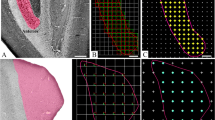
Abstract
The visual wulst (VW), the rostro-dorsal surface of the avian telencephalon extending from the midline to the lateral region of the brain, is a laminated “bulge” consisting in four histologically distinct rostro-caudally arranged laminae with a specific sequence: hyperpallium apicale, interstitial nucleus of hyperpallium apicale, hyperpallium intercalatum and hyperpallium densocellulare. The VW has been proposed to be the avian equivalent of the mammalian striate cortex. Various behavioral studies including lesion experiments have indicated the importance of the VW, which receives visual and/or auditory cues. We have investigated qualitatively and quantitatively the fascinating structural changes occurring in VW neurons of the seasonally breeding bird, Ploceus philippinus (Linnaeus, 1766). The Golgi method was used to study the seasonal fluctuations in the neuronal classes of the VW with regard to dendritic thickness, spine morphology and spine density during both the non-breeding and breeding periods of male Baya weaver birds. Significant variations in parameters studied among the various neuronal types located in the different well-demarcated regions of the VW are believed to contribute to the functional differences reported among the wulst regions. Thus, this study extends our view demonstrating naturally occurring neuronal plasticity in a seasonally dynamic avian brain of a bird that hones not only its learning and memorizing system but also its social and sexual system in preparation for the breeding season.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams VL, Goodman RL, Salm AK, Coolen LM, Karsch FJ, Lehman MN (2006) Morphological plasticity in the neuronal circuitry responsible for seasonal breeding in the ewe. Endocrinology 147:4843–4851
Alvarez-Buylla A, Ling CY, Yu WS (1994) Contribution of neurons born during embryonic, juvenile, and adult life to the brain of adult canaries: regional specificity and delayed birth of neurons in the song-control nuclei. J Comp Neurol 347:233–248
Bagnoli P, Fontanesi G, Alesci R, Erichsen JT (1992) Distribution of neuropeptide Y, substance P, and choline acetyltransferase in the developing visual system of the pigeon and effects of unilateral retina removal. J Comp Neurol 318:392–414
Ball GF, Balthazart J (2002) Neuroendocrine mechanisms regulating reproductive cycles and reproductive behavior in birds. In: Pfaff DW, Arnold AP, Etgen AM, Fahrbach SE, Rubin RT (eds) Hormones, brain and behavior, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 649–798
Ball GF, Balthazart J (2004) Hormonal regulation of brain circuits mediating male sexual behavior in birds. Physiol Behav 83:329–346
Ball GF, Wingfield JC (1987) Changes in plasma-levels of luteinizing-hormone and sex steroid-hormone in relation to multiple-broodedness and nest-site density in male starlings. Physiol Zool 60:191–199
Balthazart J, Baillien M, Charlier TD, Cornil CA, Ball GF (2003) Multiple mechanisms control brain aromatase activity at the genomic and nongenomic level. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 86:367–379
Belichenko PV, Krasnov I (1991) The dendritic spines of the pyramidal neurons in layer V of the rat sensorimotor cortex following a 14-day space flight (in Russian). Biull Eksp Biol Med 112:541–42
Bernard DJ, Ball GF (1997) Photoperiodic condition modulates the effects of testosterone on song control nuclei volumes in male European starlings. Gen Comp Endocrinol 105:276–283
Blaesing B, Nossoll M, Teuchert Noodt G, Dawirs RR (2001) Postnatal maturation of prefrontal pyramidal neurons is sensitive to a single early dose of methamphetamine in gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). J Neural Trans 103:101–103
Bradley P, Horn G (1979) Neuronal plasticity in the chick brain: morphological effects of visual experience on neurons in hyperstriatum accessorium. Brain Res 162:148–153
Brandon JG, Coss RG (1982) Rapid dendritic spine stem shortening during one-trial learning: the honeybee’s first orientation flight. Brain Res 252:51–61
Budzynski CA, Gagliardo A, Ioale P, Bingman VP (2002) Participation of the homing pigeon thalamofugal visual pathway in sun-compass associative learning. Eur J Neurosci 15:197–210
Chand P, Srivastava UC (2010) Morphological characteristics of the projection neurons in the hyperpallium apicale of the strawberry finch, Estrilda amandava. Natl Acad Sci Lett 33:377–382
Dawson A, Goldsmith AR (1984) Effects of gonadectomy on seasonal changes in plasma LH and prolactin concentrations in male and female European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris). J Endocrinol 100:213–218
