Abstract
Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) increases the morbidity of critically ill children. Thus, it is necessary to identify better renal biomarkers to follow the outcome of these patients. This prospective case–control study explored the clinical value of a urinary biomarker profile comprised of neutrophil gelatinase lipocalin (uNGAL), fibroblast growth factor-2 (uFGF-2), and epidermal growth factor (uEGF) to follow these patients.
Methods
Urine samples were collected from 21 healthy children, and 39 critically ill children (mean age 7.5 years ± 6.97 SD) admitted to a pediatric intensive care unit with sepsis or requiring extra corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). uNGAL, uFGF-2, and uEGF levels were measured using ELISA kits during the first 24 h of admission to PICU, at peak of illness, and upon resolution of the critical illness.
Results
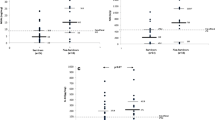
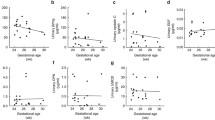
On admission, the uNGAL and uFGF-2 levels were increased, and the uEGF levels were decreased, in critically ill children with AKI (n = 19) compared to those without AKI (n = 20), and healthy controls. A biomarker score using the combined cut-off values of uNGAL, uFGF-2, and uEGF (AUC = 0.90) showed the highest specificity to identify children with AKI, relative to each biomarker alone. uNGAL and uFGF-2 on admission showed high sensitivity and specificity to predict mortality (AUC = 0.82).
Conclusions
The biomarker profile comprised of uNGAL, uFGF-2, and uEGF increased the specificity to detect AKI in critically ill children, when compared to each biomarker used alone. uNGAL and uFGF-2 may also predict the risk of death. Further validation of these findings in a large sample size is warranted.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora P, Kher V, Rai PK, Singhal MK, Gulati S, Gupta A (1997) Prognosis of acute renal failure in children: a multivariate analysis. Pediatr Nephrol 11:153–155
Williams DM, Sreedhar SS, Mickell JJ, Chan JC (2002) Acute kidney failure: a pediatric experience over 20 years. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 156:893–900
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C (2005) Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294:813–818
Bailey D, Phan V, Litalien C, Ducruet T, Merouani A, Lacroix J, Gauvin F (2007) Risk factors of acute renal failure in critically ill children: a prospective descriptive epidemiological study. Pediatr Crit Care Med 8:29–35
Ricci Z, Cruz D, Ronco C (2008) The RIFLE criteria and mortality in acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int 73:538–546
Goldstein SL, Devarajan P (2010) Pediatrics: acute kidney injury leads to pediatric patient mortality. Nat Rev Nephrol 6:393–394
Basu RK, Devarajan P, Wong H, Wheeler DS (2011) An update and review of acute kidney injury in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 12:339–347
Bunchman TE, McBryde KD, Mottes TE, Gardner JJ, Maxvold NJ, Brophy PD (2001) Pediatric acute renal failure: outcome by modality and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 16:1067–1071
Goldstein SL (2011) Acute kidney injury in children: prevention, treatment and rehabilitation. Contrib Nephrol 174:163–172
Goldstein SL, Devarajan P (2011) Acute kidney injury in childhood: should we be worried about progression to CKD? Pediatr Nephrol 26:509–522
Goldstein SL (2011) Acute kidney injury biomarkers: renal angina and the need for a renal troponin I. BMC Med 9:135
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Askenazi DJ, Bunchman TE (2007) Pediatric acute kidney injury: the use of the RIFLE criteria. Kidney Int 71:963–964
Ricci Z, Cruz D, Ronco C (2009) The RIFLE classification for acute kidney injury definition. Am J Surg 198:152–153
Plotz FB, Bouma AB, van Wijk JA, Kneyber MC, Bokenkamp A (2008) Pediatric acute kidney injury in the ICU: an independent evaluation of pRIFLE criteria. Intensive Care Med 34:1713–1717
Waikar SS, Liu KD, Chertow GM (2008) Diagnosis, epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:844–861
Moran SM, Myers BD (1985) Course of acute renal failure studied by a model of creatinine kinetics. Kidney Int 27:928–937
Foland JA, Fortenberry JD, Warshaw BL, Pettignano R, Merritt RK, Heard ML, Rogers K, Reid C, Tanner AJ, Easley KA (2004) Fluid overload before continuous hemofiltration and survival in critically ill children: a retrospective analysis. Crit Care Med 32:1771–1776
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 62:237–244
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Parikh CR, Abraham E, Ancukiewicz M, Edelstein CL (2005) Urine IL-18 is an early diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3046–3052
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Parikh CR, Goldstein SL (2007) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 11:R84
Xu SY, Pauksen K, Venge P (1995) Serum measurements of human neutrophil lipocalin (HNL) discriminate between acute bacterial and viral infections. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 55:125–131
Parikh CR, Devarajan P (2008) New biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med 36:S159–S165
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA, Dent CL, Devarajan P, Bonventre JV (2008) Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 73:863–869
Parravicini E, Nemerofsky SL, Michelson KA, Huynh TK, Sise ME, Bateman DA, Lorenz JM, Barasch JM (2010) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a promising biomarker for late-onset culture-positive sepsis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 67:636–640
Parravicini E (2010) The clinical utility of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the neonatal ICU. Curr Opin Pediatr 22:146–150
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q, Harmon K, Monaco M, Cvijanovich N, Wong HR (2008) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med 36:1297–1303
