Aydın H, Özarslan A (2014) ISRM suggested method for determining the abrasivity of rock by the CERCHAR abrasivity test. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:261–266
ASTM G75-01 (2001) Standard test method for determination of slurry abrasivity (Miller Number) and slurry abrasion response of materials (SAR Number). ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
Barzegari G, Uromeihy A, Zhao J (2013) A newly developed soil abrasion testing method for tunnelling using shield machines. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 46:63–74
Bruland A (1998) Hard rock tunnel boring: drillability test methods. Project report 13A-98, NTNU Trondheim
Dobkins JE, Folk RL (1970) Shape development of Tahiti-Nui. J Sediment Petrol 40:1167–1203
Drucker P (2012) Abrasivität von Lockergestein und der Werkzeugverschleiß im Tief- und Tunnelbau. Österr, Ingenieur- und Architekten-Zeitschrift 156
Drucker p, (2013) Über die Abrasivität von Lockergestein und den Werkzeugverschleiß im Spezialtiefbau, PhD-thesis TU Wien, 158
Folk RL (1974) Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Hempill Publishing Co., Austin 182
Hashemnejad H, Ghafoori M, Lashkaripour GhR, Tariq Azali S (2012) Effect of geological parameters on soil abrasivity using LCPC machine for predicting LAC. Int J Emerg Tech Adv Eng (IJETAE) 2(12):71–76
Jakobsen PD (2014) Estimation of soft ground tool life in TBM tunnelling. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology. http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:699962/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Jakobsen PD, Lohne J (2013) Challenges of methods and approaches for estimating soil abrasivity in soft ground TBM tunneling. Wear 308(1–2):166–173
Jakobsen PD, Bruland A, Dahl F (2013a) Review and assessment of the NTNU/SINTEF Soil Abrasion Test (SAT™) for determination of abrasiveness of soil and soft ground. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 37:107–114
Jakobsen PD, Langmaack L, Dahl F, Breivik T (2013b) Development of the Soft Ground Abrasion Tester (SGAT) to predict TBM tool wear, torque and thrust. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 38:398–408
Köppl F, Thuro K, Thewes M (2015) Factors with an influence on the wear to excavation tools in hydroshield tunnelling in soft ground. Geomech Tunn J 8(3):248–257
Moammeri H, Tarigh Azali S, (2010) Abrasive effects on TBMs used to bore current or recently completed projects in Iran. In: World tunnelling (December 2010), pp 24–27
Mosleh M, Alavi Gharahbagh E, Rostami J (2013) Effects of relative hardness and moisture on tool wear in soil excavation operations. Wear 302(1–2):1555–1559
Nilsen B, Dahl F, Holzhäuser J, Raleigh P (2006) Abrasivity of soils in TBM tunneling. Tunnels Tunnel Int 38:36–38
Nilsen B, Dahl F, Holzhauser J, Raliegh P (2007) New test methodology for estimating the abrasiveness of soils for TBM tunneling. In: Proceedings of the rapid excavation and tunneling conference (RETC), pp 104–116
Peila D, Picchio A, Chieregato A (2013) Earth pressure balance tunnelling in rock masses: laboratory feasibility study of the conditioning process. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 35:55–66
Plinninger RJ, Restner U (2008) Abrasiveness testing, Quo Vadis? A commented overview of abrasiveness testing methods. Geomech Tunn 1(1):61–70
Rostami J, Alavi Gharahbagh E, Palomino AM, Mosleh M (2012) Development of soil abrasivity testing for soft ground tunneling using shield machines. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 28:245–256
Thuro K (1997) Drillability prediction-geological influences in hard rock drill and blast tunneling. Geol Rundsch 86:426–438
Thuro K, Plinninger R (2007) Determining abrasivity with the LCPC test. Proceedings of the the 1st Canada—U.S. rock mechanics symposium. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 827–834
Wallis S (2000) Elbe Tunnel: Cutting edge technology. Tunnels Tunnel Int 32(1):24
West G (1989) Rock abrasiveness testing for tunneling. Int J Rock Mech Min 26:151–160
Acknowledgments
The authors express their thanks to Mr. Forghani and Sepadandish Consulting Engineers for their cooperation in the laboratory activities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirmehrabi, H., Ghafoori, M. & Lashkaripour, G. Impact of some geological parameters on soil abrasiveness. Bull Eng Geol Environ 75, 1717–1725 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0837-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0837-3