Dawson A, King V (1994) Thyroidectomy does not affect the daily or free-running rhythms of plasma melatonin in European starlings. J Biol Rhythms 9:137–144
De Groof G, Verhoye M, Poirier C, Leemans A, Eens M, Darras-Veerle M, Linden AV der (2009) Structural changes between seasons in the songbird auditory forebrain. J Neurosci 29:13557–13565
Eens M (1997) Understanding the complex song of the European starling: an integrated ethological approach. Adv Study Anim Behav 26:355–434
Feldman ML, Peters A (1979) A technique for estimating total spine numbers on Golgi-impregnated dendrites. J Comp Neurol 188:527–542
Fifkova E (1985) A possible mechanism of morphometric change in dendritic spines induced by stimulation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 5:47–63
Fifkova E, Anderson CL (1981) Stimulation-induced changes in dimensions of stalks of dendritic spines in the dentate molecular layer. Exp Neurol 74:621–27
Garamszegia LZ, Eens M, Hurtrez-Boussès S, Møller AP (2005) Testosterone, testes size, and mating success in birds: a comparative study. Horm Behav 27:389–409
Garey LJ, Winkelmann E, Brauer K (1985) Golgi and Nissl studies of the visual cortex of the bottlenose dolphin. J Comp Neurol 240:305–321
Gentner TQ, Hulse SH, Ball GF (2004) Functional differences in forebrain auditory regions during learned vocal recognition in songbirds. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 190:1001–1010
Hassiotis M, Ashwell KW (2003) Neuronal classes in the isocortex of a monotreme, the Australian echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus). Brain Behav Evol 61:6–27
Heimovics SA, Cornil CA, Ball GF, Riters LV (2009) D1-like dopamine receptor density in nuclei involved in social behavior correlates with song in a context-dependent fashion in male European starlings. Neuroscience 159:962–973
Heyers D, Manns M, Luksch H, Güntürkün O, Mouritsen H (2007) A visual pathway links brain structures active during magnetic compass orientation in migratory birds. PLoS ONE 2:e937
Humason GL (1972) Animal tissue techniques. WH Freeman and Co., San Francisco, pp 641
Jarvis ED, Güntürkün O, Bruce L, Csillag A, Karten H, Kuenzel W, Medina L, Paxinos G, Perkel DJ, Shimizu T, Striedter G, Wild M, Ball GF, Dugas-Ford J, Durand S, Hough G, Husband S, Kubikova L, Lee DW, Mello CV, Powers A, Siang C, Smulders TV, Wada K, White SA, Yamamoto K, Yu J, Reiner A, Butler AB (2005) Avian brains and a new understanding of vertebrate brain evolution. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:1–9
Karten HJ (1991) Homology and evolutionary origins of the “neocortex”. Brain Behav Evol 38:264–272
Karten HJ, Hodos W, Nauta WJH, Revzin AM (1973) Neural connections of the “visual wulst” of the avian telencephalon. Experimental studies in the pigeon (Columba livia) and owl (Speotyto cunicularia). J Comp Neurol 150:253–277
Lucas JR, Freeberg TM, Krishnan A, Long GR (2002) A comparative study of avian auditory brainstem responses: correlations with phylogeny and vocal complexity, and seasonal effects. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 188:981–992
Lucas JR, Freeberg TM, Long GR, Krishnan A (2007) Seasonal variation in avian auditory evoked responses to tones: a comparative analysis of Carolina chickadees, tufted titmice, and white-breasted nuthatches. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 193:201–215
Maekawa F, Komine O, Sato K, Kanamatsu T, Uchimura M, Tanaka K, Ohki-Hamazaki H (2006) Imprinting modulates processing of visual information in the visual wulst of chicks. BMC Neurosci 7:75
Malhotra L, Kant R, Baweja PK, Saxena RN (1979) Light induced changes in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal-gonadal axis of the male Indian weaver bird Ploceus philippinus. Indian J Exp Biol 17:729–731
Maney DL, Ball GF (2003) Fos-like immunoreactivity in catecholaminergic brain nuclei after territorial behavior in free-living song sparrows. J Neurobiol 56:163–170
Matsuzaki M, Ellis-Davies GC, Nemoto T, Miyashita Y, Lino M, Kasai H (2001) Dendritic spine geometry is critical for AMPA receptor expression in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci 4:1086–1092
Matsuzaki M, Honkura N, Ellis-Davies GC, Kasai H (2004) Structural basis of long-term potentiation in single dendritic spines. Nature 429:761–766
Medina L, Reiner A (2000) Do birds possess homologues of mammalian primary visual, somatosensory and motor cortices? Trends Neurosci 23:1–12
Meyer G, Ferres-Torres R, Mas M (1978) The effects of puberty and castration on hippocampal dendritic spines of mice. Brain Res 155:108–112
Montagnese CM, Krebs JR, Meyer G (1996) The dorsomedial and dorsolateral forebrain of the zebra finch, Taeniopygia guttata: a Golgi study. Cell Tissue Res 283:263–282
