Abstract
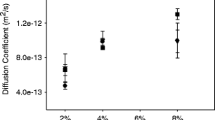
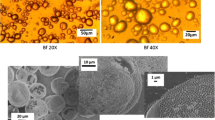
Rheological properties of concentrated oil-in-water emulsions containing dissolving polymers in both phases, partially playing a role of surfactants, were studied. Additionally, nanoparticles were added to the aqueous phase, and they had an influence on rheological behavior and emulsion stability. The main peculiarity of the objects is the superposition of viscoelastic properties related to the presence of polymers and to interface interactions. Emulsion viscoelasticity were characterized by three separate relaxation modes with very different relaxation times. They reflect relaxation processes of polymeric origin inside both phases, which are dilute polymer solutions, and elasticity of interface layers. Presence of nanoparticles strongly affects the rheological properties leading to the increase in the apparent viscosity, elastic modulus, and yield stress of emulsions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binks BP (2002) Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7:21–41
Binks BP, Whytby CP (2005) Nanoparticle silica-stabilised oil-in-water emulsions: improving emulsion stability. Colloid Surf A 253:105–115
Binks BP, Desforges A, Duff DG (2007) Synergistic stabilization of emulsions by a mixture of surface-active nanoparticles and surfactant. Langmuir 23:1098–1106
Wolf B, Lam S, Kirkland M, Frith WJ (2007) Shear thickening of an emulsion stabilized with hydrophilic silica particles. J Rheol 51:465–478
Ashbya NP, Binks BP (2000) Pickering emulsions stabilised by Laponite clay particles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2:5640–5646
Melle S, Lask M, Fuller GG (2005) Pickering emulsions with controllable stability. Langmuir 21:2158–2162
Wang J, Yang F, Tan J, Liu G, Xu J, Sun D (2010) Pickering emulsions stabilized by a lipophilic surfactant and hydrophilic platelike particles. Langmuir 26:5397–5404
Aveyard R, Binks BP, Clint JH (2003) Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 100–102:503–546
Okada M, Maeda H, Fujii S, Nakamura Y, Furuzono T (2012) Formation of Pickering emulsions stabilized via interaction between nanoparticles dispersed in aqueous phase and polymer end groups dissolved in oil phase. Langmuir 28:9405–9412
Chang SA, Gray DG (1978) The surface tension of aqueous hydroxypropyl cellulose solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 67:255–265
Mezdoura S, Cuveliera G, Cashb MJ, Michon C (2007) Surface rheological properties of hydroxypropyl cellulose at air–water interface. Food Hydrocoll 21:776–781
McNally EJ, Zografi G (1990) Spread and adsorbed monolayers of hydroxypropyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl cellulose at the air–water interface. J Colloid Interface Sci 138:61–68
Yarusso DJ, Rivard RJ, Ma J (1999) Properties of polyisoprene-based pressure sensitive adhesives crosslinked by electron beam irradiation. J Adhesion 69:201–215
Gibert FX, Marin G, Derail C, Allal A, Lechat J (2003) Rheological properties of hot melt pressure-sensitive adhesives based on styrene–isoprene copolymers. Part 1: a rheological model for [sis-si] formulations. J Adhes 79:825–852
Sasaki M, Fujita K, Adachi M, Fujii S, Nakamura Y, Urahama Y (2008) The effect of tackifier on phase structure and peel adhesion of a triblock copolymer pressure-sensitive adhesive. Int J Adhes Adhes 28:372–381
Borodulina T, Bermesheva E, Smirnova N, Ilyin S, Brantseva T, Antonov S (2014) Adhesive properties of liquid crystalline hydroxypropyl cellulose–propylene glycol blends. J Adhes Sci Technol 28:1629–1643
Class JB, Chu SG (1985) The viscoelastic properties of rubber–resin blends. I. The effect of resin structure. J Appl Polym Sci 30:805–814
Tobing S, Klein A, Sperling LH, Petrasko B (2001) Effect of network morphology on adhesive performance in emulsion blends of acrylic pressure sensitive adhesives. J Appl Polym Sci 81:2109–2117
