Abstract
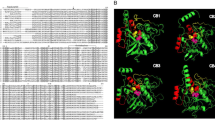
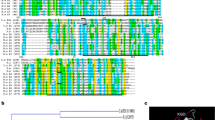
Clonorchiasis, caused by Clonorchis sinensis infection, is a zoonotic parasitic disease of hepatobiliary system in which the proteins released by adult are major pathogenetic factors. In this study, we first characterized a putative sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (CsSMPase) A-like secretory protein, which was highly expressed in the adult worm. The full-length gene was cloned. The putative protein is of relatively low homology comparing with SMPase from other species, and of rich T cell and B cell epitopes, suggesting that it is an antigen of strong antigenicity. The complete coding sequence of the gene was expressed in the Escherichia coli. The recombinant CsSMPase (rCsSMPase) can be recognized by C. sinensis-infected serum, and the protein immunoserum can recognize a specific band in excretory/secretory products (ESPs) of C. sinensis adult by western blotting. Immunolocalization revealed that CsSMPase was not only localized on tegument, ventral sucker of metacercaria, and the intestine of adult but also on the nearby epithelium of bile duct of the infected Sprague–Dawley rats, implying that CsSMPase was mainly secreted and excreted through adult intestine and directly interacted with bile duct epithelium. Although immunized rats evoked high level antibody response, the antigen level was low in clonorchiasis patients. And the sensitivity and specificity of rCsSMPase were 50.0 % (12/24) and 88.4 % (61/69), in sera IgG-ELISA, respectively. It is likely due to the fact that CsSMPase binding to the plasma membrane of biliary epithelium decreases the antigen immune stimulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcon-Chaidez FJ, Boppana VD, Hagymasi AT, Adler AJ, Wikel SK (2009) A novel sphingomyelinase-like enzyme in Ixodes scapularis tick saliva drives host CD4 T cells to express IL-4. Parasite Immunol 31:210–219
Angulo S, Morales A, Danese S, Llacuna L, Masamunt MC, Pultz N, Cifone MG, De Simone C, Delgado S, Vila J, Panes J, Donskey C, Fernandez-Checa JC, Fiocchi C, Sans M (2011) Probiotic sonicates selectively induce mucosal immune cells apoptosis through ceramide generation via neutral sphingomyelinase. PLoS One 6:e16953
Ballou LR, Laulederkind SJ, Rosloniec EF, Raghow R (1996) Ceramide signalling and the immune response. Biochim Biophys Acta 1301:273–287
Brady CP, Dowd AJ, Brindley PJ, Ryan T, Day SR, Dalton JP (1999) Recombinant expression and localization of Schistosoma mansoni cathepsin L1 support its role in the degradation of host hemoglobin. Infect Immun 67:368–374
Chen J, Xu H, Zhang Z, Zeng S, Gan W, Yu X, Hu X (2011) Cloning and expression of 21.1-kDa tegumental protein of Clonorchis sinensis and human antibody response to it as a trematode-nematode pan-specific serodiagnosis antigen. Parasitol Res 108:161–168
Chen YD, Zhou CH, Xu LQ (2012) Analysis of the results of two nationwide surveys on Clonorchis sinensis infection in China. Biomed Environ Sci 25:163–166
Choi MH, Park IC, Li S, Hong ST (2003) Excretory–secretory antigen is better than crude antigen for the serodiagnosis of clonorchiasis by ELISA. Korean J Parasitol 41:35–39
Choi BI, Han JK, Hong ST, Lee KH (2004) Clonorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma: etiologic relationship and imaging diagnosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:540–552
Chung YB, Yang HJ, Hong SJ, Kang SY, Lee M, Kim TY, Choi MH, Chai JY, Hong ST (2003) Molecular cloning and immunolocalization of the 17 kDa myoglobin of Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 90:365–368
