Abstract
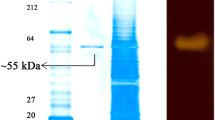
An extracellular haloalkaliphilic thermostable α-amylase producing archaeon was isolated from the saltwater Lake Urmia and identified as Halorubrum xinjiangense on the basis of morphological, biochemical, and molecular properties. The enzyme was purified to an electrophoretically homogenous state by 80 % cold ethanol precipitation, followed by affinity chromatography. The concentrated pure amylase was eluted as a single peak on fast protein liquid chromatography. The molecular mass of the purified enzyme was about 60 kDa, with a pI value of 4.5. Maximum amylase activity was at 4 M NaCl or 4.5 M KCl, 70 °C, and pH 8.5. The K m and V max of the enzyme were determined as 3.8 mg ml−1 and 12.4 U mg−1, respectively. The pure amylase was stable in the presence of SDS, detergents, and organic solvents. In addition, the enzyme (20 U) hydrolyzed 69 % of the wheat starch after a 2-h incubation at 70 °C in an aqueous/hexadecane two-phase system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrangi S, Faramarzi MA, Shahverdi AR, Sepehrizadeh Z (2010) Purification and characterization of two extracellular endochitinases from Massilia timonae. Carbohydr Res 345:402–407
Amoozegar MA, Malekzadeh F, Malik KA (2003) Production of amylase by newly isolated moderate halophile, Halobacillus sp. strain MA-2. J Microbiol Methods 52:353–359
Arikan B (2008) Highly thermostable, thermophilic, alkaline, SDS and chelator resistant amylase from a thermophilic Bacillus sp. isolate A3–15. Bioresour Technol 99:3071–3076
Averhoff B, Müller V (2010) Exploring research frontiers in microbiology: recent advances in halophilic and thermophilic extremophiles. Res Microbiol 161:506–514
Bailey RW, Bourne EJ (1960) Colour reactions given by sugars and diphenylamine-aniline spray reagents on paper chromatograms. J Chromatogr A 4:206–213
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burhan A, Nisa U, Gökhan C, Ömer C, Ashabil A, Osman G (2003) Enzymatic properties of a novel thermostable, thermophilic, alkaline and chelator resistant amylase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. isolate ANT-6. Process Biochem 38:1397–1403
Delgado-García M, Valdivia-Urdiales B, Aguilar-González CN, Contreras-Esquivel JC, Rodríguez-Herrera R (2012) Halophilic hydrolases as a new tool for the biotechnological industries. J Sci Food Agric 92:2575–2580
Doukyu N, Ogino H (2010) Organic solvent-tolerant enzymes. Biochem Eng J 48:270–282
Doukyu N, Yamagishi W, Kuwahara H, Ogino H, Furuki N (2007) Production and characterization of a maltooligosaccharide-forming amylase that improves product selectivity in water-miscible organic solvents, from dimethylsulfoxide-tolerant Brachybacterium sp. strain LB25. Extremophiles 11:781–788
Ebrahimpour A, Rahman RN, Basri M, Salleh AB (2011) High level expression and characterization of a novel thermostable, organic solvent tolerant, 1,3-regioselective lipase from Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. Bioresour Technol 102:6972–6981
Falb M, Müller K, Königsmaier L, Oberwinkler T, Horn P, Gronau SV, Gonzalez O, Pfeiffer F, Bornberg-Bauer E, Oesterhelt D (2008) Metabolism of halophilic archaea. Extremophiles 12:177–196
Feng J, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2004) Halorubrum xinjiangense sp. nov., a novel halophile isolated from saline lakes in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1789–1791
Fukushima T, Mizuki T, Echigo A, Inoue A, Usami R (2005) Organic solvent tolerance of halophilic α-amylase from a haloarchaeon, Haloarcula sp. strain S-1. Extremophiles 9:85–89
Hutcheon GW, Vasisht N, Bolhuis A (2005) Characterization of a highly stable α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. Extremophiles 9:487–495
Jain D, Pancha I, Mishra SK, Shrivastav A, Mishra S (2012) Purification and characterization of haloalkaline thermoactive, solvent stable and SDS-induced protease from Bacillus sp.: a potential additive for laundry detergents. Bioresour Technol 115:228–236
Karen R, Capes MD, Dassarma S (2012) Function and biotechnology of extremophilic enzymes in low water activity. Aquat Biosyst 8:1–15
Kiran KK, Chandra TS (2008) Production of surfactant and detergent-stable, halophilic, and alkalitolerant alpha-amylase by a moderately halophilic Bacillus sp. strain TSCVKK. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:1023–1031
