Abstract
Background
Current definitions of acute kidney injury (AKI) are not sufficiently sensitive to identify all newborns with AKI during the first week of life.
Methods
To determine whether the rate of decline of serum creatinine (SCr) during the first week of life can be used to identify newborns with AKI, we reviewed the medical records of 106 term neonates at risk of AKI who were treated with hypothermia for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
Results
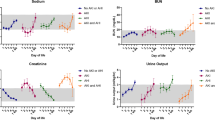
Of the newborns enrolled in the study, 69 % showed a normal rate of decline of SCr to ≥50 % and/or reached SCr levels of ≤0.6 mg/dl before the 7th day of life, and therefore had an excellent clinical outcome (control group). Thirteen newborns with HIE (12 %) developed AKI according to an established neonatal definition (AKI–KIDGO group), and an additional 20 newborns (19 %) showed a rate of decline of SCr of <33, <40, and <46 % from birth to days 3, 5, or 7 of life, respectively (delayed rise in estimated SCr clearance group). Compared to the control group, newborns in the other two groups required more days of mechanical ventilation and vasopressor drugs and had higher gentamicin levels, more fluid overload, lower urinary epidermal growth factor levels, and a prolonged length of stay.
Conclusions
The rate of decline of SCr provides a sensitive approach to identify term newborns with AKI during the first week of life.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shankaran S (2014) Outcomes of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates treated with hypothermia. Clin Perinatol 41:149–159
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, Fanaroff AA, Poole WK, Wright LL, Higgins RD, Finer NN, Carlo WA, Duara S, Oh W, Cotten CM, Stevenson DK, Stoll BJ, Lemons JA, Guillet R, Jobe AH, National Institute of Child H Human Development Neonatal Research N (2005) Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 353:1574–1584
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, McDonald SA, Higgins RD, Tyson JE, Ehrenkranz RA, Das A, Sant’Anna G, Goldberg RN, Bara R, Walsh MC, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child H, Human Development Neonatal Research Network (2012) Temperature profile and outcomes of neonates undergoing whole body hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Crit Care Med 13:53–59
Sarkar S, Askenazi DJ, Jordan BK, Bhagat I, Bapuraj JR, Dechert RE, Selewski DT (2014) Relationship between acute kidney injury and brain MRI findings in asphyxiated newborns after therapeutic hypothermia. Pediatr Res 75:431–435
Selewski DT, Jordan BK, Askenazi DJ, Dechert RE, Sarkar S (2013) Acute kidney injury in asphyxiated newborns treated with therapeutic hypothermia. J Pediatr 162(725–729):e721
Thomas ME, Blaine C, Dawnay A, Devonald MA, Ftouh S, Laing C, Latchem S, Lewington A, Milford DV, Ostermann M (2015) The definition of acute kidney injury and its use in practice. Kidney Int 87:62–73
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL (2009) Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol 24:265–274
Drukker A, Guignard JP (2002) Renal aspects of the term and preterm infant: a selective update. Curr Opin Pediatr 14:175–182
Karlowicz MG, Adelman RD (1995) Nonoliguric and oliguric acute renal failure in asphyxiated term neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 9:718–722
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A, Acute Kidney Injury N (2007) Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Section 2: AKIdefinition. Kidney Int Suppl 2:19–36
Schwartz GJ, Furth SL (2007) Glomerular filtration rate measurement and estimation in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1839–1848
Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ (1984) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr 104:849–854
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP, Spitzer A (1987) The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular filtration rate in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am 34:571–590
Jetton JG, Askenazi DJ (2012) Update on acute kidney injury in the neonate. Curr Opin Pediatr 24:191–196
Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, Kent AL (2015) Neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatrics 136:e463–e473
Singbartl K, Kellum JA (2012) AKI in the ICU: definition, epidemiology, risk stratification, and outcomes. Kidney Int 81:819–825
Alinei P, Guignard JP (1987) Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in infants. Comparison of three methods used in clinical practice. Helv Paediatr Acta 42:253–262
Guignard JP, Torrado A, Feldman H, Gautier E (1980) Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in children. Helv Paediatr Acta 35:437–447
