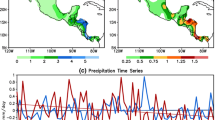
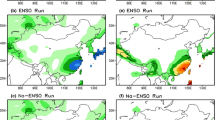
Abstract
In this study, the possible influence of the springtime Arctic oscillation (AO) on precipitation along the East Asian rain belt has been studied for the period of 1979 to 2014. To capture the features of the large-scale variability of the atmospheric circulation and precipitation, singular value decomposition (SVD) analysis was performed. The domain for precipitation is from 21.25 to 33.75° N and 111.25 to 133.25° E, and the 1000 hPa heights are from 20° N northward. Prior to analysis, the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) signals were linearly fitted and subtracted from the variables of interest. The first paired modes explain 51.1 % of the total squared covariance. The spatial feature of the pressure mode is almost identical to that of the positive AO pattern, while the precipitation mode displays an overall less-than-normal anomaly along the rain belt. The AO indices are highly correlated with the time coefficients of the pressure mode at a value of 0.91, and for the time coefficients of the precipitation mode, the correlation is −0.44, both of which are significant at the 99 % level. The regional atmospheric circulation anomalies in association with the negative phase AO mode display consistent changes, including the anomalous southerly winds and vapor flux convergence in the lower troposphere over East Asia, the stronger East Asian westerly jet stream, and the enhanced ascending air motion between 20 and 30° N. There are two possible mechanisms linking the AO and East Asian circulation and precipitation, i.e., the wave-trains along the westerly jet stream from North Africa to the Middle East and East Asia and the dipole of an anti-cyclone and a cyclone over the North Pacific.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branstator G (2002) Circumglobal teleconnections, the jet stream waveguide, and the North Atlantic oscillation. J Clim 15(14):1893–1910
Bretherton SC, Smith C, Wallace MJ (1992) An intercomparison of methods for finding coupled patterns in climate data. J Clim 5(6):541–560
Chen JM, Li T, Shih CF (2008) Asymmetry of the El Niño-spring rainfall relationship in Taiwan. J Meteor Soc Jpn 86(2):297–312
Chen JP, Wen ZP, Wu RG, Chen ZS, Zhao P (2014) Interdecadal changes in the relationship between southern China winter-spring precipitation and ENSO. Clim Dyn 43(5):1327–1338
Choi K, Wu CC, Byun HY (2012) Possible connection between summer tropical cyclone frequency and spring Arctic oscillation over East Asia. Clim Dyn 38(11):2613–2629
Feng J, Li JP (2011) Influence of El Niño Modoki on spring rainfall over South China. J Geophys Res 116(D13):102–111
Feng GL, Yang H, Zhang SX, Wang K, Shen BZ (2012) A preliminary research on the reason of a sharp turn from drought to flood in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in late spring and early summer of 2011. Chin J Atmos Sci 36(5):1009–1026
Gao MN, Yang J, Gong DY, Kim SJ (2014) Unstable relationship between spring Arctic oscillation and East Asian summer monsoon. Int J Climatol 34(7):2522–2528
Gong DY, Ho CH (2003) Arctic oscillation signals in East Asian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res 108(D2):4066–4071
Gong DY, Gao YQ, Guo D, Mao R, Yang J, Hu M, Gao MN (2014) Interannual linkage between Arctic/North Atlantic oscillation and tropical Indian Ocean precipitation during boreal winter. Clim Dyn 42(3):1007–1027
Gong DY, Wang SW, Zhu JH (2001) East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 28(10):2073–2076
Gong DY, Zhu JH, Wang SW (2002) Significant relationship between spring AO and the summer rainfall along the Yangtze River. Chin Sci Bull 47(11):948–952
He SP, Wang HJ (2013) Impact of the November/December Arctic oscillation on the following January temperature in East Asia. J Geophys Res 118(23):12981–12998