Kumar S, Khare SK (2012) Purification and characterization of maltooligosaccharide-forming α- amylase from moderately halophilic Marinobacter sp. EMBB. Bioresour Technol 116:247–251
Lacks SA, Springhorn SS (1980) Renaturation of enzymes after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem 255:7467–7473
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Liu XD, Xu Y (2008) A novel raw starch digesting α-amylase from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. Yx-1: purification and characterization. Bioresour Technol 99:4315–4320
Madern D, Ebel C, Zaccai G (2000) Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 4:91–98
Manikandan M, Pašić L, Kannan V (2009) Purification and biological characterization of a halophilic thermostable protease from Haloferax lucentensis VKMM 007. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:2247–2256
Mehta D, Satyanarayana T (2013) Biochemical and molecular characterization of recombinant acidic and thermostable raw-starch hydrolysing α-amylase from an extreme thermophile Geobacillus thermoleovorans. J Mol Catal B Enzym 85–86:229–238
Mendu DR, Ratnam BVV, Purnima A, Ayyanna C (2005) Affinity chromatography of α-amylase from Bacillus licheniformis. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:712–717
Michelin M, Silva TM, Benassi VM, Peixoto-Nogueira SC, Moraes LAB, Leão JM, Jorge JA, Teranzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2010) Purification and characterization of a thermostable α-amylase produced by the fungus Paecilomyces variotii. Carbohydr Res 345:2348–2353
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Morita T, Karube I (1995) Enzymatic hydrolysis of starch in water immiscible organic solvent, two-phase systems. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 55:75–86
Najafi MF, Kembhavi A (2005) One step purification and characterization of an extracellular α-amylase from marine Vibrio sp. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:535–539
Nascimento WCA, Martins MLL (2004) Production and properties of an extracellular protease from thermophilic Bacillus sp. Braz J Microbiol 35:91–96
Pérez-Pomeras F, Bautista V, Ferrer J, Pire C, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Bonete MJ (2003) α-Amylase activity from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 7:299–306
Prakash B, Vidyasagar M, Madhukumar MS, Muralikrishna G, Sreeramulu K (2009) Production, purification, and characterization of two halotolerant, thermostable, and alkali-stable α-amylases from Chromohalobacter sp. TVSP 101. Process Biochem 44:210–215
Shafiei M, Ziaee A, Amoozegar MA (2010) Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel SDS and surfactant stable, raw starch digesting, and halophilic bacterium Nesterenkonia sp. strain F. Process Biochem 45:694–699
Shafiei M, Ziaee A, Amoozegar MA (2011) Purification and characterization of an organic-solvent-tolerant halophilic α-amylase from the moderately halophilic Nesterenkonia sp. strain F. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:275–281
Shafiei M, Ziaee A, Amoozegar MA (2012) Purification and characterization of a halophilic α-amylase with increased activity in the presence of organic solvents from the moderately halophilic Nesterenkonia sp. strain F. Extremophiles 16:627–635
Van der Maarel MJEC, Van der Veen B, Uitdehaag JCM, Leemhuis H, Dijkhuizen L (2002) Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the α-amylase family. J Biotechnol 94:137–155
Zhuang X, Han Z, Bai Z, Zhuang G, Shim H (2010) Progress in decontamination by halophilic microorganisms in saline wastewater and soil. Environ Pollut 158:1119–1126
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by Grant Number 88-04-33-9700 from Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Albers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moshfegh, M., Shahverdi, A.R., Zarrini, G. et al. Biochemical characterization of an extracellular polyextremophilic α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Halorubrum xinjiangense . Extremophiles 17, 677–687 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0551-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0551-7