Moore MC, Kranz R (1983) Evidence for androgen independence of male mounting behavior in white-crowned sparrows (Zonotrichia leucophrys gambelii). Horm Behav 17:414–23
Nakamori T, Sato K, Atoji Y, Kanamatsu T, Tanaka K, Ohki-Hamazaki H (2010) Demonstration of a neural circuit critical for imprinting behavior in chicks. J Neurosci 30:4467–4480
Nieuwenhuys R (1994) The neocortex. An overview of its evolutionary development, structural organization and synaptology. Anat Embryol 190:307–337
Nusser Z, Lujan R, Laube G, Roberts JD, Molnar E, Somogyi P (1998) Cell type and pathway dependence of synaptic AMPA receptor number and variability in the hippocampus. Neuron 21:545–559
Patel SN, Rose SP, Stewart MG (1988) Training induced dendritic spine density changes are specifically related to memory formation processes in the chick, Gallus domesticus. Brain Res 463:168–73
Peters A, Fairén A (1978) Smooth and sparsely spined stellate cells in the visual cortex of the rat: a study using a combined Golgi-electron microscope technique. J Comp Neurol 181:129–172
Pettigrew JD (1979) Binocular visual processing in the owl’s telencephalon. Proc R Soc London B Biol Sci 204:435–454
Popov VI, Bocharova L (1992) Hibernation induced structural changes in synaptic contacts between mossy fibres and hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience 48:53–62
Popov VI, Bocharova LS, Bragin AG (1992) Repeated changes of dendritic morphology in the hippocampus of ground squirrels in the course of hibernation. Neuroscience 48:45–51
Quader S (2006) Sequential settlement by nesting in male and female Baya weaverbirds Ploceus philippinus: the role of monsoon winds. J Avian 37:396–404
Rasmussen PC, Anderton JC (2005) The birds of South Asia. The Ripley guide. Smithsonian Institution/Lynx Edicions, Washington D.C./Barcelona
Reiner A (1991) A comparison of neurotransmitter-specific and neuropeptide-specific neuronal cell types present in the dorsal cortex in turtles with those present in the isocortex in mammals: implications for the evolution of isocortex. Brain Behav Evol 38:53–91
Reiner A (1993) Neurotransmitter organization and connections of turtle cortex: implications for the evolution of mammalian isocortex. Comp Biochem Physiol 104A:735–748
Reiner A, Karten HJ (1983) The laminar source of efferent projections from the avian wulst. Brain Res 275:349–354
Riters LV, Ball GF (1999) Lesions to the medial preoptic area affect singing in the male European starling (Sturnus vulgaris). Horm Behav 36:276–286
Riters LV, Eens M, Pinxten R, Duffy DL, Balthazart J, Ball GF (2000) Seasonal changes in courtship song and the medial preoptic area in male European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris). Horm Behav 38:250–261
Riters LV, Eens M, Pinxten R, Ball GF (2002) Seasonal changes in the densities of alpha(2) noradrenergic receptors are inversely related to changes in testosterone and the volumes of song control nuclei in male European starlings. J Comp Neurol 444:63–74
Rollenhagen A, Bischof H-J (1994) Phase specific morphological changes induced by social experience in two forebrain areas of the zebra finch. Behav Brain Res 65:83–88
Rollenhagen A, Bischof H-J (1996) Activity-dependent plasticity in visual forebrain areas of the zebra finch. Behav Brain Res 81:207–213
Saldanha CJ, Tuerk MJ, Kim YH, Fernandes AO, Arnold AP, Schlinger BA (2000) Distribution and regulation of telencephalic aromatase expression in the zebra finch revealed with a specific antibody. J Comp Neurol 423:619–630
Salim A (2002) The book of Indian birds, 13th edn. Bombay Natural History Society/Oxford University Press, Mumbai
Sartor JJ, Ball GF (2005) Social suppression of song is associated with a reduction in volume of a song-control nucleus in European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris). Behav Neurosci 119:233–244
Schikorski T, Stevens CF (1999) Quantitative fine-structural analysis of olfactory cortical synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4107–4112
Shimizu T, Hodos W (1989) Reversal learning in pigeons: effects of selective lesions of the wulst. Behav Neurosci 103:262–272
Shimizu T, Karten HJ (1990) Immunohistochemical analysis of the visual wulst of the pigeon (Columba livia). J Comp Neurol 300:346–369
Shimizu T, Cox K, Karten HJ (1995) Intratelencephalic projections of the visual wulst in pigeons (Columba livia). J Comp Neurol 359:551–572
Smith MS, Freeman ME, Neill JD (1975) The control of progesterone secretion during the estrous cycle and early pseudopregnancy in the rat: prolactin, gonadotropin, and steroid levels associated with the rescue of the corpus luteum of pseudopregnancy. Endocrinology 96:219–226