Hu M, Gong DY, Wang L, Zhou TJ, Zhang ZY (2012) Possible influence of January-March Arctic oscillation on the convection of tropical North Pacific and North Atlantic. Acta Meteorol Sin 70(3):479–491
Huang RH, Chen JL, Wang L, Lin ZD (2012) Characteristics, processes, and causes of the spatio-temporal variabilities of the East Asian monsoon system. Adv Atmos Sci 29(5):910–942
Huang G, Hu KM, Xie SP (2010) Strengthening of tropical Indian Ocean teleconnection to the Northwest Pacific since the mid-1970s: an atmospheric GCM study. J Clim 23(19):5294–5304
Jiang PP, Zhao P (2012) The interannual variability of spring rainy belt over southern China and the associated atmospheric circulation anomalies. Acta Meteorol Sin 70(4):681–689
Liang PD, Liu AX (1994) Winter Asia jet stream and seasonal precipitation in East China. Adv Atmos Sci 11(3):311–318
Liang XZ, Wang WC (1998) Associations between China monsoon rainfall and tropospheric jets. Q J R Meteorol Soc 124(552):2597–2623
Liao QH, Gao ST, Wang HJ, Tao SY (2004) Anomalies of the extratropical westerly jet in the north hemisphere and their impacts on east Asian summer monsoon climate anomalies. Chinese J Geophys 47(1):10–18
Liu XD, Wang Y (2011) Contrasting impacts of spring thermal conditions over Tibetan Plateau on late-spring to early-summer precipitation in Southeast China. Atmos Sci Lett 12(3):309–315
Lu E, Liu SY, Luo YL, Zhao W, Li H, Chen HX, Zeng YT, Liu P, Wang XM, Higgins WR, Halpert SM (2014) The atmospheric anomalies associated with the drought over the Yangtze River basin during spring 2011. J Geophys Res 119(10):5581–5894
Mao R, Gong DY, Yang J, Bao JD (2011) Linkage between the Arctic oscillation and winter extreme precipitation over Central-Southern China. Clim Res 50(2–3):187–201
Nitta T (1987) Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the northern hemisphere summer circulation. J Meteor Soc Jpn 65(3):373–390
Qi L, He JH, Zhang ZQ, Song JN (2008) Seasonal cycle of the zonal land-sea thermal contrast and East Asian subtropical monsoon circulation. Chin Sci Bull 53(1):131–136
Qu JX, Gong DY, Li S (2015) The possible influence of Arctic oscillation on South China Sea climate during boreal spring. Chin Sci Bull 60(24):2327–2337
Qu X, Huang G, Zhou W (2013) Consistent responses of East Asian summer mean rainfall to global warming in CMIP5 simulations. Theor Appl Climatol 117(1):123–131
Sampe T, Xie SP (2010) Large-scale dynamics of the Meiyu-Baiu rainband: environmental forcing by the westerly jet. J Clim 23(1):113–134
Sui CH, Chung PH, Li T (2007) Interannual and interdecadal variability of the summer time western North Pacific subtropical high. Geophys Res Lett 34(11):701–706
Sun JQ, Wang HJ (2006) Relationship between Arctic oscillation and Pacific decadal oscillation on decadal timescale. Chin Sci Bull 51(1):75–79
Sun CH, Yang S (2012) Persistent severe drought in southern China during winter–spring 2011: large-scale circulation patterns and possible impacting factors. J Geophys Res 117(D10):112–129
Takaya K, Nakamura H (2001) A formulation of a phase-independent wave-activity flux for stationary quasigeostrophic eddies on a zonally varying basic flow. J Atmos Sci 58(6):608–627
Tao SY, Chen LX (1987) A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. Oxford University Press. In: Chang CP, Krishramurti TN (eds) Monsoon meteorology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 60–92
Thompson WJD, Wallace MJ (2000) Annular modes in the extratropical circulation. Part I: month-to-month variability. J Clim 13(5):1000–1015
Tian SF, Yasunari T (1998) Climatological aspects and mechanism of spring persistent rains over Central China. J Meteor Soc Jpn 76(1):57–71
Wan RJ, Wu GX (2007) Mechanism of the spring persistent rains climate over southeastern China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci 50(1):130–144