Barnett HL, Hare WK, McNamara H, Hare RS (1948) Influence of postnatal age on kidney function of premature infants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 69:55–57
Leake RD, Trygstad CW, Oh W (1976) Inulin clearance in the newborn infant: relationship to gestational and postnatal age. Pediatr Res 10:759–762
Sertel H, Scopes J (1973) Rates of creatinine clearance in babies less than one week of age. Arch Dis Child 48:717–720
Aperia A, Broberger O, Elinder G, Herin P, Zetterstrom R (1981) Postnatal development of renal function in pre-term and full-term infants. Acta Paediatr Scand 70:183–187
Feldman H, Guignard JP (1982) Plasma creatinine in the first month of life. Arch Dis Child 57:123–126
Hoffman SB, Massaro AN, Soler-Garcia AA, Perazzo S, Ray PE (2013) A novel urinary biomarker profile to identify acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill neonates: a pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol 28:2179–2188
Carmody JB, Swanson JR, Rhone ET, Charlton JR (2014) Recognition and reporting of AKI in very low birth weight infants. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2036–2043
Wai K, Soler-Garcia AA, Perazzo S, Mattison P, Ray PE (2013) A pilot study of urinary fibroblast growth factor-2 and epithelial growth factor as potential biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill children. Pediatr Nephrol 28:2189–2198
Askenazi DJ, Montesanti A, Hunley H, Koralkar R, Pawar P, Shuaib F, Liwo A, Devarajan P, Ambalavanan N (2011) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and mortality in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 159(907–912):e901
Grund B, Sabin C (2010) Analysis of biomarker data: logs, odds ratios, and receiver operating characteristic curves. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 5:473–479
Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW (2005) Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3365–3370
Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, Tchervenkov CI, Gottesman R, Dancea A, Hyder A, Alkandari O (2009) A small post-operative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 76:885–892
Pottel H, Vrydags N, Mahieu B, Vandewynckele E, Croes K, Martens F (2008) Establishing age/sex related serum creatinine reference intervals from hospital laboratory data based on different statistical methods. Clin Chim Acta 396:49–55
Paragas N, Qiu A, Zhang Q, Samstein B, Deng SX, Schmidt-Ott KM, Viltard M, Yu W, Forster CS, Gong G, Liu Y, Kulkarni R, Mori K, Kalandadze A, Ratner AJ, Devarajan P, Landry DW, D’Agati V, Lin CS, Barasch J (2011) The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat Med 17:216–222
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q, Harmon K, Monaco M, Cvijanovich N, Wong HR (2008) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med 36:1297–1303
Lavery AP, Meinzen-Derr JK, Anderson E, Ma Q, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, Schibler KR (2008) Urinary NGAL in premature infants. Pediatr Res 64:423–428
Parravicini E (2010) The clinical utility of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the neonatal ICU. Curr Opin Pediatr 22:146–150
Parravicini E, Nemerofsky SL, Michelson KA, Huynh TK, Sise ME, Bateman DA, Lorenz JM, Barasch JM (2010) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a promising biomarker for late onset culture-positive sepsis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 67:636–640
Chen L, Liu W (1997) Effect of asphyxia on urinary epidermal growth factor levels in newborns. J Tongji Med Univ 17:144–146
Boer DP, de Rijke YB, Hop WC, Cransberg K, Dorresteijn EM (2010) Reference values for serum creatinine in children younger than 1 year of age. Pediatr Nephrol 25:2107–2113
Acknowledgments
We thank Sofia Perazzo for assistance in data analysis and presentation and Glenn M. Chertow for helpful discussions. This study was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) awards R0-1 HL-102497, R01-DK 49419, and U54HD071601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics statement
This Institutional Review Board at Children’s National Health System approved the study protocol in adherence to the Declaration of Helsinki and waived the need for consent.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Table S1
Serum Creatinine values in newborns with HIE during the first week of life (DOC 47 kb)
Supplemental Table S2
ROC curves for SCr and SCr decline combined. Samples from Controls and AKI-KDIGO + DReCrCl groups combined (n = 106) (DOC 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, C., Massaro, A.N. & Ray, P. A new approach to define acute kidney injury in term newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Nephrol 31, 1167–1178 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-016-3317-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-016-3317-5