Summary
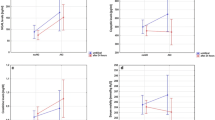
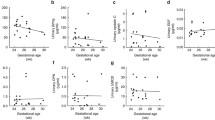
Urinary epidermal growth factor (EGF) excretion in normal newborn as well as neonates with asphyxia was investigated by using radioimmunoassay, and serum creatinine (Scr) levels determined at the same time. The results showed that in severe asphyxia group the ratio of urinary EGF to urinary creatinine (Cr) (EGF/Cr), an index reflecting EGF excretion, was decreased on the first day (P<0. 05) and reached the lowest level on the third day (P<0. 01). However, EGF/Cr values were decreased only on the third day in neonates with mild asphyxia (P<0. 05). On the seventh day, EGF/Cr values of neonates with asphyxia rose to normal. There were a negative correlation between urinary EGF/ Cr and Scr. It is suggested that EGF may play a role in the repair of acute renal injury after asphyxia and the detection of urinary EGF concentration is useful in the judgment of severity of renal injury and in the evaluation of the recovery of renal tubule after injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gesualdo L, Paolo S D, Calabro Aet al. Expression of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in normal and diseased human kidney-An immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study. Kidney Int, 1996, 49:656
Schaudies R P, Johnson J P. Increased soluble EGF after ischemia is accompanied by decrease in membrane-associated precursors. Am J Physiol, 1993, 264:F523
Coimbra T M, Cieslinski D A, Humes D. Epidermal growth factor accelerates renal repair in mercuric chloride nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol, 1990, 259:F438
Safirstein R, Price P M, Saggi S Jet al. Changes in expression after temporary renal ischemia. Kidney Int, 1990, 37:1515
Norman J, Ysau Y K, Bacay Aet al. Epidermal growth factor accelerates functional recovery from ischaemic acute tubular necrosis in the rat: role of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Sci, 1990, 78:445
Goodyer P R, Mulligan L, Goodyer C G. Expression of growth-related genes in human fetal kidney. Am J Kidey Dis, 1991, 152:608
Tsau Y K, Sheu J N, Chen CHet al. Decreased urinary epidermal growth factor in children with acute renal failure. Pediatr Res, 1996, 39:20
Behrens M T, Corbin A L, Hise M K. Epidermal growth factor receptor regulation in rat kidney: two models of renal growth. Am J Physiol, 1989, 257:F1059
Humes H D, Cieslinski D A, Coimbra TMet al. Epidermal growth factor enhances renal tubule cell regeneration and repair and accelerates the recovery of renal function in postischemic acute renal failure. J Clin Invest, 1989, 84:1757
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, C., Wanjun, L. Effect of asphyxia on urinary epidermal growth factor levels in newborns. Current Medical Science 17, 144–146 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888289
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888289