Washburn KK, Zappitelli M, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Yalavarthy R, Parikh CR, Edelstein CL, Goldstein SL (2008) Urinary interleukin-18 is an acute kidney injury biomarker in critically ill children. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:566–572
Otukesh H, Hoseini R, Hooman N, Chalian M, Chalian H, Tabarroki A (2006) Prognosis of acute renal failure in children. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1873–1878
Mankhambo LA, Banda DL, Jeffers G, White SA, Balmer P, Nkhoma S, Phiri H, Molyneux EM, Hart CA, Molyneux ME, Heyderman RS, Carrol ED (2010) The role of angiogenic factors in predicting clinical outcome in severe bacterial infection in Malawian children. Crit Care 14:R91
Molitoris BA, Sutton TA (2004) Endothelial injury and dysfunction: role in the extension phase of acute renal failure. Kidney Int 66:496–499
Basile DP (2007) The endothelial cell in ischemic acute kidney injury: implications for acute and chronic function. Kidney Int 72:151–156
Villanueva S, Cespedes C, Gonzalez A, Vio CP (2006) bFGF induces an earlier expression of nephrogenic proteins after ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:R1677–R1687
Villanueva S, Cespedes C, Gonzalez AA, Roessler E, Vio CP (2008) Inhibition of bFGF-receptor type 2 increases kidney damage and suppresses nephrogenic protein expression after ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R819–R828
Haimovitz-Friedman A, Cordon-Cardo C, Bayoumy S, Garzotto M, McLoughlin M, Gallily R, Edwards CK 3rd, Schuchman EH, Fuks Z, Kolesnick R (1997) Lipopolysaccharide induces disseminated endothelial apoptosis requiring ceramide generation. J Exp Med 186:1831–1841
Mattison PC, Soler-Garcia AA, Das JR, Jerebtsova M, Perazzo S, Tang P, Ray PE (2012) Role of circulating fibroblast growth factor-2 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Pediatr Nephrol 27:469–483
Chen L, Liu W (1997) Effect of asphyxia on urinary epidermal growth factor levels in newborns. J Tongji Med Univ 17:144–146
Tsau YK, Sheu JN, Chen CH, Teng RJ, Chen HC (1996) Decreased urinary epidermal growth factor in children with acute renal failure: epidermal growth factor/creatinine ratio not a reliable parameter for urinary epidermal growth factor excretion. Pediatr Res 39:20–24
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Hundley HE, Montesanti A, Parwar P, Sonjara S, Ambalavanan N (2012) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury in newborns. J Pediatr 161(270–275):e271
Kwon O, Ahn K, Zhang B, Lockwood T, Dhamija R, Anderson D, Saqib N (2010) Simultaneous monitoring of multiple urinary cytokines may predict renal and patient outcome in ischemic AKI. Ren Fail 32:699–708
Krawczeski CD, Woo JG, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr 158(1009–1015):e1
Ku PT, D’Amore PA (1995) Regulation of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) gene and protein expression following its release from sublethally injured endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem 58:328–343
Ray P, Acheson D, Chitrakar R, Cnaan A, Gibbs K, Hirschman GH, Christen E, Trachtman H (2002) Basic fibroblast growth factor among children with diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:699–707
Soler-Garcia AA, Rakhmanina NY, Mattison PC, Ray PE (2009) A urinary biomarker profile for children with HIV-associated renal diseases. Kidney Int 76:207–214
Kiley SC, Chevalier RL (2009) Urinary biomarkers: the future looks promising. Kidney Int 76:133–134
Gupta GK, Milner L, Linshaw MA, McCauley RG, Connors S, Folkman J, Bianchi DW (2000) Urinary basic fibroblast growth factor: a noninvasive marker of progressive cystic renal disease in a child. Am J Med Genet 93:132–135
Grandaliano G, Gesualdo L, Bartoli F, Ranieri E, Monno R, Leggio A, Paradies G, Caldarulo E, Infante B, Schena FP (2000) MCP-1 and EGF renal expression and urine excretion in human congenital obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:182–192
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP, Spitzer A (1987) The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular filtration rate in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am 34:571–590
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL (2009) Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol 24:265–274
Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ (1984) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr 104:849–854
Askenazi DJ, Montesanti A, Hunley H, Koralkar R, Pawar P, Shuaib F, Liwo A, Devarajan P, Ambalavanan N (2011) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and mortality in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 159(907–912):e901
Erdman LK, Dhabangi A, Musoke C, Conroy AL, Hawkes M, Higgins S, Rajwans N, Wolofsky KT, Streiner DL, Liles WC, Cserti-Gazdewich CM, Kain KC (2011) Combinations of host biomarkers predict mortality among Ugandan children with severe malaria: a retrospective case–control study. PLoS One 6:e17440
Carlson M, Raab Y, Seveus L, Xu S, Hallgren R, Venge P (2002) Human neutrophil lipocalin is a unique marker of neutrophil inflammation in ulcerative colitis and proctitis. Gut 50:501–506
Paragas N, Qiu A, Zhang Q, Samstein B, Deng SX, Schmidt-Ott KM, Viltard M, Yu W, Forster CS, Gong G, Liu Y, Kulkarni R, Mori K, Kalandadze A, Ratner AJ, Devarajan P, Landry DW, D’Agati V, Lin CS, Barasch J (2011) The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat Med 17:216–222
Ray PE, Liu XH, Xu L, Rakusan T (1999) Basic fibroblast growth factor in HIV-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 13:586–593
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants R0-1 HL-102497, R0-1HL 55605, R0-1 DK 049419, and U54 HD071601.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wai, K., Soler-García, Á.A., Perazzo, S. et al. A pilot study of urinary fibroblast growth factor-2 and epithelial growth factor as potential biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill children. Pediatr Nephrol 28, 2189–2198 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2543-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2543-3