Creaney J, Wilson L, Dosen M, Sandeman RM, Spithill TW, Parsons JC (1996) Fasciola hepatica: irradiation-induced alterations in carbohydrate and cathepsin-B protease expression in newly excysted juvenile liver fluke. Exp Parasitol 83:202–215
Deng C, Sun J, Li X, Wang L, Hu X, Wang X, Chen W, Lv X, Liang C, Li W, Huang Y, Li R, Wu Z, Yu X, Xu J (2012) Molecular identification and characterization of leucine aminopeptidase 2, an excretory–secretory product of Clonorchis sinensis. Mol Biol Rep 39:9817–9826
Goni FM, Alonso A (2002) Sphingomyelinases: enzymology and membrane activity. FEBS Lett 531:38–46
Hanada K, Mitamura T, Fukasawa M, Magistrado PA, Horii T, Nishijima M (2000) Neutral sphingomyelinase activity dependent on Mg2+ and anionic phospholipids in the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem J 346(Pt 3):671–677
Hannun YA, Obeid LM (2002) The Ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. J Biol Chem 277:25847–25850
Hong ST, Fang Y (2012) Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis, an update. Parasitol Int 61:17–24
Hu F, Hu X, Ma C, Zhao J, Xu J, Yu X (2009) Molecular characterization of a novel Clonorchis sinensis secretory phospholipase A(2) and investigation of its potential contribution to hepatic fibrosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 167:127–134
Islam MK, Miyoshi T, Yokomizo Y, Tsuji N (2005) Molecular cloning and partial characterization of a nematode-specific 24 kDa protein from Ascaris suum. Parasitology 130:131–139
Ju JW, Joo HN, Lee MR, Cho SH, Cheun HI, Kim JY, Lee YH, Lee KJ, Sohn WM, Kim DM, Kim IC, Park BC, Kim TS (2009) Identification of a serodiagnostic antigen, legumain, by immunoproteomic analysis of excretory–secretory products of Clonorchis sinensis adult worms. Proteomics 9:3066–3078
Keiser J, Utzinger J (2009) Food-borne trematodiases. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:466–483
Kim YJ, Choi MH, Hong ST, Bae YM (2009) Resistance of cholangiocarcinoma cells to parthenolide-induced apoptosis by the excretory-secretory products of Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 104:1011–1016
Lai DH, Wang QP, Chen W, Cai LS, Wu ZD, Zhu XQ, Lun ZR (2008) Molecular genetic profiles among individual Clonorchis sinensis adults collected from cats in two geographic regions of China revealed by RAPD and MGE-PCR methods. Acta Trop 107:213–216
Li Y, Hu X, Liu X, Huang Y, Xu J, Zhao J, Wu Z, Yu X (2012a) Serological diagnosis of clonorchiasis: using a recombinant propeptide of cathepsin L proteinase from Clonorchis sinensis as a candidate antigen. Parasitol Res 110:2197–2203
Li Y, Huang Y, Hu X, Liu X, Ma C, Zhao J, Wu Z, Xu J, Yu X (2012b) 41.5-kDa cathepsin L protease from Clonorchis sinensis: expression, characterization, and serological reactivity of one excretory–secretory antigen. Parasitol Res 111:673–680
Lightowlers MW, Rickard MD (1988) Excretory-secretory products of helminth parasites: effects on host immune responses. Parasitology 96(Suppl):S123–S166
Ma C, Hu X, Hu F, Li Y, Chen X, Zhou Z, Lu F, Xu J, Wu Z, Yu X (2007) Molecular characterization and serodiagnosis analysis of a novel lysophospholipase from Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 101:419–425
Marchesini N, Hannun YA (2004) Acid and neutral sphingomyelinases: roles and mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Cell Biol 82:27–44
Pak JH, Kim DW, Moon JH, Nam JH, Kim JH, Ju JW, Kim TS, Seo SB (2009) Differential gene expression profiling in human cholangiocarcinoma cells treated with Clonorchis sinensis excretory–secretory products. Parasitol Res 104:1035–1046
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Segui B, Andrieu-Abadie N, Adam-Klages S, Meilhac O, Kreder D, Garcia V, Bruno AP, Jaffrezou JP, Salvayre R, Kronke M, Levade T (1999) CD40 signals apoptosis through FAN-regulated activation of the sphingomyelin-ceramide pathway. J Biol Chem 274:37251–37258