Smulders TV (2002) Natural breeding conditions and artificial increases in testosterone have opposite effects on the brains of adult male songbirds: a meta-analysis. Horm Behav 41:156–169
Sorenson EM, Chiappinelli VA (1992) Localization of 3Hnicotine, 125I-kappa-bungarotoxin, and 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding to nicotinic sites in the chicken forebrain and midbrain. J Comp Neurol 323:1–12
Srivastava UC, Singh S (2012) Seasonal plasticity in neurons of APH in female Indian ringneck parrot (Psittacula krameri). Natl Acad Sci Lett 35:259–262
Srivastava UC, Chand P, Maurya RC (2007) Cytoarchitectonic organization and morphology of the cells of hippocampal complex in strawberry finch, Estrilda amandava. Cell Mol Biol 53:103–120
Srivastava UC, Chand P, Maurya RC (2009) Neuronal classes in the corticoid complex of the telencephalon of the strawberry finch, Estrilda amandava. Cell Tissue Res 336:393–409
Srivastava UC, Singh S, Singh D (2012) Seasonal fluctuation in the neuronal classes of parahippocampal area of P. krameri (Scopoli, 1769) and E. scolopaceus (Linnaeus, 1758). Cell Mol Biol 58 (Suppl):OL1768–OL1779
Stettner LJ, Schultz WJ (1967) Brain lesions in birds: effects on discrimination acquisition and reversal. Science 155:1689–1692
Terleph TA, Lu K, Vicario DS (2008) Response properties of the auditory telencephalon in songbirds change with recent experience and season. PLoS ONE 3:e2854
Thompson CK, Brenowitz EA (2005) Seasonal change in neuron size and spacing but not neuronal recruitment in a basal ganglia nucleus in the avian song control system. J Comp Neurol 481:276–283
Todd FR, Katherine AT, Marguerita EK, Mooney R (2010) Rapid spine stabilization and synaptic enhancement at the onset of behavioural learning. Nature 463:948–952
Tömböl T (1995) Golgi structure of telencephalon of the chicken. Abaevo, Budapest
Tömböl T, Maglόczky Z (1990) Cytoarchitecture of chicken wulst: a Golgi study in cell types and their maturation after hatching. Acta Morphol Hung 38:35–53
Tömböl T, Davies DC, Németh A, Sebestény T, Alpár A (2000) A comparative Golgi study of chicken (Gallus domesticus) and homing pigeon (Columba livia) hippocampus. Anat Embryol 201:85–101
Tramontin AD, Smith GT, Breuner CW, Brenowitz EA (1998) Seasonal plasticity and sexual dimorphism in the avian song control system: stereological measurement of neuron density and number. J Comp Neurol 396:186–192
Veenman CL, Reiner A (1996) Ultrastructural study of the targets of cortical afferents in the avian striatum. Brain Res 707:1–12
Veenman CL, Wild JM, Reiner A (1995) Organization of the avian “corticostriatal” projection system: a retrograde and anterograde pathway tracing study in pigeons. J Comp Neurol 354:87–126
Watanabe S (2003) Effects of wulst and ectostriatum lesions on repeated acquisition of spatial discrimination in pigeons. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 17:286–292
Watanabe M, Ito H, Masi H (1983) Cytoarchitecture and visual receptive neurons in the wulst of the Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). J Comp Neurol 213:188–198
Wild JM, Williams MN (1999) Rostral wulst of passerine birds. II. Intratelencephalic projections to nuclei associated with the auditory and song systems. J Comp Neurol 413:520–534
Wild JM, Williams MN (2000) Rostral wulst in passerine birds. I. Origin, course, and terminations of an avian pyramidal tract. J Comp Neurol 416:429–450
Wingfield JC, Farner DS (1980) Control of seasonal reproduction in temperate-zone birds. Prog Reprod Biol 5:62–101
Woolley CS, Gould E, Frankfurt M, McEwen BS (1990) Naturally occurring fluctuation in dendritic spine density on adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 10:4035–4039
Yang G, Pan F, Gan WB (2009) Stably maintained dendritic spines are associated with lifelong memories. Nature 462:920–924
Yuste R, Bonhoeffer T (2001) Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1071–1089
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the Head of Department of Zoology, University of Allahabad, Allahabad, India for providing essential facilities for the present investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research work was supported by UGC Fellowship no. F.4-1/2006 (BSR)/7-16/2007 (BSR) (order no. 05/R/867/2011) awarded to P.G.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, U.C., Gaur, P. Naturally occurring neuronal plasticity in visual wulst of the Baya weaver, Ploceus philippinus (Linnaeus, 1766). Cell Tissue Res 352, 445–467 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1579-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1579-9