Leong YC, Lee LMS, Gan SN (2003) The viscoelastic properties of natural rubber pressure‐sensitive adhesive using acrylic resin as a tackifier. J Appl Polym Sci 88:2118–2123
Tan HS, Pfister WR (1999) Pressure-sensitive adhesives for transdermal drug delivery systems. Pharm Sci Technol Today 2:60–69
Valenta C, Auner BG (2004) The use of polymers for dermal and transdermal delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 58:279–289
Krägel J, Derkatch SR (2010) Interfacial shear rheology. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 15:246–255
Erni P, Fischer P, Windhab EJ, Kuznezov V, Stettin H, Läuger J (2003) Stress- and strain-controlled measurements of interfacial shear viscosity and viscoelasticity at liquid/liquid and gas/liquid interfaces. Rev Sci Instr 74:4916–4924
Ilyin S, Kulichikhin V, Malkin A (2014) Characterization of material viscoelasticity at large deformations. Appl Rheol 24:13653
Møller PCF, Fall A, Bonn D (2009) Origin of apparent viscosity in yield stress fluids below yielding. EPL 87:38004
Masalova I, Taylor M, Kharatiyan E, Malkin AY (2005) Rheopexy in highly concentrated emulsions. J Rheol 49:839–849
Malkin A, Ilyin S, Roumyantseva T, Kulichikhin V (2013) Rheological evidence of gel formation in dilute poly (acrylonitrile) solutions. Macromolecules 46:257–266
Coussot P, Nguyen QD, Huynh HT, Bonn D (2002) Viscosity bifurcation in thixotropic, yielding fluids. J Rheol 46:573–589
Malkin A, Ilyin S, Semakov A, Kulichikhin V (2012) Viscoplasticity and stratified flow of colloid suspensions. Soft Matter 8:2607–2617
Ilyin SO, Pupchenkov GS, Krasheninnikov AI, Kulichikhin VG, Malkin AY (2013) Rheology of aqueous poly (ethylene oxide) solutions reinforced with bentonite clay. Colloid J 75:267–273
Berret JF, Porte G, Decruppe JP (1997) Inhomogeneous shear flows of wormlike micelles: mA master dynamic phase diagram. Phys Rev E 55:1668
Britten MM, Callaghan TP (1997) Two-phase shear band structures at uniform stress. Phys Rev Lett 78:4930
Salmon JB, Manneville S, Colin A (2003) Shear banding in a lyotropic lamellar phase. I. Time-averaged velocity profiles. Phys Rev E 68:051503
Olmsted PD (2008) Perspectives on shear banding in complex fluids. Rheol Acta 47:283–300
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2008) Gradient and vorticity banding. Rheol Acta 47:257–281
Ilyin S, Roumyantseva T, Spiridonova V, Semakov A, Frenkin E, Malkin A, Kulichikhin V (2011) Gels of cysteine/Ag-based dilute colloid systems and their rheological properties. Soft Matter 7:9090–9103
Derkach SR (2009) Rheology of emulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 151:1–23
Princen HM (1986) Osmotic pressure of foams and highly concentrated emulsions. I. Theoretical considerations. Langmuir 2:519–524
Mason TG, Lacasse MD, Grest GS, Levine D, Bibette J, Weitz DA (1997) Osmotic pressure and viscoelastic shear moduli of concentrated emulsions. Phys Rev E 56:2150–3166
Foudazi R, Masalova I, Malkin AY (2010) The role of interdroplet interaction in the physics of highly concentrated emulsions. Colloid J 72:74–92
Kragel J, Derkatch SR (2009) Interfacial shear rheology—an overview of measuring techniques and their applications. In: Miller R, Liggieri L (eds) Interfacial rheology. Brill Publ, Leiden, pp 372–428
Fainerman VB, Möbius D, Miller R (2001) Surfactants: chemistry, interfacial properties, applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to the Russian Scientific Foundation (agreement #14-23-00003 of August 7, 2014) for financial support of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilyin, S.O., Kulichikhin, V.G. & Malkin, A.Y. Rheological properties of emulsions formed by polymer solutions and modified by nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 1647–1654 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3543-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3543-6