Shin HR, Oh JK, Masuyer E, Curado MP, Bouvard V, Fang YY, Wiangnon S, Sripa B, Hong ST (2010) Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma: an update focusing on risk factors. Cancer Sci 101:579–585
Spence MW (1993) Sphingomyelinases. Adv Lipid Res 26:3–23
Tallima H, Al-Halbosiy MF, El RR (2011) Enzymatic activity and immunolocalization of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium neutral sphingomyelinase. Mol Biochem Parasitol 178:23–28
Tomiuk S, Hofmann K, Nix M, Zumbansen M, Stoffel W (1998) Cloned mammalian neutral sphingomyelinase: functions in sphingolipid signaling? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3638–3643
Wang X, Liang C, Chen W, Fan Y, Hu X, Xu J, Yu X (2009) Experimental model in rats for study on transmission dynamics and evaluation of Clonorchis sinensis infection immunologically, morphologically, and pathologically. Parasitol Res 106:15–21
Wang X, Chen W, Huang Y, Huang Y, Sun J, Men J, Liu H, Luo F, Guo L, Lv X, Deng C, Zhou C, Fan Y, Li X, Huang L, Hu Y, Liang C, Hu X, Xu J, Yu X (2011) The draft genome of the carcinogenic human liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis. Genome Biol 12:R107
Wu W, Chen J, Zeng S, Zhang Z, Gan W, Yu X, Hu X (2011) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of cyclophilin A from Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 109:345–351
Xuan NT, Shumilina E, Schmid E, Bhavsar SK, Rexhepaj R, Gotz F, Gulbins E, Lang F (2010) Role of acidic sphingomyelinase in thymol-mediated dendritic cell death. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:1833–1841
Yabu T, Imamura S, Yamashita M, Okazaki T (2008) Identification of Mg2+-dependent neutral sphingomyelinase 1 as a mediator of heat stress-induced ceramide generation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283:29971–29982
Yoo WG, Kim TI, Li S, Kwon OS, Cho PY, Kim TS, Kim K, Hong SJ (2009) Reference genes for quantitative analysis on Clonorchis sinensis gene expression by real-time PCR. Parasitol Res 104:321–328
Young SA, Smith TK (2010) The essential neutral sphingomyelinase is involved in the trafficking of the variant surface glycoprotein in the bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Microbiol 76:1461–1482
Zhang O, Wilson MC, Xu W, Hsu FF, Turk J, Kuhlmann FM, Wang Y, Soong L, Key P, Beverley SM, Zhang K (2009) Degradation of host sphingomyelin is essential for Leishmania virulence. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000692
Zhao QP, Moon SU, Lee HW, Na BK, Cho SY, Kong Y, Jiang MS, Li AH, Kim TS (2004) Evaluation of Clonorchis sinensis recombinant 7-kilodalton antigen for serodiagnosis of clonorchiasis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:814–817
Zheng M, Hu K, Liu W, Hu X, Hu F, Huang L, Wang P, Hu Y, Huang Y, Li W, Liang C, Yin X, He Q, Yu X (2011) Proteomic analysis of excretory secretory products from Clonorchis sinensis adult worms: molecular characterization and serological reactivity of a excretory–secretory antigen-fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Parasitol Res 109:737–744
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China National Great Basic Research Program (973 program, no. 2010CB530003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Zheng, Y., Li, Y. et al. Expression, immunolocalization, and serological reactivity of a novel sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase-like protein, an excretory/secretory antigen from Clonorchis sinensis . Parasitol Res 112, 2197–2206 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3388-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3388-1