Wan RJ, Wang TM, Wu GX (2008) Temporal variations of the spring persistent rains and SCS subtropical high and their correlations to the circulation and precipitation of the East Asia summer monsoon. Acta Meteorol Sin 66(5):800–807
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu GX, Liu YM (2008) Tibetan Plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 35(14):702–706
Wang B, Wu RG, Fu XH (2000) Pacific–East Asian teleconnection: how does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Clim 13(9):1517–1536
Wang B, Wu RG, Lau KM (2001) Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific–East Asian monsoons. J Clim 14(20):4073–4090
Wang B, Xiang BQ, Lee JY (2013) Subtropical high predictability establishes a promising way for monsoon and tropical storm predictions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(8):2718–2722
Wu GX, Liu HZ (1995) Neighborhood response of rainfall to tropical sea surface temperature anomalies. Part I: numerical experiment. Chin J Atmos Sci 19(4):422–434
Wu BJ, Peng ZB (1996) Progress in persistant rainy precesses in spring over areas between south of Changjiang river and north of five ridges. Bull Sci Technol 2:65–70
Wu RG, Hu ZZ, Kirtman PB (2003) Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J Clim 16(22):3742–3758
Wu GX, Liu P, Liu YM, Li WP (2000) Impacts of the sea surface temperature anomaly in the Indian Ocean on the subtropical anticyclone over the western Pacific—two-stage thermal adaptation in the atmosphere. Acta Meteorol Sin 58(5):514–522
Xie SP, Hu KM, Hafner J, Tokinaga H, Du Y, Huang G, Sampe T (2009) Indian ocean capacitor effect on Indo–western Pacific climate during the summer following El Niño. J Clim 22(3):730–747
Yang H (2011) The significant relationship between the Arctic oscillation (AO) in December and the January climate over South China. Adv Atmos Sci 28(2):398–407
Yang FL, Lau KM (2004) Trend and variability of China precipitation in spring and summer: linkage to sea-surface temperatures. Int J Climatol 24(13):1625–1644
Yang J, Gong DY, Wang WS, Hu M, Mao R (2012) Extreme drought event of 2009/2010 over southwestern China. Meteorog Atmos Phys 115(3):173–174
Zhang HL (1987) A study of the fluctuation of the cereal’s gibberellin prevalence and the weather factors in the middle and lower Chang-Jiang. Acta Meteorol Sin 45(3):309–345
Zhang YC, Kuang XY, Guo WD, Zhou TJ (2006) Seasonal evolution of the upper-tropospheric westerly jet core over East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 33(11):708–711
Zhang J, Zhou TJ, Yu RC, Xin XG (2009) Atmospheric water vapor transport and corresponding typical anomalous spring rainfall patterns in China. Chin J Atmos Sci 33(1):121–134
Zhao P, Jiang PP, Zhou XJ, Zhu CW (2009) Modeling impacts of East Asian ocean-land thermal contrast on spring southwesterly winds and rainfall in eastern China. Chin Sci Bull 54(16):2372–2378
Zhao P, Zhang RH, Liu JP, Zhou XJ, He JH (2007) Onset of southwesterly wind over eastern China and associated atmospheric circulation and rainfall. Clim Dyn 28(7):797–811
Zhou LT (2011) Impact of East Asian winter monsoon on rainfall over southeastern China and its dynamical process. Int J Climatol 31(5):677–686
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by projects NSFC-41375071 and NSFC-41321001 of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and 2012CB955401 and PE15010 of the Korea Polar Research Institute. The NCEP-NCAR reanalysis data and GPCP precipitation data in this study were provided by the NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD, Boulder, CO, USA, from their Web site at http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Gong, D., Mao, R. et al. Possible influence of Arctic oscillation on precipitation along the East Asian rain belt during boreal spring. Theor Appl Climatol 130, 487–495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1900-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1900-0